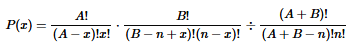Back
BackProblem 1
Internet Traffic Data Set 27 “Internet Traffic” includes 9000 arrivals of Internet traffic at the Digital Equipment Corporation, and those 9000 arrivals occurred over a period of 19,130 thousandths of a minute. Let the random variable x represent the number of such Internet traffic arrivals in one thousandth of a minute. It appears that these Internet arrivals have a Poisson distribution. If we want to use Formula 5-9 to find the probability of exactly 2 arrivals in one thousandth of a minute, what are the values of μ, x, and e that would be used in that formula?
Problem 3
For the distribution described in Exercise 1, find the probability of exactly 2 arrivals in one thousandth of a minute.
Problem 5.2.25
In Exercises 25–28, find the probabilities and answer the questions.
Whitus v. Georgia In the classic legal case of Whitus v. Georgia, a jury pool of 90 people was supposed to be randomly selected from a population in which 27% were minorities. Among the 90 people selected, 7 were minorities. Find the probability of getting 7 or fewer minorities if the jury pool was randomly selected. Is the result of 7 minorities significantly low? What does the result suggest about the jury selection process?
Problem 5.1.7
Identifying Probability Distributions. In Exercises 7–14, determine whether a probability distribution is given. If a probability distribution is given, find its mean and standard deviation. If a probability distribution is not given, identify the requirements that are not satisfied.
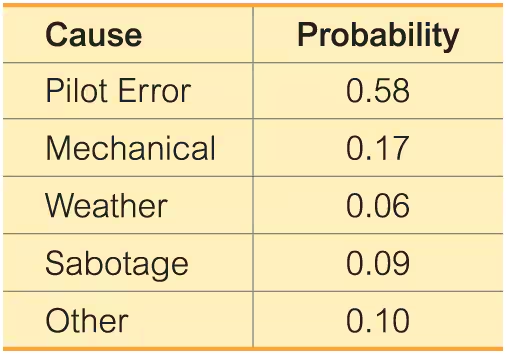
Plane Crashes The table lists causes of fatal plane crashes with their corresponding probabilities.
Problem 5.1.22
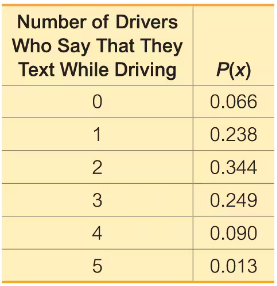
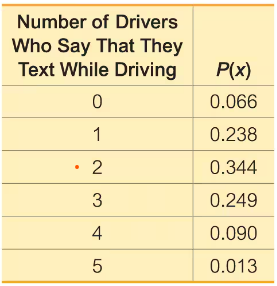
Texting and Driving. In Exercises 21–26, refer to the accompanying table, which describes probabilities for groups of five drivers. The random variable x is the number of drivers in a group who say that they text while driving (based on data from an Arity survey of drivers).
Range Rule of Thumb for Significant Events Use the range rule of thumb to determine whether 4 is a significantly high number of drivers who say that they text while driving.
Problem 5.2.3
Independent Events Again assume that when randomly selecting a speaking character in a movie, the probability of getting a female is 0.331, as in Exercise 1. If we want to find the probability of 20 females when 50 different speaking characters are randomly selected from a population of 1500 speaking characters, are the 50 selections independent? Using the 5% guideline for cumbersome calculations, can they be treated as being independent?
Problem 5.2.18
40% of consumers believe that cash will be obsolete in the next 20 years (based on a survey by J.P. Morgan Chase). In each of Exercises 15–20, assume that 8 consumers are randomly selected. Find the indicated probability.
Find the probability that no more than 3 of the selected consumers believe that cash will be obsolete in the next 20 years.
