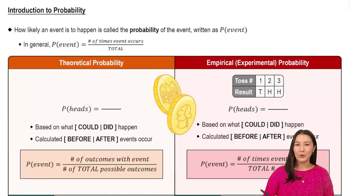
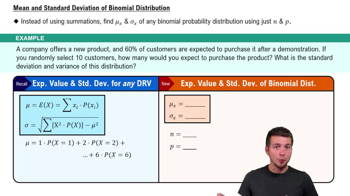
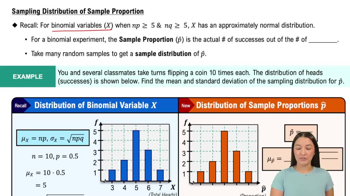
Kentucky Pick 4 In the Kentucky Pick 4 lottery game, you can pay \$1 for a “straight” bet in which you select four digits with repetition allowed. If you buy only one ticket and win, your prize is \$2500.
a. If you buy one ticket, what is the probability of winning?