Textbook Question
Draw a structure for a compound that meets each of the following descriptions:
b. An aldehyde with four carbons

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
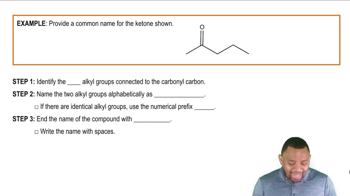

Draw a structure for a compound that meets each of the following descriptions:
b. An aldehyde with four carbons
Draw a structure for a compound that meets each of the following descriptions:
a. A 6-carbon cyclic ketone with a methyl group on the beta carbon
Draw a structure for a compound that meets each of the following descriptions:
c. An alpha-bromoaldehyde, C4H7BrO
Draw a structure for a compound that meets each of the following descriptions:
d. A cyclic alpha-hydroxyketone, C5H8O2
Indicate which compounds contain aldehyde or ketone carbonyl groups.
a.
Indicate which compounds contain aldehyde or ketone carbonyl groups.
c. CH3CH2–O–CH2–CHO