6. Intro to Forces (Dynamics)
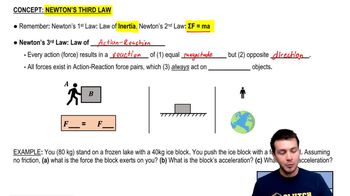
Newton's Third Law & Action-Reaction Pairs
6. Intro to Forces (Dynamics)
Newton's Third Law & Action-Reaction Pairs
Additional 5 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 8 of 8 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Which of the options is NOT an action-reaction pair in the following situation? A book slides across the floor, slowing down due to friction.
- Multiple ChoiceTaylor (150 lbs.) and Josh (200 lbs.) are standing on frictionless ice. Taylor pushes on Josh. During the push which person exerts the greater force on the other?
- Multiple ChoiceTaylor (150 lbs.) and Josh (200 lbs.) are standing on frictionless ice. Taylor pushes on Josh. During the push who experiences the greater magnitude of acceleration?
- Multiple ChoiceA book is at rest on a horizontal table. The main forces acting on the book are the normal force from the table and the weight of the book. What is the best description of Newton's third law reaction force to the weight?
- Open QuestionBoxes A and B are in contact on a horizontal, frictionless surface (Fig. E4.23). Box A has mass 20.0 kg and box B has mass 5.0 kg. A horizontal force of 250 N is exerted on box A. What is the magnitude of the force that box A exerts on box B?
- Open QuestionWorld-class sprinters can accelerate out of the starting blocks with an acceleration that is nearly horizontal and has magnitude 15 m/s2. How much horizontal force must a 55-kg sprinter exert on the starting blocks to produce this acceleration? Which body exerts the force that propels the sprinter: the blocks or the sprinter herself?
- Open QuestionA small car of mass 380 kg is pushing a large truck of mass 900 kg due east on a level road. The car exerts a horizontal force of 1600 N on the truck. What is the magnitude of the force that the truck exerts on the car?
- Open QuestionAn 85 kg cheerleader stands on a scale that reads in kg.b. What does the scale read if the 85 kg cheerleader lifts the 50kg cheerleader upward with an acceleration of 2.0 m/s²?