Textbook Question
Write the structure of benzylamine hydrochloride in two different ways, and name the hydrochloride as an ammonium salt.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Write the structure of benzylamine hydrochloride in two different ways, and name the hydrochloride as an ammonium salt.
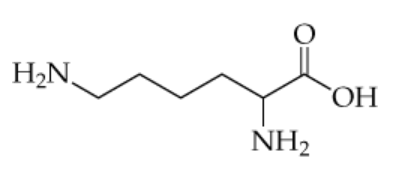
a. For the compound above, identify each nitrogen as either a primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary, or aromatic amine.
The structure of the amino acid lysine (in its uncharged form) is shown below.
a. Which amine groups would be able to participate in hydrogen bonding?
Explain what bonds must be made or broken and where the electrons go when the hydrogen-bonded water between the two amines shown on page 507 reacts to form an amine, ammonium ion, and OH⁻.
Complete the following equations:
b.
Draw the structures corresponding to the following names:
a. N-Methylpentylamine