Which of the reactants in the citric acid cycle have two chiral carbon atoms?

Each of these reactions is involved in one of the four stages of metabolism shown in Figure 21.4. Identify the stage in which each reaction occurs.
<IMAGE>
b. Oxidation of NADH coupled with synthesis of ATP
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
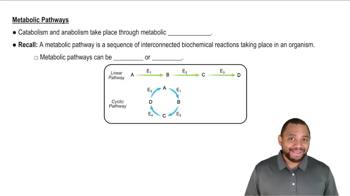
Key Concepts
Metabolism
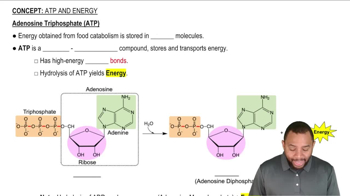
NADH and ATP
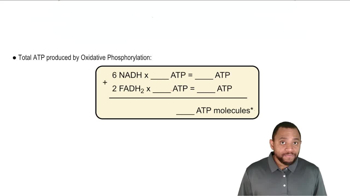
Oxidative Phosphorylation
The reduced coenzymes NADH and FADH2 are oxidized in the ETS. What is the final electron acceptor of the ETS? What is the function of the H+ ion in ATP synthesis?
Each of these reactions is involved in one of the four stages of metabolism shown in Figure 21.4. Identify the stage in which each reaction occurs.
<IMAGE>
a. Hydrolysis of starch to produce glucose
Each of these reactions is involved in one of the four stages of metabolism shown in Figure 21.4. Identify the stage in which each reaction occurs.
<IMAGE>
c. Conversion of glucose to acetyl-CoA
For the first step in fatty acid catabolism, we say that ATP is used to “drive” the reaction that links the fatty acid with coenzyme-A. Without ATP hydrolysis, would you predict that the linking of fatty acid to coenzyme-A would be exergonic or endergonic? In fatty acid CoA synthesis, the hydrolysis of the ATP portion is based on what major strategy of metabolism?
Since no molecular oxygen participates in the citric acid cycle, the steps in which acetyl groups are oxidized to CO2 involve removal of hydride ions and hydrogen ions. What is the acceptor of hydride ions? What is the acceptor of hydrogen ions?
