Back
BackProblem 5.CRE.2b
Kentucky Pick 4 In the Kentucky Pick 4 lottery game, you can pay $1 for a “straight” bet in which you select four digits with repetition allowed. If you buy only one ticket and win, your prize is $2500.
b. If you play this game once every day, find the mean number of wins in years with exactly 365 days.
Problem 5.CRE.2c
Kentucky Pick 4 In the Kentucky Pick 4 lottery game, you can pay $1 for a “straight” bet in which you select four digits with repetition allowed. If you buy only one ticket and win, your prize is $2500.
c. If you play this game once every day, find the probability of no wins in 365 days.
Problem 5.CRE.1ab
Planets The planets of the solar system have the numbers of moons listed below in order from the sun. (Pluto is not included because it was uninvited from the solar system party in 2006.) Include appropriate units whenever relevant.
0 0 1 2 17 28 21 8
a. Find the mean.
b. Find the median.
Problem 5.CRE.3c
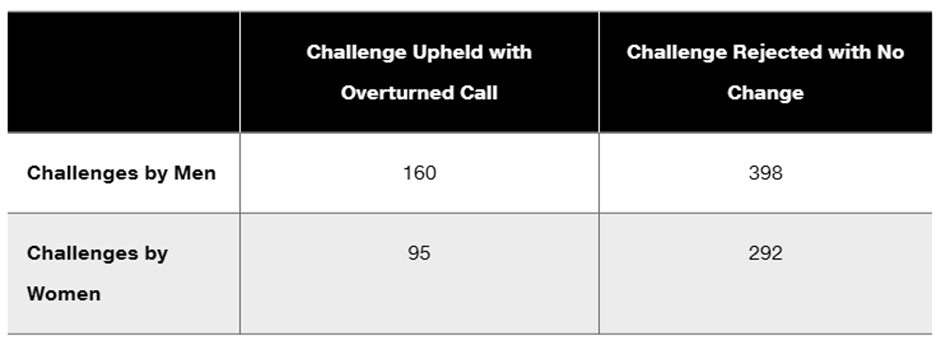
Tennis Challenge In a recent U.S. Open tennis tournament, there were 945 challenges made by singles players, and 255 of them resulted in referee calls that were overturned. The accompanying table lists the results by gender.
c. If two different challenges are randomly selected without replacement, find the probability that they both resulted in an overturned call.
Problem 5.CRE.1cd
Planets The planets of the solar system have the numbers of moons listed below in order from the sun. (Pluto is not included because it was uninvited from the solar system party in 2006.) Include appropriate units whenever relevant.
0 0 1 2 17 28 21 8
c. Find the mode.
d. Find the range.
Problem 5.Q.4
Find the mean of the random variable x described in the preceding exercise.
Problem 5.Q.5
Is the mean found in the preceding exercise a statistic or a parameter?
Problem 5.Q.10
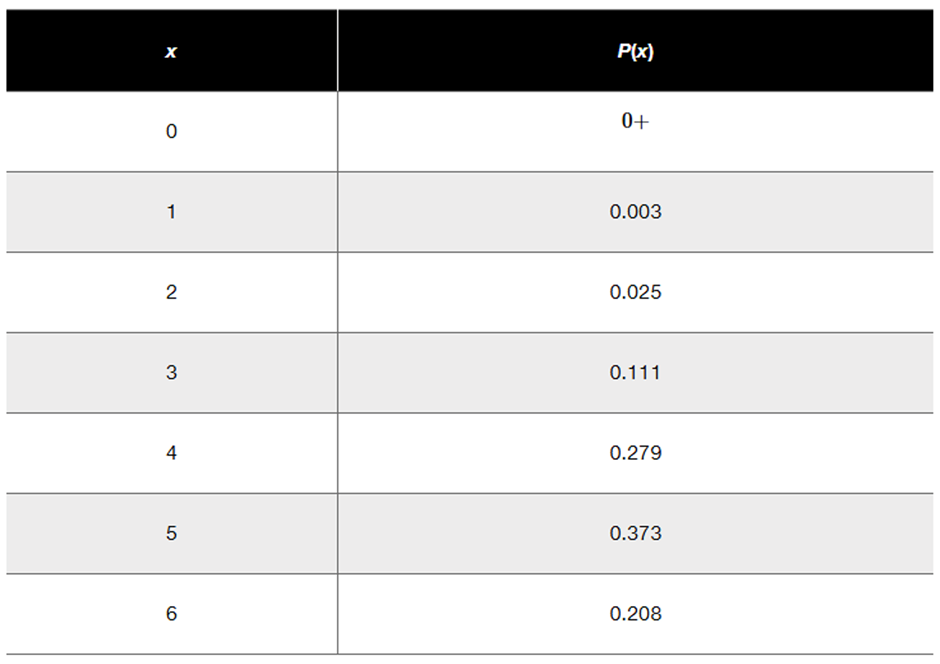
In Exercises 6–10, refer to the accompanying table, which describes the numbers of adults in groups of five who reported sleepwalking (based on data from “Prevalence and Comorbidity of Nocturnal Wandering In the U.S. Adult General Population,” by Ohayon et al., Neurology, Vol. 78, No. 20).