Problem 5.1.5
Identifying Discrete and Continuous Random Variables. In Exercises 5 and 6, refer to the given values, then identify which of the following is most appropriate: discrete random variable, continuous random variable, or not a random variable.
a. IQ scores of statistics students
b. Exact heights of statistics students
c. Shoe sizes (such as 8 or 8½) of statistics students
d. Majors (such as history) of statistics students
e. The number of rolls of a die required for a statistics student to get the number 4
Problem 5.1.17
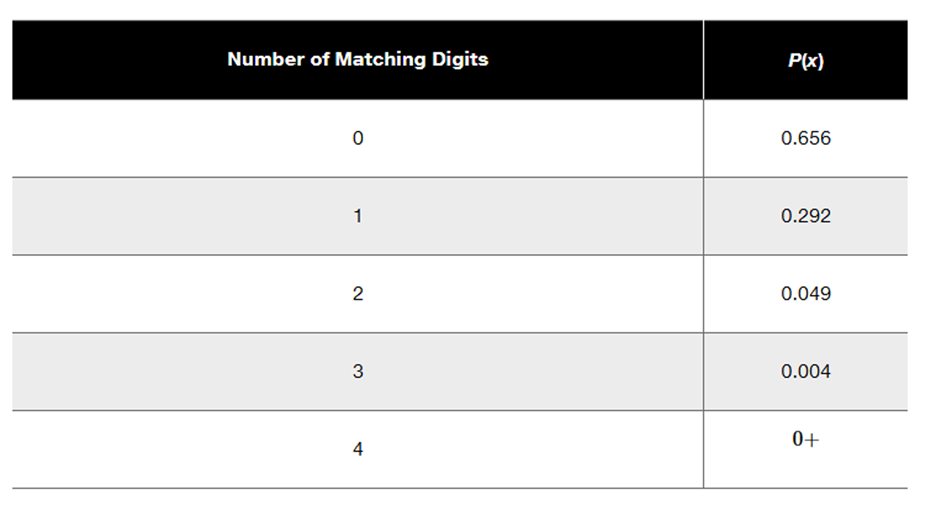
Lottery. In Exercises 15–20, refer to the accompanying table, which describes probabilities for the California Daily 4 lottery. The player selects four digits with repetition allowed, and the random variable x is the number of digits that match those in the same order that they are drawn (for a “straight” bet).
Range Rule of Thumb for Significant Events Use the range rule of thumb to determine whether 4 matches is a significantly high number of matches.
Problem 5.2.16
40% of consumers believe that cash will be obsolete in the next 20 years (based on a survey by J.P. Morgan Chase). In each of Exercises 15–20, assume that 8 consumers are randomly selected. Find the indicated probability.
Find the probability that at least 6 of the selected consumers believe that cash will be obsolete in the next 20 years.
Problem 5.1.27
Biometric Security In a USA Today survey of 510 people, 270 (or 53%) said that we should replace passwords with biometric security, such as fingerprints. Use the following probabilities related to determining whether the result of 270 is significantly high (assuming the true rate is 50%). Is 270 significantly high? What should be concluded about the claim that the majority of the population says that we should replace passwords with biometric security? Explain.
Problem 5.1.9
Identifying Probability Distributions. In Exercises 7–14, determine whether a probability distribution is given. If a probability distribution is given, find its mean and standard deviation. If a probability distribution is not given, identify the requirements that are not satisfied.
Online Courses College students are randomly selected and arranged in groups of three. The random variable x is the number in the group who say that they take one or more online courses (based on data from Sallie Mae).
Problem 5.1.4
Significant For 100 births, P(exactly 56 girls) and P(56 or more girls) Is 56 girls in 100 births a significantly high number of girls? Which probability is relevant to answering that question?
Problem 5.4.43
If we sample from a small finite population without replacement, the binomial distribution should not be used because the events are not independent. If sampling is done without replacement and the outcomes belong to one of two types, we can use the hypergeometric distribution. If a population has A objects of one type (such as lottery numbers you selected), while the remaining B objects are of the other type (such as lottery numbers you didn’t select), and if n objects are sampled without replacement (such as six drawn lottery numbers), then the probability of getting x objects of type A and objects of type B is
In New Jersey’s Pick 6 lottery game, a bettor selects six numbers from 1 to 49 (without repetition), and a winning six-number combination is later randomly selected. Find the probability of getting exactly four winning numbers with one ticket.
Problem 5.2.15
40% of consumers believe that cash will be obsolete in the next 20 years (based on a survey by J.P. Morgan Chase). In each of Exercises 15–20, assume that 8 consumers are randomly selected. Find the indicated probability.
Find the probability that exactly 6 of the selected consumers believe that cash will be obsolete in the next 20 years.
Problem 5.2.17
40% of consumers believe that cash will be obsolete in the next 20 years (based on a survey by J.P. Morgan Chase). In each of Exercises 15–20, assume that 8 consumers are randomly selected. Find the indicated probability.
