If bromocyclohexane were converted into cyclohexene, what kind of reaction would that be?
Ch.13 Alkenes, Alkynes, and Aromatic Compounds

Chapter 13, Problem 60c
What alkene could you use to make the following products? Draw the structure of the alkene, and tell what other reagent is also required for the reaction to occur.
c. 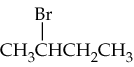
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Analyze the product structure provided in the problem. Identify the functional groups and any new bonds formed compared to a potential alkene starting material. This will help determine the type of reaction that occurred.
Recall the reaction mechanism that converts an alkene into the given product. For example, if the product contains an alcohol group (-OH), the reaction might involve hydration of the alkene. If the product contains a halogen, it might involve halogenation.
Determine the structure of the alkene by 'reversing' the reaction. For example, if the product is an alcohol, remove the -OH group and replace it with a double bond to deduce the alkene structure.
Identify the reagent required for the reaction. For example, if the reaction is hydration, the reagent could be water (H₂O) in the presence of an acid catalyst (e.g., H₂SO₄). If the reaction is halogenation, the reagent could be a halogen molecule (e.g., Br₂ or Cl₂).
Draw the structure of the alkene and specify the reagent. Ensure the structure matches the product when the reaction is applied, and confirm the reagent aligns with the reaction mechanism.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Alkenes
Alkenes are hydrocarbons that contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond (C=C). They are unsaturated compounds, meaning they have fewer hydrogen atoms than alkanes with the same number of carbon atoms. Alkenes are reactive and can undergo various chemical reactions, including addition reactions, where other atoms or groups are added across the double bond.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Naming Alkenes Example 1
Addition Reactions
Addition reactions are a type of chemical reaction where two or more reactants combine to form a single product. In the context of alkenes, these reactions often involve the addition of halogens, hydrogen, or water across the double bond. Understanding the specific conditions and reagents required for these reactions is crucial for predicting the products formed from a given alkene.
Recommended video:
Guided course
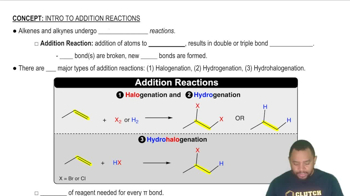
Addition Reactions Concept 1
Reagents
Reagents are substances that are added to a system to bring about a chemical reaction or to see if a reaction occurs. In the case of alkenes, common reagents include hydrogen (for hydrogenation), halogens (for halogenation), and acids (for hydration). Identifying the correct reagent is essential for determining the products of the reaction and understanding the mechanism involved.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Limiting Reagent
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Identify the type of reaction for the following:
a.
b.
Textbook Question
What alkene could you use to make the following products? Draw the structure of the alkene, and tell what other reagent is also required for the reaction to occur.
a.
Textbook Question
What alkene could you use to make the following products? Draw the structure of the alkene, and tell what other reagent is also required for the reaction to occur.
d.
Textbook Question
2,2,3,3-Tetrabromopentane can be prepared by an addition reaction of excess Br2 with an alkyne. Draw the structure of the alkyne and name it.
Textbook Question
1-Pentyne reacts with HBr in a 1:1 molar ratio to yield two different addition products, both being bromopentenes and having the chemical formula C5H9Br. Draw the structures of two possible products.
