Back
BackProblem 4.2.1
Notation When randomly selecting a new smartphone, D denotes the event that it has a manufacturing defect. What do P(D) and P(D) represent?
Problem 4.4.21
Phone Numbers Current rules for telephone area codes allow the use of digits 2–9 for the first digit, and 0–9 for the second and third digits, but the last two digits cannot both be 1 (to avoid confusion with area codes such as 911). How many different area codes are possible with these rules? That same rule applies to the exchange numbers, which are the three digits immediately preceding the last four digits of a phone number. Given both of those rules, how many 10-digit phone numbers are possible? Given that these rules apply to the United States and Canada and a few islands, are there enough possible phone numbers? (Assume that the combined population is about 400,000,000.)
Problem 4.4.8
Soccer Shootout In the FIFA Women’s World Cup 2019, a tie at the end of two overtime periods leads to a “shootout” with five kicks taken by each team from the penalty mark. Each kick must be taken by a different player. How many ways can 5 players be selected from the 11 eligible players? For the 5 selected players, how many ways can they be designated as first, second, third, fourth, and fifth?
Problem 4.2.2
Notation When randomly selecting adults, let M denote the event of randomly selecting a male and let B denote the event of randomly selecting someone with blue eyes. What does P (M|B) represent? Is P (M|B) the same as P (B|M)?
Problem 4.3.26
Unseen Coins A statistics professor tosses two coins that cannot be seen by any students. One student asks this question: “Did one of the coins turn up heads?” Given that the professor’s response is “yes,” find the probability that both coins turned up heads.
Problem 4.3.18
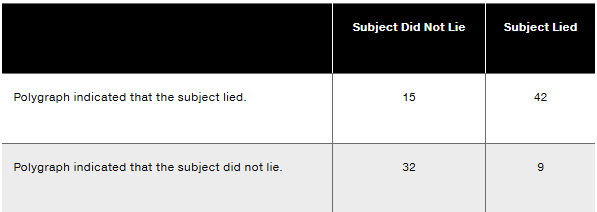
In Exercises 17–20, refer to the accompanying table showing results from experiments conducted by researchers Charles R. Honts (Boise State University) and Gordon H. Barland (Department of Defense Polygraph Institute). In each case, it was known whether or not the subject lied, so the table indicates when the polygraph (lie detector) test was correct.
False Negative Find the probability of selecting a subject with a negative polygraph result, given that the subject lied. What would be an unfavorable consequence of this error?
Problem 4.1.15
In Exercises 13–20, express the indicated degree of likelihood as a probability value between 0 and 1.
Movies Based on a study of the movies made in a recent year, 33 out of every 100 movies have a female lead or co-lead.
Problem 4.4.1
Notation What does the symbol ! represent? The five starting players of an NBA basketball team can stand in a line 5! different ways, so what is the actual number of ways that the five players can stand in a line?
Problem 4.2.9
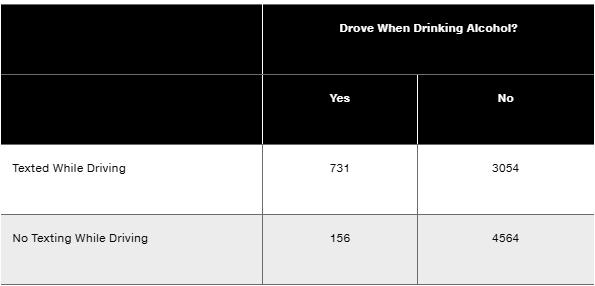
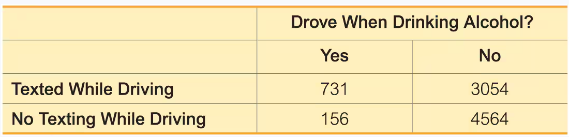
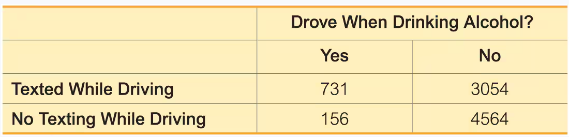
In Exercises 9–20, use the data in the following table, which lists survey results from high school drivers at least 16 years of age (based on data from “Texting While Driving and Other Risky Motor Vehicle Behaviors Among U.S. High School Students,” by O’Malley, Shults, and Eaton, Pediatrics, Vol. 131, No. 6). Assume that subjects are randomly selected from those included in the table. Hint: Be very careful to read the question correctly.
Drinking and Driving If one of the high school drivers is randomly selected, find the probability of getting one who drove when drinking alcohol.
Problem 4.1.1
California Lottery Let A denote the event of placing a $1 straight bet on the California Daily 4 lottery and winning. There are 10,000 different ways that you can select the four digits (with repetition allowed) in this lottery, and only one of those four-digit numbers will be the winner. What is the value of P(A)? What is the value of P(Abar)?
Problem 4.2.18
In Exercises 9–20, use the data in the following table, which lists survey results from high school drivers at least 16 years of age (based on data from “Texting While Driving and Other Risky Motor Vehicle Behaviors Among U.S. High School Students,” by O’Malley, Shults, and Eaton, Pediatrics, Vol. 131, No. 6). Assume that subjects are randomly selected from those included in the table. Hint: Be very careful to read the question correctly.
Texting and Alcohol If one of the high school drivers is randomly selected, find the probability that the selected driver did not text while driving and did not drive when drinking.
