Textbook Question
What is the formula for the diammonium salt of fumaric acid?

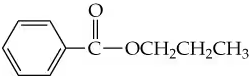
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
What is the formula for the diammonium salt of fumaric acid?
Give systematic names for the following structures and structures for the names:
d. Phenyl-o-hydroxybenzoate
Give systematic names for the following structures and structures for the names:
b. Ethyl 2-hydroxypropanoate
Draw structures of the carboxylic acids and alcohols you would use to prepare each ester in Problem 17.54.
a.
b.
c. Cyclohexyl acetate
d. Phenyl-o-hydroxybenzoate
Give systematic names for the following structures and structures for the names:
c. N-Ethyl-N-methylbenzamide
Give systematic names for the following structures and structures for the names:
a. 3-Methylpentanamide