Significant Events Is 4 a significantly high number of sleepwalkers in a group of 5 adults? Explain.
Problem 5.R.10c
Poisson: Deaths Currently, an average of 7 residents of the village of Westport (population 760) die each year (based on data from the U.S. National Center for Health Statistics).
c. Find the probability that on a given day, there is more than one death.
Problem 5.R.4
In Exercises 1–5, assume that 4.2% of workers test positive when tested for illegal drugs (based on data from Quest Diagnostics). Assume that a group of ten workers is randomly selected.
Workplace Drug Testing If none of the ten workers tests positive for illegal drugs, is that a significantly low result?
Problem 5.R.3
In Exercises 1–5, assume that 4.2% of workers test positive when tested for illegal drugs (based on data from Quest Diagnostics). Assume that a group of ten workers is randomly selected.
Workplace Drug Testing Find the mean and standard deviation for the numbers of workers in groups of ten who test positive for illegal drugs.
Problem 5.R.10a
Poisson: Deaths Currently, an average of 7 residents of the village of Westport (population 760) die each year (based on data from the U.S. National Center for Health Statistics).
a. Find the mean number of deaths per day.
Problem 5.R.2
In Exercises 1–5, assume that 4.2% of workers test positive when tested for illegal drugs (based on data from Quest Diagnostics). Assume that a group of ten workers is randomly selected.
Workplace Drug Testing Find the probability that at least one of the ten workers tests positive for illegal drugs.
Problem 5.R.10b
Poisson: Deaths Currently, an average of 7 residents of the village of Westport (population 760) die each year (based on data from the U.S. National Center for Health Statistics).
b. Find the probability that on a given day, there are no deaths.
Problem 5.R.1
In Exercises 1–5, assume that 4.2% of workers test positive when tested for illegal drugs (based on data from Quest Diagnostics). Assume that a group of ten workers is randomly selected.
Workplace Drug Testing Find the probability that exactly two of the ten workers test positive for illegal drugs.
Problem 5.RE.5
In Exercises 1–5, assume that 4.2% of workers test positive when tested for illegal drugs (based on data from Quest Diagnostics). Assume that a group of ten workers is randomly selected.
Workplace Drug Testing If four of the ten workers test positive for illegal drugs, is that a significantly high result?
Problem 5.RE.8
Family/Partner Groups of people aged 15–65 are randomly selected and arranged in groups of six. The random variable x is the number in the group who say that their family and/or partner contribute most to their happiness (based on a Coca-Cola survey). The accompanying table lists the values of x along with their corresponding probabilities. Does the table describe a probability distribution? If so, find the mean and standard deviation.
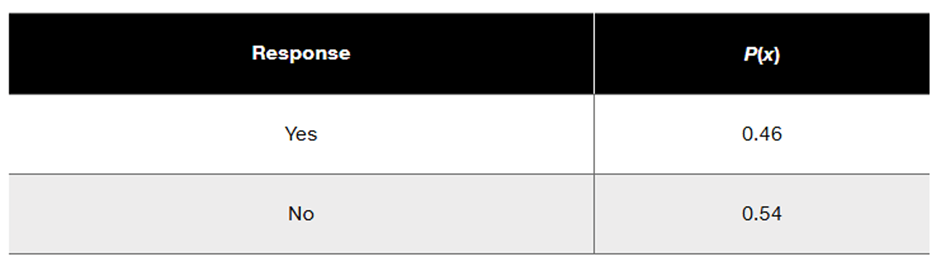
Problem 5.RE.6
Acrophobia USA Today reported results from a survey in which subjects were asked if they are afraid of heights in tall buildings. The results are summarized in the accompanying table. Does this table describe a probability distribution? Why or why not?
