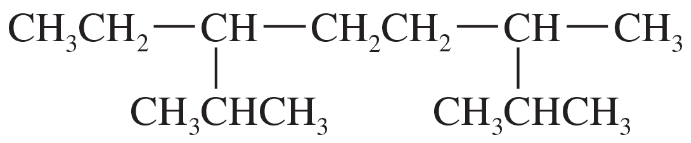Back
BackProblem 34c
Which of the following structures represent the same compound? Which ones represent different compounds?
(c)
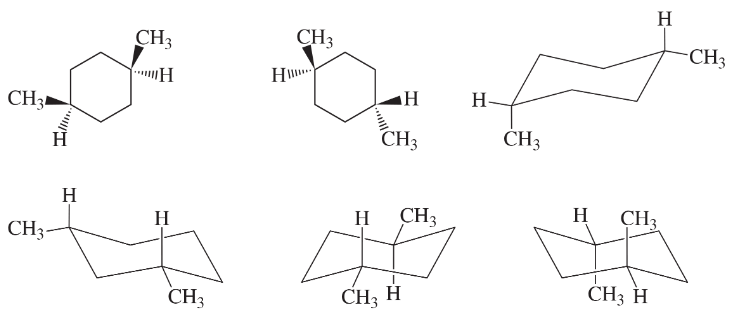
Problem 34e
Which of the following structures represent the same compound? Which ones represent different compounds?
(e)
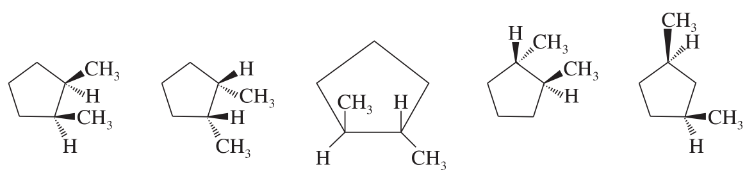
Problem 34f
Which of the following structures represent the same compound? Which ones represent different compounds?
(f)
Problem 35a
Draw and name the five cycloalkane structures of formula C5H10. Can any of these structures give rise to geometric (cis-trans) isomerism? If so, show the cis and trans stereoisomers.
Problem 36a,b
Draw the structure that corresponds with each name.
a. 3-ethyloctane
b. 4-isopropyldecane
Problem 36c,d
Draw the structure that corresponds with each name.
c. sec-butylcycloheptane
d. 2,3-dimethyl-4-propylnonane
Problem 36e,f
Draw the structure that corresponds with each name.
e. 2,2,4,4-tetramethylhexane
f. trans-1,3-diethylcyclopentane
Problem 36i,j
Draw the structure that corresponds with each name.
i. tert-butylcyclohexane
j. pentylcyclohexane
Problem 37a,b
Each of the following descriptions applies to more than one alkane. In each case, draw and name two structures that match the description.
a. an isopropylheptane
b. a diethyldecane
Problem 37c,d
Each of the following descriptions applies to more than one alkane. In each case, draw and name two structures that match the description.
c. a cis-diethylcyclohexane
d. a trans-dihalocyclopentane
Problem 37e
Each of the following descriptions applies to more than one alkane. In each case, draw and name two structures that match the description.
e. a (2,3-dimethylpentyl)cycloalkane
Problem 37f
Each of the following descriptions applies to more than one alkane. In each case, draw and name two structures that match the description.
f. a bicyclononane
Problem 39a,b
Give the IUPAC names of the following alkanes.
(a) CH3C(CH3)2CH(CH2CH3)CH2CH2CH(CH3)2
(b)
Problem 40a,b
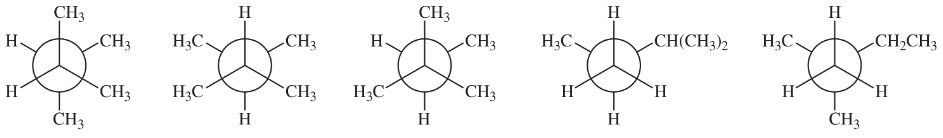
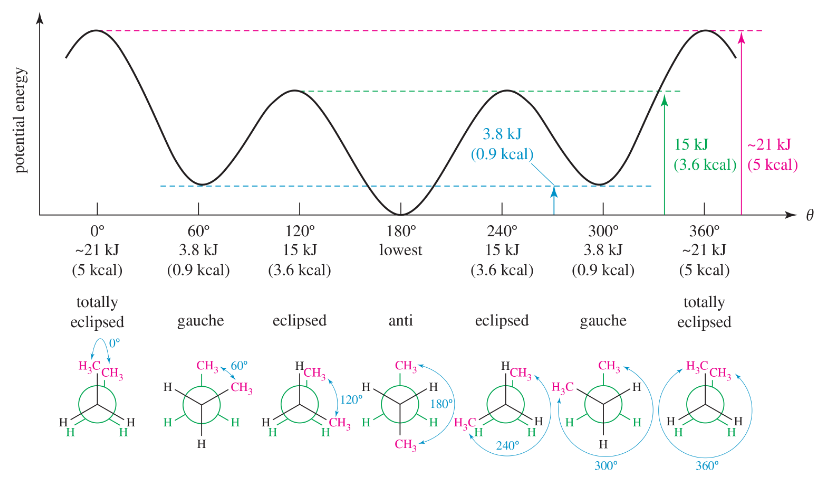
Construct a graph, similar to Figure 3-11, of the torsional energy of 3-methylpentane along the C2―C3 bond.
