Textbook Question
Distinguish between the following:
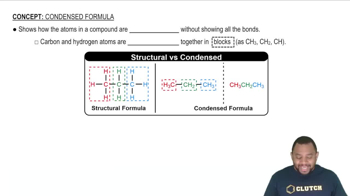
b. A structural formula and a condensed structure

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Distinguish between the following:
b. A structural formula and a condensed structure
Distinguish between the following:
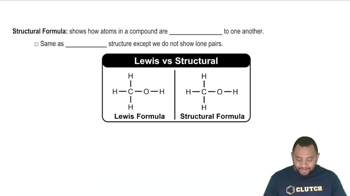
c. A lone pair and a shared pair of electrons
Consider the following possible structural formulas for C3H6O2. If a structure is not reasonable, explain what changes could be made to convert it to a reasonable structure.
a.
Draw a Lewis structure for the following molecules:
e. BeCl2 (Note: This molecule does not follow the octet rule.)
Draw a Lewis structure for the following polyatomic ions:
b. Sulfite, SO32–
Sketch the three-dimensional shape of the following molecules:
a. Methylamine, CH3NH2