33. Geometric Optics
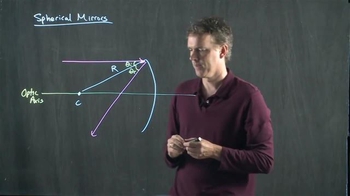
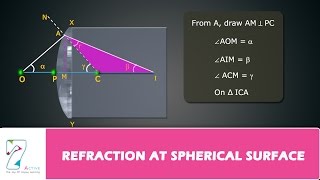
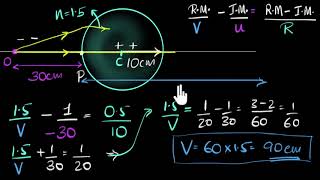
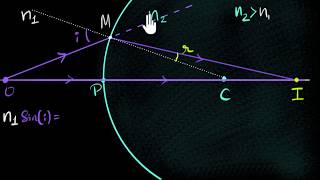
Refraction At Spherical Surfaces
33. Geometric Optics
Refraction At Spherical Surfaces
Additional 1 creators.
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
An object is embedded in glass as shown in the following figure. If the glass has a concave face, and is embedded in water, where will the image be located? Will the image be real or virtual?
- Multiple ChoiceA student observes a goldfish in a flat sided aquarium. The goldfish observes the student. If the student observes that the image of the fish's nose is from the side of the tank, how far behind the glass is the nose of the fish?
- Multiple ChoiceOne side of a biconvex glass lens (n=1.5) has a radius of curvature of , while the other side has a radius of curvature of . What is its focal length?
- Multiple Choice
An object is embedded in glass as shown in the following figure. If the glass has a concave face, and is embedded in water, where will the image be located? Will the image be real or virtual?
- Open QuestionA Spherical Fish Bowl. A small tropical fish is at the center of a water-filled, spherical fish bowl 28.0 cm in diameter. (a) Find the apparent position and magnification of the fish to an observer outside the bowl. The effect of the thin walls of the bowl may be ignored.
- Open QuestionThe left end of a long glass rod 8.00 cm in diameter, with an index of refraction of 1.60, is ground and polished to a convex hemispherical surface with a radius of 4.00 cm. An object in the form of an arrow 1.50 mm tall, at right angles to the axis of the rod, is located on the axis 24.0 cm to the left of the vertex of the convex surface. Find the position and height of the of the arrow formed by paraxial rays incident on the convex surface. Is the erect or inverted?