Textbook Question
Draw the structures corresponding to the following names:
a. N-Methylpentylamine
3
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Draw the structures corresponding to the following names:
a. N-Methylpentylamine
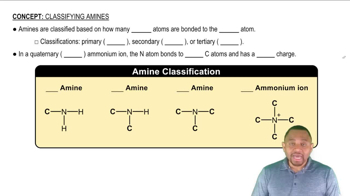
Name the following amines, and identify them as primary, secondary, or tertiary:
b.
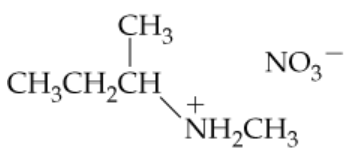
Give names or structures for the following ammonium salts. Indicate whether each is the ammonium salt of a primary, secondary, or tertiary amine.
a.
Give names or structures for the following ammonium salts. Indicate whether each is the ammonium salt of a primary, secondary, or tertiary amine.
c. N-Butyl-N-isopropylhexylammonium chloride
Identify the functional groups in cocaine
Draw the structures of the ammonium ions formed when the amines in Problem 16.30 are treated with acid.
a. N-Methylpentylamine
b. N-Ethylcyclobutylamine
c. p-Propylaniline