Since no molecular oxygen participates in the citric acid cycle, the steps in which acetyl groups are oxidized to CO2 involve removal of hydride ions and hydrogen ions. What is the acceptor of hydride ions? What is the acceptor of hydrogen ions?

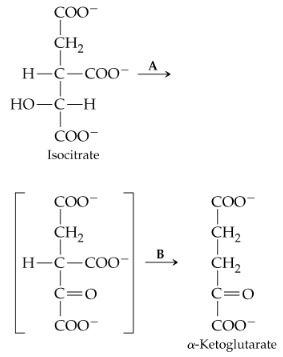
The reaction that follows is catalyzed by isocitrate dehydrogenase and occurs in two steps, the first of which (step A) is formation of an unstable intermediates (shown in brackets).
c. Which of the structures shown can be described as a β-keto acid?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
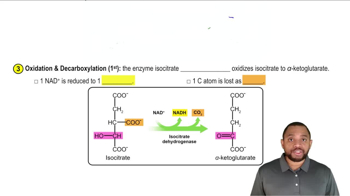
Isocitrate Dehydrogenase
ß-Keto Acid
Unstable Intermediates

The reaction that follows is catalyzed by isocitrate dehydrogenase and occurs in two steps, the first of which (step A) is formation of an unstable intermediates (shown in brackets).
a. In which step is a coenzyme needed? Identify the coenzyme.
The reaction that follows is catalyzed by isocitrate dehydrogenase and occurs in two steps, the first of which (step A) is formation of an unstable intermediates (shown in brackets).
b. In which step is CO2 evolved and a hydrogen ion added?
The reaction that follows is catalyzed by isocitrate dehydrogenase and occurs in two steps, the first of which (step A) is formation of an unstable intermediates (shown in brackets).
d. To what class of enzymes does isocitrate dehydrogenase, the enzyme that catalyzes this reaction, belong?
The electron-transport chain uses several different metal ions, especially iron, copper, zinc, and manganese. Why are metals used frequently in these two pathways? What can metals do better than organic biomolecules?
What energy requirements must be met in order for a reaction to be favorable?
