24. Electric Force & Field; Gauss' Law
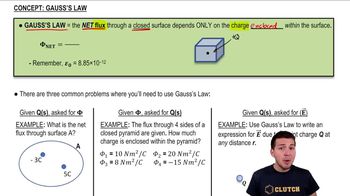
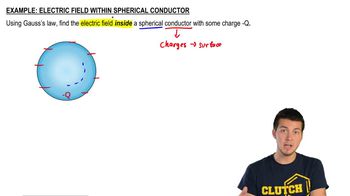
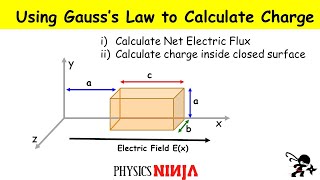
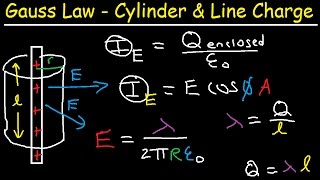
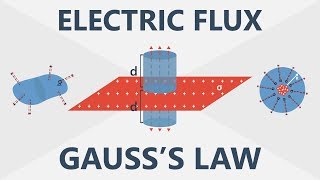
Gauss' Law
24. Electric Force & Field; Gauss' Law
Gauss' Law
Additional 6 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 9 of 9 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
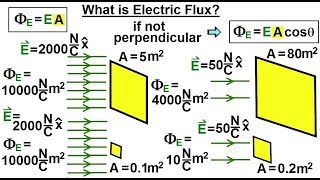
Rank the flux through surfaces A, B and C in the figure below from greatest to smallest.
- Multiple Choice
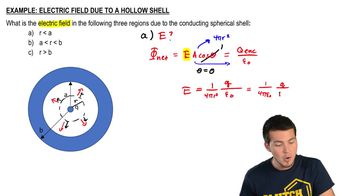
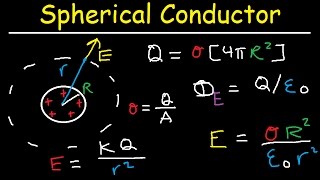
A spherical, thin conducting shell of radius 8cm has a charge of –6C. If a 4C charge were placed at the center of the shell, what is the electric field 4 cm from the center? At 12 cm?
- Multiple ChoiceA cube has sides equal to . The net flux through the cube is outward. Is the net charge in the cube positive, negative or zero?
- Multiple ChoiceAn electric field with strength exists just outside a face of a large block of aluminum. If the electric field points towards the block, what is the surface charge density on the face of the block?
- Open QuestionA charged paint is spread in a very thin uniform layer over the surface of a plastic sphere of diameter 12.0 cm, giving it a charge of −49.0 μ C. Find the electric field (b) just outside the paint layer;
- Open QuestionA charged paint is spread in a very thin uniform layer over the surface of a plastic sphere of diameter 12.0 cm, giving it a charge of −49.0 μ C. Find the electric field (a) just inside the paint layer;
- Open QuestionThe nuclei of large atoms, such as uranium, with 92 protons, can be modeled as spherically symmetric spheres of charge. The radius of the uranium nucleus is approximately 7.4×10−15 m. (c) The electrons can be modeled as forming a uniform shell of negative charge. What net electric field do they produce at the location of the nucleus?
- Open QuestionThe nuclei of large atoms, such as uranium, with 92 protons, can be modeled as spherically symmetric spheres of charge. The radius of the uranium nucleus is approximately 7.4×10−15 m. (b) What magnitude of electric field does it produce at the distance of the electrons, which is about 1.0×10−10 m?