Find the probability that fewer than 3 of the selected consumers believe that cash will be obsolete in the next 20 years.
Problem 5.1.1
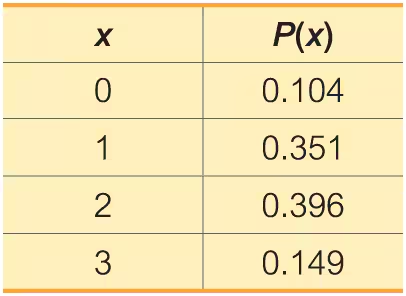
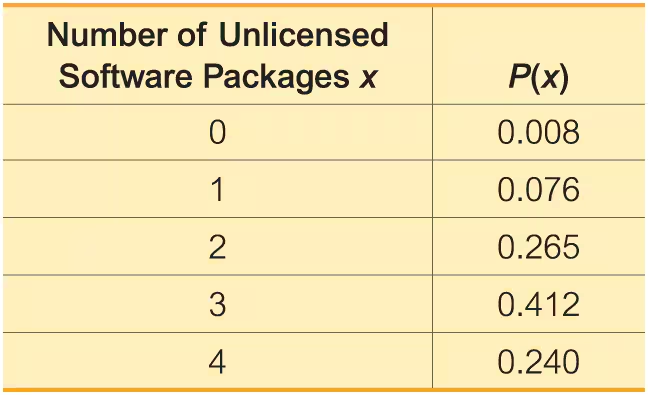
Random Variable The accompanying table lists probabilities for the corresponding numbers of unlicensed software packages when four software packages are randomly selected in China. What is the random variable, what are its possible values, and are its values numerical?
Problem 5.2.33
Exercises 33 and 34 involve the method of composite sampling, whereby a medical testing laboratory saves time and money by combining blood samples for tests so that only one test is conducted for several people. A combined sample tests positive if at least one person has the disease. If a combined sample tests positive, then individual blood tests are used to identify the individual with the disease or disorder.
HIV It is estimated that in the United States, the proportion of people infected with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is 0.00343. In tests for HIV, blood samples from 50 different people are combined. What is the probability that the combined sample tests positive for HIV? Is it unlikely for such a combined sample to test positive?
Problem 5.1.28
Stem Cell Survey In a Newsweek poll of 882 adults, 481 (or 55%) said that they were in favor of using federal tax money to fund medical research using stem cells obtained from human embryos. A politician claims that people don’t really understand the stem cell issue and their responses to such questions are random responses equivalent to a coin toss. Use the following probabilities related to determining whether the result of 481 is significantly high (assuming the true rate is 50%). Is 481 significantly high? What should be concluded about the politician’s claim? Explain.
P(respondent says to use the federal tax money) = 0.5
P(among 882, exactly 481 says to use federal tax money) = 0.000713
P(among 882,481 or more say to use federal tax money) = 0.00389
Problem 5.1.24
Texting and Driving. In Exercises 21–26, refer to the accompanying table, which describes probabilities for groups of five drivers. The random variable x is the number of drivers in a group who say that they text while driving (based on data from an Arity survey of drivers).
Using Probabilities for Significant Events
a. Find the probability of getting exactly 3 drivers who say that they text while driving.
Problem 5.1.12
Identifying Probability Distributions. In Exercises 7–14, determine whether a probability distribution is given. If a probability distribution is given, find its mean and standard deviation. If a probability distribution is not given, identify the requirements that are not satisfied.
Fear of Heights The table lists results from a survey of 285 subjects who were asked, “Are you afraid of heights in tall buildings?” The results are from USA Today.
Problem 5.2.2
Notation Assume that we want to find the probability that when five speaking characters in movies are randomly selected, exactly two of them are females. Also assume that when randomly selecting a speaking character in a movie, the probability of getting a female is 0.331. Identify the values of n, x, p, and q.
Problem 5.2.6
In Exercises 5–12, determine whether the given procedure results in a binomial distribution or a distribution that can be treated as binomial (by applying the 5% guideline for cumbersome calculations). For those that are not binomial and cannot be treated as binomial, identify at least one requirement that is not satisfied.
In a Pew Research Center survey, 3930 subjects were asked if they have ever fired a gun, and the responses consist of “yes” or “no.”
Problem 5.1.2
Discrete or Continuous? Is the random variable given in the table from Exercise 1 discrete or continuous? Explain.