Problem 4.4.39
Pick 10 Lottery For the New York Pick 10 lottery, the player first selects 10 numbers from 1 to 80. Then there is an official drawing of 20 numbers from 1 to 80. The prize of $500,000 is won if the 10 numbers selected by the player are all included in the 20 numbers that are drawn. Find the probability of winning that prize.
Problem 4.4.6
Social Security Numbers A Social Security number consists of nine digits in a particular order, and repetition of digits is allowed. After seeing the last four digits printed on a receipt, if you randomly select the other digits, what is the probability of getting the correct Social Security number of the person who was given the receipt?
Problem 4.4.4
Combination Lock The typical combination lock uses three numbers, each between 0 and 49. Opening the lock requires entry of the three numbers in the correct order. Is the name “combination” lock appropriate? Why or why not?
Problem 4.1.23
In Exercises 21-28, find the probability and answer the questions.
Mendelian Genetics When Mendel conducted his famous genetics experiments with peas, one sample of offspring consisted of 428 green peas and 152 yellow peas. Based on those results, estimate the probability of getting an offspring pea that is green. Is the result reasonably close to the expected value of as Mendel claimed?
Problem 4.2.20
In Exercises 9–20, use the data in the following table, which lists survey results from high school drivers at least 16 years of age (based on data from “Texting While Driving and Other Risky Motor Vehicle Behaviors Among U.S. High School Students,” by O’Malley, Shults, and Eaton, Pediatrics, Vol. 131, No. 6). Assume that subjects are randomly selected from those included in the table. Hint: Be very careful to read the question correctly.
Texting and Alcohol If four different high school drivers are randomly selected, find the probability that they all texted while driving.
Problem 4.3.25
Shared Birthdays Find the probability that of 25 randomly selected people, at least 2 share the same birthday.
Problem 4.1.34
In Exercises 33–40, use the given probability value to determine whether the sample results are significant.
Voting Repeat the preceding Exercise 33 after replacing 40 Democrats being placed on the first line of voting ballots with 26 Democrats being placed on the first line. The probability of getting a result as high as 26 is 0.058638.
Problem 4.1.14
In Exercises 13–20, express the indicated degree of likelihood as a probability value between 0 and 1.
SAT Test When making a random guess for an answer to a multiple choice question on an SAT test, the possible answers are a, b, c, d, e, so there is 1 chance in 5 of being correct.
Problem 4.1.29
In Exercises 29–32, use the given sample space or construct the required sample space to find the indicated probability.
Three Children Use this sample space listing the eight simple events that are possible when a couple has three children (as in Example 2): {bbb, bbg, bgb, bgg, gbb, gbg, ggb, ggg}. Assume that boys and girls are equally likely, so that the eight simple events are equally likely. Find the probability that when a couple has three children, there is exactly one girl.
Problem 4.3.6
Probability of a Girl Assuming that boys and girls are equally likely, find the probability of a couple having a boy when their third child is born, given that the first two children were both girls.
Problem 4.2.32
Same Birthdays If 25 people are randomly selected, find the probability that no 2 of them have the same birthday. Ignore leap years.
Problem 4.1.6
Penicillin “Who discovered penicillin: Marcel Bich, William Penn, Jonas Salk, Alexander Fleming, or Louis Pasteur?” If you make a random guess for the answer to that question, what is the probability that your answer is the correct answer of Alexander Fleming?
Problem 4.4.16
DNA Nucleotides DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is made of nucleotides. Each nucleotide can contain any one of these nitrogenous bases: A (adenine), G (guanine), C (cytosine), T (thymine). If one of those four bases (A, G, C, T) must be selected three times to form a linear triplet, how many different triplets are possible? All four bases can be selected for each of the three components of the triplet.
Problem 4.2.23
In Exercises 21–24, use these results from the “1-Panel-THC” test for marijuana use, which is provided by the company Drug Test Success: Among 143 subjects with positive test results, there are 24 false positive (incorrect) results; among 157 negative results, there are 3 false negative (incorrect) results. (Hint: Construct a table similar to Table 4-1.)
Testing for Marijuana Use If one of the test subjects is randomly selected, find the probability that the subject tested positive or did not use marijuana.
Problem 4.3.1
Language: Complement of “At Least One” Let A=the event of getting at least one defective calculator when four are randomly selected with replacement from a batch. Write a statement describing event A
Problem 4.2.7
Laundry Symbols Based on a New Generation of Stains survey, 13% of U.S. adults know that the care-instruction symbol on clothing means that any bleach can be used. Find the probability of randomly selecting an adult in the U.S. who does not know that.
Problem 4.1.21
In Exercises 21-28, find the probability and answer the questions.
YSORT Gender Selection MicroSort’s YSORT gender selection technique is designed to increase the likelihood that a baby will be a boy. At one point before clinical trials of the YSORT gender selection technique were discontinued, 291 births consisted of 239 baby boys and 52 baby girls (based on data from the Genetics & IVF Institute). Based on these results, what is the probability of a boy born to a couple using MicroSort’s YSORT method? Does it appear that the technique is effective in increasing the likelihood that a baby will be a boy?
Problem 4.2.33
Exclusive Or The exclusive or means either one or the other event occurs, but not both.
If one of the high school drivers is randomly selected, find the probability of getting one who texted while driving or drove when drinking alcohol.
b. Repeat Exercise 11 “Texting or Drinking” using the exclusive or instead of the inclusive or.
Problem 4.3.5
Notation For a polygraph (lie detector) used when a subject is presented with a question, let L= the subject lied and let Y = the polygraph indicated that the subject told a lie. Use your own words to translate the notation P (Y|L) into a verbal statement.