Draw the structure of the sphingomyelin that contains a myristic acid acyl group. Identify the hydrophilic head group and the hydrophobic tails in this molecule.

Which of the following terms apply to the compound shown below? (Hint: Look at the functional groups and the bonds involved to begin analyzing the compound part by part in comparison to the lipids discussed in this chapter.)
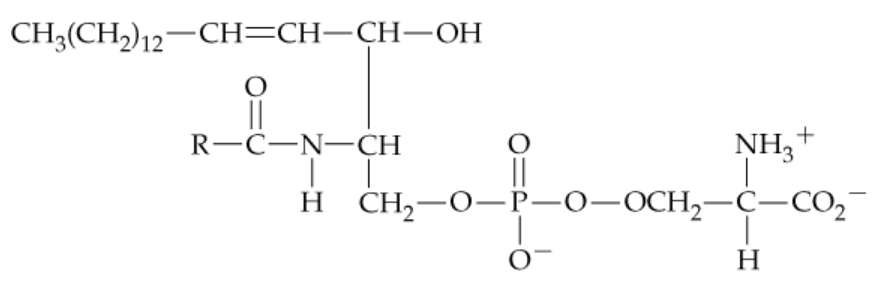
e. A lipid
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Functional Groups
Lipids

Chemical Bonds

Draw the structure of the glycerophospholipid that contains a stearic acid acyl group, an oleic acid acyl group, and a phosphate bonded to ethanolamine.
Which of the following terms apply to the compound shown below? (Hint: Look at the functional groups and the bonds involved to begin analyzing the compound part by part in comparison to the lipids discussed in this chapter.)
a. A phospholipid
As noted earlier (Section 22.3), he first step in glycolysis, which occurs within cells, is phosphorylation of glucose to glucose 6-phosphate. Why does this step prevent passive diffusion of glucose back out of the cell?
Complete hydrogenation of triacylglycerol C in Problem 23.20 yields a triacylglycerol of what fatty acid composition? Would the hydrogenation product of triacylglycerol C be more like the hydrogenation product of triacylglycerol A or B? Explain.
A membrane lipid was isolated and completely hydrolyzed. The following products were detected: ethanolamine, phosphate, glycerol, palmitic acid, and oleic acid. Propose a structure for this membrane lipid, and name the family to which it belongs.
