Textbook Question
Draw the following three isomers of C5H12 as condensed structures:
a.

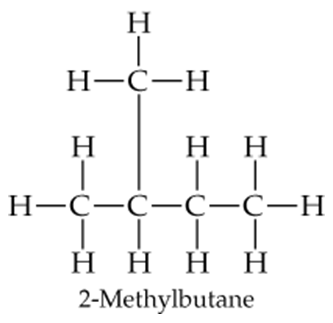
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Draw the following three isomers of C5H12 as condensed structures:
a.
Draw the straight-chain isomer with the formula (b) C9H20.
There are two branched-chain isomers with the formula C7H16, where the longest chain in the molecule is six carbons long. Draw them.
Draw the following three isomers of C5H12 as condensed structures:
c.
Convert the following line structures to condensed structures:
a.
Convert the following line structures to condensed structures:
b.