Is the bond formed between each pair in Problem 18.76 covalent or noncovalent?
a. Cysteine and cysteine
b. Alanine and leucine
c. Aspartic acid and asparagine
d. Serine and lysine

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
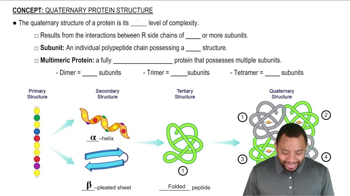


Is the bond formed between each pair in Problem 18.76 covalent or noncovalent?
a. Cysteine and cysteine
b. Alanine and leucine
c. Aspartic acid and asparagine
d. Serine and lysine
What is meant by the following terms as they apply to protein structure, and what bonds or molecular interactions stabilize that level of structure?
a. Primary structure
What is meant by the following terms as they apply to protein structure, and what bonds or molecular interactions stabilize that level of structure?
b. Secondary structure
What level of protein structure is determined by the following:
a. Peptide bonds between amino acids?
What level of protein structure is determined by the following:
b. Hydrogen bonds between backbone carbonyl oxygen atoms and hydrogen atoms attached to backbone nitrogen atoms?
How do the following noncovalent interactions help to stabilize the tertiary and quaternary structure of a protein? Give an example of a pair of amino acids that could give rise to each interaction.
a. Hydrophobic interactions