Give the structure of the repeating units in the polymers that are formed in the reactions of the following compounds.
a.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
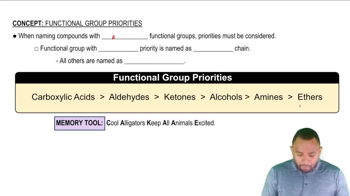
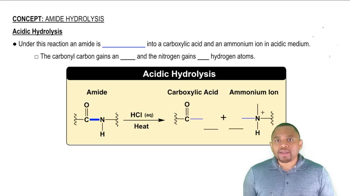
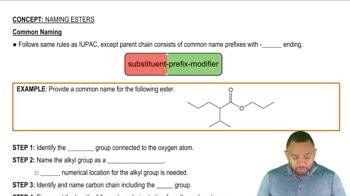
Give the structure of the repeating units in the polymers that are formed in the reactions of the following compounds.
a.
Write the formula for the phosphate monoester formed from isopropyl alcohol and phosphoric acid.
Identify the functional group in the following compounds and give the structures of the products of hydrolysis for these compounds.
a.
N-Acetylglucosamine (also known as NAG) is an important component on the surfaces of cells.
b. Draw the structures of the products of acid hydrolysis.
One phosphorylated form of glycerate is 3-phosphoglycerate
a. Identify the type of linkage between glycerate and phosphate.
Consider the following unnatural amino acid:
a. If two molecules react to form an ester, what is the structure of the ester product?