Problem 5.2.7
In Exercises 5–12, determine whether the given procedure results in a binomial distribution or a distribution that can be treated as binomial (by applying the 5% guideline for cumbersome calculations). For those that are not binomial and cannot be treated as binomial, identify at least one requirement that is not satisfied.
LOL In a U.S. Cellular survey of 500 smartphone users, subjects are asked if they find abbreviations (such as LOL or BFF) annoying, and each response was recorded as “yes,” “no,” or “not sure.”
Problem 5.2.5
In Exercises 5–12, determine whether the given procedure results in a binomial distribution or a distribution that can be treated as binomial (by applying the 5% guideline for cumbersome calculations). For those that are not binomial and cannot be treated as binomial, identify at least one requirement that is not satisfied.
Pew Survey In a Pew Research Center survey of 3930 subjects, the ages of the respondents are recorded.
Problem 5.C.1.5
Planets The planets of the solar system have the numbers of moons listed below in order from the sun. (Pluto is not included because it was uninvited from the solar system party in 2006.) Include appropriate units whenever relevant.
0 0 1 2 17 28 21 8
i. What is the level of measurement of the data: nominal, ordinal, interval, or ratio?
j. Are the data discrete or continuous?
Problem 5.CRE.2b
Kentucky Pick 4 In the Kentucky Pick 4 lottery game, you can pay $1 for a “straight” bet in which you select four digits with repetition allowed. If you buy only one ticket and win, your prize is $2500.
b. If you play this game once every day, find the mean number of wins in years with exactly 365 days.
Problem 5.CRE.3a
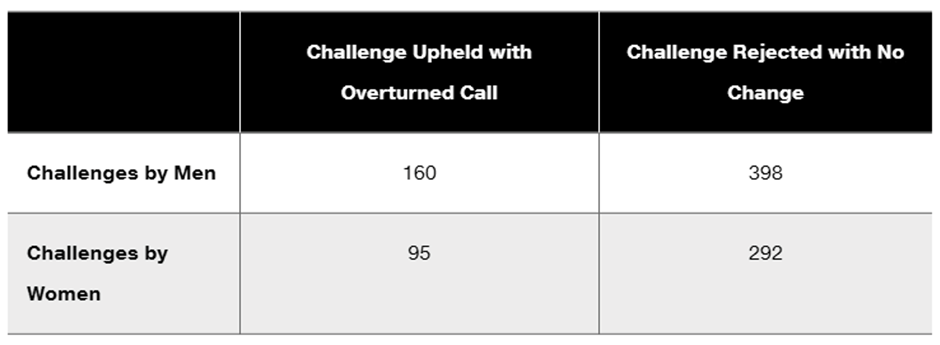
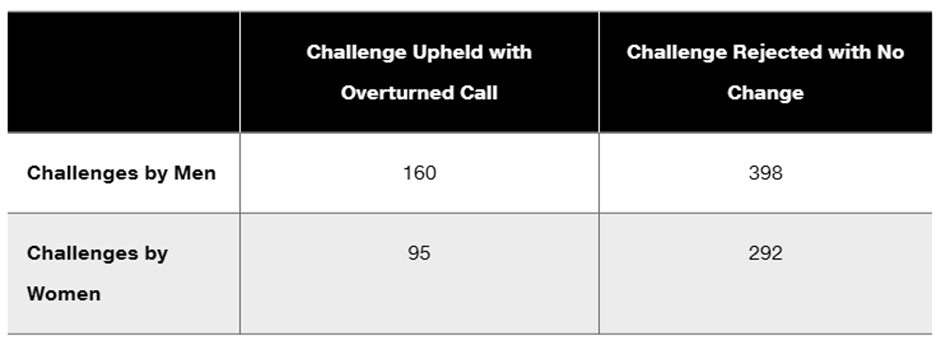
Tennis Challenge In a recent U.S. Open tennis tournament, there were 945 challenges made by singles players, and 255 of them resulted in referee calls that were overturned. The accompanying table lists the results by gender.
a. If 1 of the 945 challenges is randomly selected, what is the probability that it resulted in an overturned call?
Problem 5.CRE.3c
Tennis Challenge In a recent U.S. Open tennis tournament, there were 945 challenges made by singles players, and 255 of them resulted in referee calls that were overturned. The accompanying table lists the results by gender.
c. If two different challenges are randomly selected without replacement, find the probability that they both resulted in an overturned call.