a. Place C2 in front, represented by three bonds coming together in a Y shape, and C3 in back, represented by a circle with three bonds pointing out from it.
b. Define the dihedral angle as the angle between the methyl group on the front carbon and the ethyl group on the back carbon.
Problem 40c
Construct a graph, similar to Figure 3-11, of the torsional energy of 3-methylpentane along the C2―C3 bond.
c. Begin your graph at the 0° dihedral angle and begin to turn the front carbon.
Problem 40e
Construct a graph, similar to Figure 3-11, of the torsional energy of 3-methylpentane along the C2―C3 bond.
e. Indicate which conformations are the most stable (lowest energy) and the least stable (highest energy).
Problem 41a,b
The following names are all incorrect or incomplete, but they represent real structures. Draw each structure and name it correctly.
a. 2-ethylpentane
b. 3-isopropylhexane
Problem 41c,d
The following names are all incorrect or incomplete, but they represent real structures. Draw each structure and name it correctly.
c. 5-chloro-4-methylhexane
d. 2-dimethylbutane
Problem 41e,f
The following names are all incorrect or incomplete, but they represent real structures. Draw each structure and name it correctly.
e. 2-cyclohexylbutane
f. 2,3-diethylcyclopentane
Problem 42a
In each pair of compounds, which compound has the higher boiling point? Explain your reasoning.
a. octane or 2,2,3-trimethylpentane
Problem 42b
In each pair of compounds, which compound has the higher boiling point? Explain your reasoning.
b. nonane or 2-methylheptane
Problem 42c
In each pair of compounds, which compound has the higher boiling point? Explain your reasoning.
c. 2,2,5-trimethylhexane or nonane
Problem 43a,b
There are eight different five-carbon alkyl groups.
a. Draw them.
b. Give them systematic names.
Problem 43c
There are eight different five-carbon alkyl groups.
c. In each case, label the degree of substitution (primary, secondary, or tertiary) of the head carbon atom bonded to the main chain.
Problem 44a
Use a Newman projection about the indicated bond to draw the most stable conformer for each compound.
a. 3-methylpentane about the C2―C3 bond
Problem 44b
Use a Newman projection about the indicated bond to draw the most stable conformer for each compound.
b. 3,3-dimethylhexane about the C3―C4 bond
Problem 45
a. Draw the two chair conformations of cis-1,3-dimethylcyclohexane, and label all the positions as axial or equatorial.
b. Label the higher-energy conformation and the lower-energy conformation.
c. The energy difference in these two conformations has been measured to be about 23 kJ (5.4 kcal) per mole. How much of this energy difference is due to the torsional energy of gauche relationships?
d. How much energy is due to the additional steric strain of the 1,3-diaxial interaction?
Problem 46a,b
Draw the two chair conformations of each compound, and label the substituents as axial and equatorial. In each case, determine which conformation is more stable.
a. cis-1-ethyl-2-isopropylcyclohexane
b. trans-1-ethyl-2-isopropylcyclohexane
Problem 46c,d
Draw the two chair conformations of each compound, and label the substituents as axial and equatorial. In each case, determine which conformation is more stable.
c. cis-1-ethyl-3-methylcyclohexane
d. trans-1-ethyl-3-methylcyclohexane
Problem 46e,f
Draw the two chair conformations of each compound, and label the substituents as axial and equatorial. In each case, determine which conformation is more stable.
e. cis-1-ethyl-4-methylcyclohexane
f. trans-1-ethyl-4-methylcyclohexane