How many steps in gluconeogenesis are not the exact reversal of the steps in glycolysis? What kind of conversion of substrate to product does each involve? What is the common theme in each of these reactions?
Ch.22 Carbohydrate Metabolism

Chapter 22, Problem 73b
How many moles of ATP are generated from the catabolism of fructose (by glycolysis) in
(b) muscle cells?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the context: Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose or fructose into pyruvate, generating ATP in the process. In muscle cells, glycolysis occurs anaerobically (without oxygen).
Recall the key stoichiometry of glycolysis: For each molecule of fructose (C6H12O6) that enters glycolysis, it is converted into two molecules of pyruvate. During this process, a net of 2 ATP molecules are produced per molecule of fructose.
Set up the relationship: The number of moles of ATP generated is directly proportional to the number of moles of fructose metabolized. Specifically, for every 1 mole of fructose, 2 moles of ATP are produced.
Write the mathematical expression: If the number of moles of fructose is denoted as \( n_{\text{fructose}} \), then the number of moles of ATP generated is \( n_{\text{ATP}} = 2 \times n_{\text{fructose}} \).
To find the exact number of moles of ATP, substitute the given number of moles of fructose (if provided) into the equation \( n_{\text{ATP}} = 2 \times n_{\text{fructose}} \). If no specific value is given, the relationship remains as described.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that converts glucose or other sugars, such as fructose, into pyruvate, producing energy in the form of ATP. This process occurs in the cytoplasm of cells and consists of ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions. In muscle cells, glycolysis is crucial for generating ATP quickly, especially during anaerobic conditions.
Recommended video:
Guided course
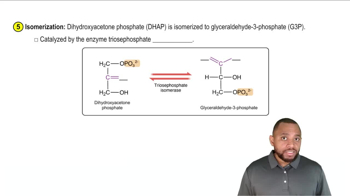
Glycolysis Concept 5
ATP Yield from Fructose
The catabolism of fructose through glycolysis yields a specific amount of ATP. Fructose is phosphorylated and enters the glycolytic pathway, ultimately producing two molecules of pyruvate. Each molecule of pyruvate can generate a net gain of 2 ATP during glycolysis, leading to a total of 4 ATP from one molecule of fructose, considering the initial investment of 2 ATP.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Percent Yield
Muscle Cell Metabolism
Muscle cells have a unique metabolic profile that allows them to efficiently produce ATP during physical activity. They rely heavily on glycolysis for rapid ATP production, especially under anaerobic conditions. This is important for muscle contraction and energy supply during intense exercise, where oxygen availability may be limited.
Recommended video:
Guided course
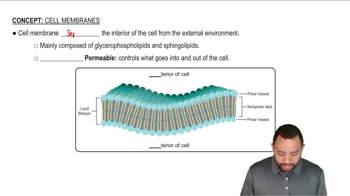
Cell Membranes Concept 1
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Explain why the Cori cycle is necessary and when your cells would use this cycle.
Textbook Question
How many moles of ATP are generated from the catabolism of fructose (by glycolysis) in
(a) liver cells?
1
views
Textbook Question
Which of the following conversions would you expect to consume energy and which would you expect to yield energy based on the final oxidation state of the coenzymes involved in each reaction?
a. pyruvate → lactate
Textbook Question
Why is it important for muscle cells to export lactate into the bloodstream during heavy exercise?
Textbook Question
Why is it important for the cell that the NADH produced when pyruvate is converted to lactate be converted back to NAD+?
