Phenols undergo the same kind of substitution reactions that other aromatic compounds do. Formulate the reaction of p-methylphenol with Br2 to give a mixture of two substitution products.
Ch.14 Some Compounds with Oxygen, Sulfur, or a Halogen

Chapter 14, Problem 67d
Write the formulas and IUPAC names for the following common alcohols.
d. Diol used as antifreeze (two answers)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the term 'diol'—a diol is an alcohol containing two hydroxyl (-OH) groups. The problem specifies that the diol is used as antifreeze, which hints at common compounds like ethylene glycol and propylene glycol.
Step 2: Write the chemical formula for ethylene glycol. Ethylene glycol is a diol with the formula \( \text{C}_2\text{H}_6\text{O}_2 \), where two hydroxyl groups are attached to a two-carbon chain.
Step 3: Write the IUPAC name for ethylene glycol. The IUPAC name is 'ethane-1,2-diol,' indicating the hydroxyl groups are attached to the first and second carbons of the ethane backbone.
Step 4: Write the chemical formula for propylene glycol. Propylene glycol is a diol with the formula \( \text{C}_3\text{H}_8\text{O}_2 \), where two hydroxyl groups are attached to a three-carbon chain.
Step 5: Write the IUPAC name for propylene glycol. The IUPAC name is 'propane-1,2-diol,' indicating the hydroxyl groups are attached to the first and second carbons of the propane backbone.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Alcohols
Alcohols are organic compounds characterized by the presence of one or more hydroxyl (-OH) groups attached to a carbon atom. They are classified based on the number of hydroxyl groups: primary, secondary, and tertiary. Common examples include methanol and ethanol, which are widely used in various applications, including as solvents and fuels.
Recommended video:
Guided course
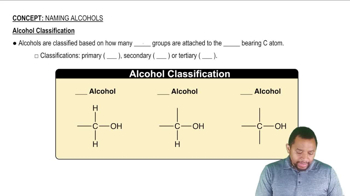
Alcohol Classification Concept 2
Diols
Diols, also known as glycols, are a specific type of alcohol that contain two hydroxyl groups. They can be classified as either vicinal (adjacent) or geminal (on the same carbon). Diols are important in industrial applications, such as antifreeze formulations, where they lower the freezing point of water, enhancing the performance of cooling systems.
IUPAC Nomenclature
IUPAC nomenclature is a systematic method for naming chemical compounds, ensuring that each name conveys specific information about the structure of the molecule. For alcohols, the name typically includes the longest carbon chain followed by the suffix '-ol' to indicate the presence of the hydroxyl group. Understanding this system is essential for accurately identifying and communicating the structure of chemical compounds.
Recommended video:
Guided course
IUPAC Naming Concept 3
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Which of the alcohols pictured in Problem 14.48 are chiral? Indicate the chiral carbons for those that are chiral.
a.
b.
c. 2,3-Pentanediol
d.
e.
f.
Textbook Question
Write the formulas and IUPAC names for the following common alcohols.
a. Rubbing alcohol
Textbook Question
Name the following compounds:
c.
d.
Textbook Question
Name the following compounds:
e.
f.
Textbook Question
'Designer vinegars' have become very popular over the past decade. Vinegars made from champagne, merlot, and other wines are but a few of these. All wines contain ethanol, and these vinegars are simply wines containing microorganisms that have caused oxidation of the ethanol present. If vinegar is simply ethanol that has been oxidized, what is the structure of the acid formed?