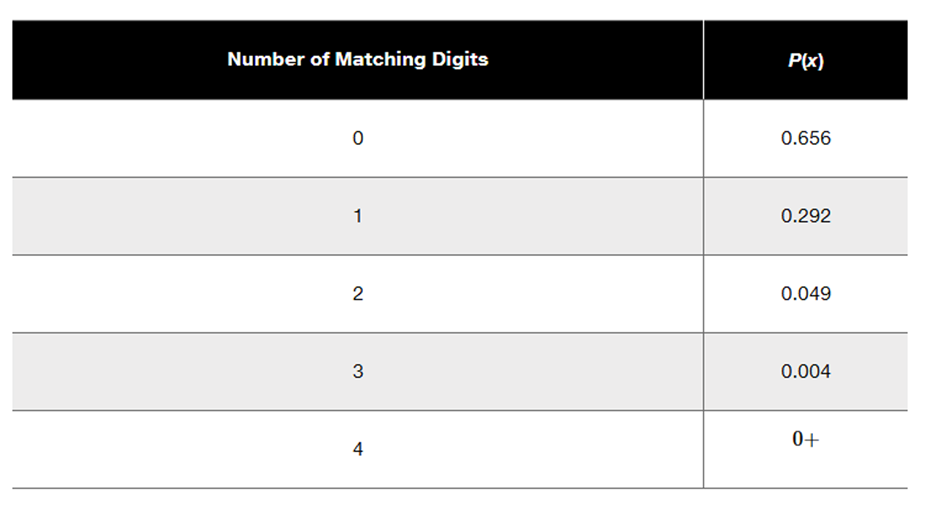
Problem 5.1.19a
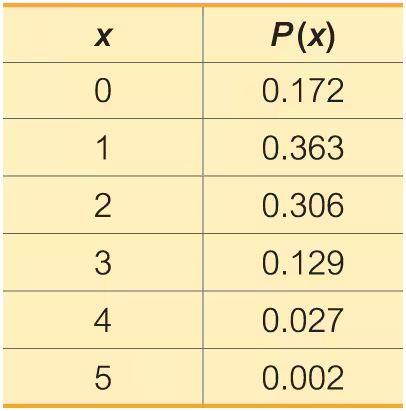
Lottery. In Exercises 15–20, refer to the accompanying table, which describes probabilities for the California Daily 4 lottery. The player selects four digits with repetition allowed, and the random variable x is the number of digits that match those in the same order that they are drawn (for a “straight” bet).
Using Probabilities for Significant Events
a. Find the probability of getting exactly 3 matches.
Problem 5.1.18a
Lottery. In Exercises 15–20, refer to the accompanying table, which describes probabilities for the California Daily 4 lottery. The player selects four digits with repetition allowed, and the random variable x is the number of digits that match those in the same order that they are drawn (for a “straight” bet).
Using Probabilities for Significant Events
a. Find the probability of getting exactly 2 matches.
Problem 5a
In Exercises 5–8, assume that the Poisson distribution applies; assume that the mean number of Atlantic hurricanes in the United States is 5.5 per year, as in Example 1; and proceed to find the indicated probability.
Hurricanes
a. Find the probability that in a year, there will be 7 hurricanes.
Problem 5.2.40a
One of Mendel’s famous experiments with peas resulted in 580 offspring, and 152 of them were yellow peas. Mendel claimed that under the same conditions, 25% of offspring peas would be yellow. Assume that Mendel’s claim of 25% is true, and assume that a sample consists of 580 offspring peas.
a. Use the range rule of thumb to identify the limits separating values that are significantly low and those that are significantly high. Based on the results, is the result of 152 yellow peas either significantly low or significantly high?
Problem 5.1.30a
Expected Value in North Carolina’s Pick 4 Game In North Carolina’s Pick 4 lottery game, you can pay $1 to select a four-digit number from 0000 through 9999. If you select the same sequence of four digits that are drawn, you win and collect $5000.
a. How many different selections are possible?
Problem 5.2.32a
In Exercises 31 and 32, assume that hybridization experiments are conducted with peas having the property that for offspring, there is a 0.75 probability that a pea has green pods (as in one of Mendel’s famous experiments).
Hybrids Assume that offspring peas are randomly selected in groups of 16.
a. Find the mean and standard deviation for the numbers of peas with green pods in the groups of 16.
Problem 5.2.38a
Politics The County Clerk in Essex, New Jersey, was accused of cheating by not using randomness in assigning the order in which candidates’ names appeared on voting ballots. Among 41 different ballots, Democrats were assigned the desirable first line 40 times. Assume that Democrats and Republicans are assigned the first line using a method of random selection so that they are equally likely to get that first line.
a. Use the range rule of thumb to identify the limits separating values that are significantly low and those that are significantly high. Based on the results, is the result of 40 first lines for Democrats significantly high?
Problem 5.2.28a
In Exercises 25–28, find the probabilities and answer the questions.
Too Young to Tat Based on a Harris poll, among adults who regret getting tattoos, 20% say that they were too young when they got their tattoos. Assume that five adults who regret getting tattoos are randomly selected, and find the indicated probability.
a. Find the probability that none of the selected adults say that they were too young to get tattoos.
Problem 5.3.9a
In Exercises 9–16, use the Poisson distribution to find the indicated probabilities.
Births In a recent year (365 days), NYU-Langone Medical Center had 5942 births.
a. Find the mean number of births per day.
Problem 5.3.8a
In Exercises 5–8, assume that the Poisson distribution applies; assume that the mean number of Atlantic hurricanes in the United States is 5.5 per year, as in Example 1; and proceed to find the indicated probability.
a. Find the probability that in a year, there will be 10 hurricanes.
Problem 5.1.20a
Using Probabilities for Significant Events
a. Find the probability of getting exactly 1 match.
Problem 5.3.7a
In Exercises 5–8, assume that the Poisson distribution applies; assume that the mean number of Atlantic hurricanes in the United States is 5.5 per year, as in Example 1; and proceed to find the indicated probability.
a. Find the probability that in a year, there will be no hurricanes.