24. Electric Force & Field; Gauss' Law
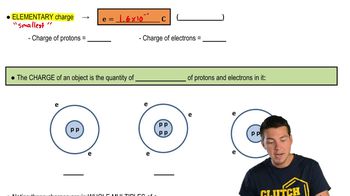
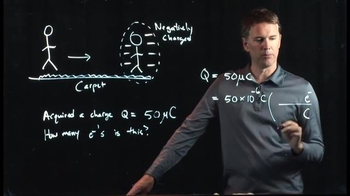
Electric Charge
24. Electric Force & Field; Gauss' Law
Electric Charge
Additional 6 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 9 of 9 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
How many electrons make up −1.5 × 10−5 C?
- Multiple Choice
How many electrons do you have to add to decrease the charge of an object by 16 μC?
- Multiple ChoiceA glass rod is rubbed with silk, and a plastic rod is rubbed with wool. Afterward, to which object or objects will the glass rod be attracted?
- Multiple ChoiceA ring of charge lies in the xy-plane with its center at the origin. The ring has a radius of 87 cm and a total charge of . What is the linear charge density on the ring?
- Open QuestionTwo small aluminum spheres, each having mass 0.0250 kg, are separated by 80.0 cm. (a) How many electrons does each sphere contain? (The atomic mass of aluminum is 26.982 g/mol, and its atomic number is 13.)
- Open QuestionLightning occurs when there is a flow of electric charge (principally electrons) between the ground and a thundercloud. The maximum rate of charge flow in a lightning bolt is about 20,000 C/s; this lasts for 100 ms or less. How much charge flows between the ground and the cloud in this time? How many electrons flow during this time?
- Open QuestionWhat mass of aluminum has a total nuclear charge of 1.0 C? Aluminum has atomic number 13.
- Open QuestionA proton orbits a long charged wire, making 1.0×10^6 revolutions per second. The radius of the orbit is 1.0 cm. What is the wire's linear charge density?