Back
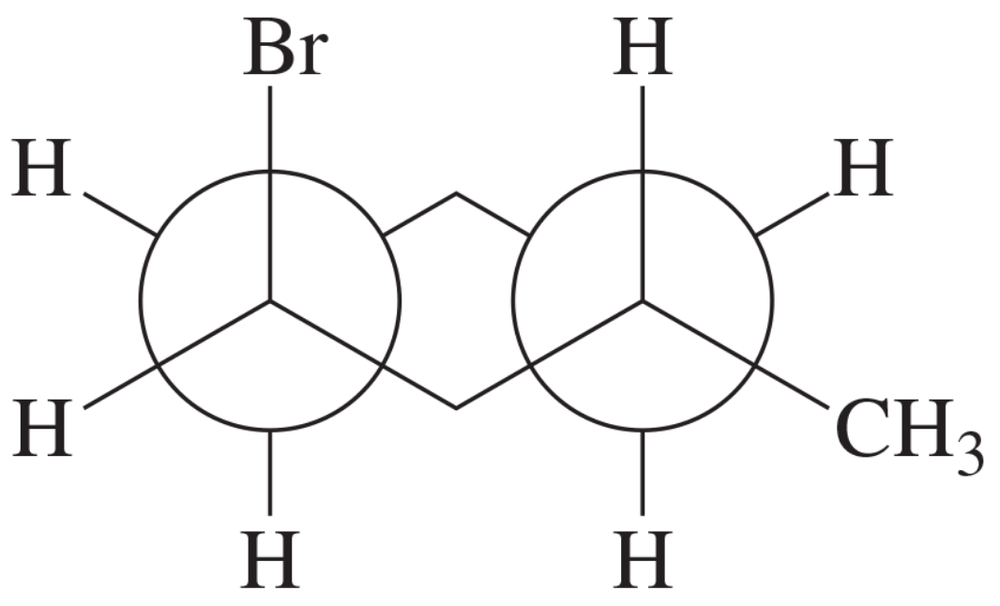
BackProblem 47
Using what you know about the conformational energetics of substituted cyclohexanes, predict which of the two decalin isomers is more stable. Explain your reasoning.
Problem 48a,b
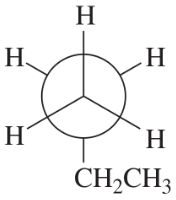
Convert each Newman projection to the equivalent line–angle formula, and assign the IUPAC name.
(a)
(b)
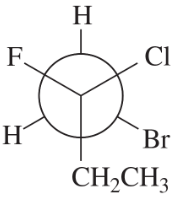
Problem 48c,d
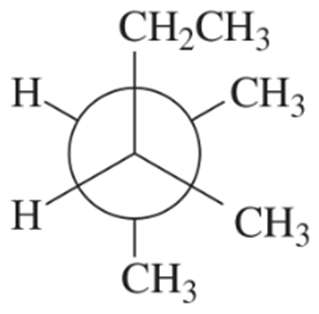
Convert each Newman projection to the equivalent line–angle formula, and assign the IUPAC name.
(c)
(d)
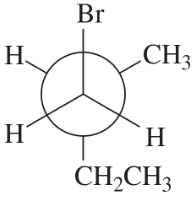
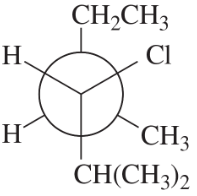
Problem 48g,h
Convert each Newman projection to the equivalent line–angle formula, and assign the IUPAC name. g.
(g)
(h)
Problem 49
Draw Newman projections along the C3―C4 bond to show the most stable and least stable conformations of 3-ethyl-2,4,4-trimethylheptane.
Problem 50
Conformational studies on ethane-1,2-diol (HOCH2–CH2OH) have shown the most stable conformation about the central C―C bond to be the gauche conformation, which is 9.6 kJ/mol (2.3 kcal/mol) more stable than the anti conformation. Draw Newman projections of these conformers, and explain this curious result.
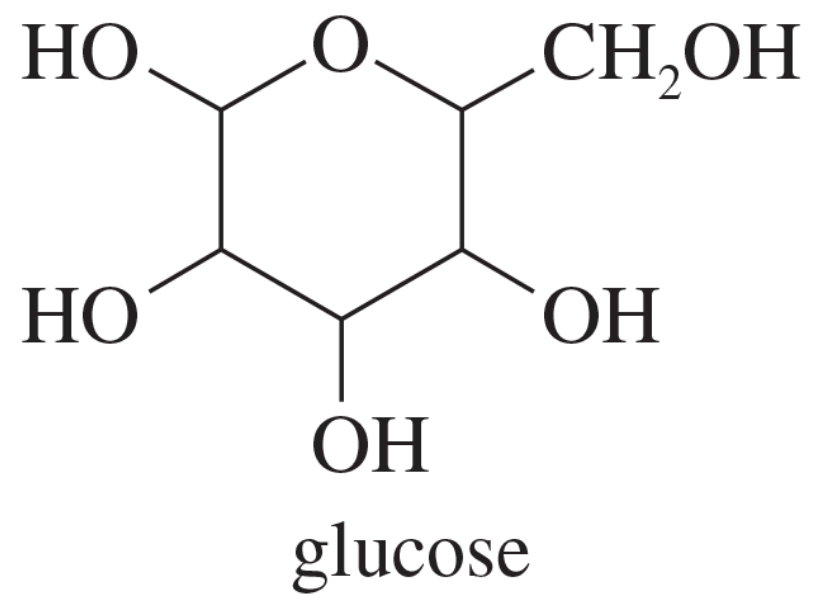
Problem 51
The most stable form of the common sugar glucose contains a six-membered ring in the chair conformation with all the substituents equatorial. Draw this most stable conformation of glucose.
Problem 52a
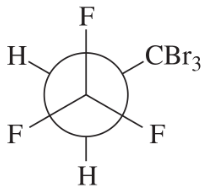
This is a Newman projection of a substituted cyclohexane. a. Draw the equivalent chair form.
Problem 52b
This is a Newman projection of a substituted cyclohexane.
b. Draw the equivalent structure using wedge and dash notation on a cyclohexane hexagon.
Problem 52c
This is a Newman projection of a substituted cyclohexane.
c. Give the IUPAC name.