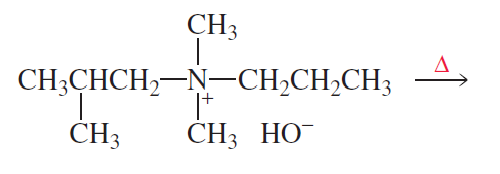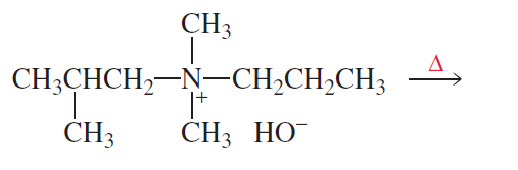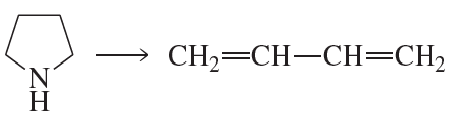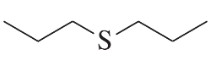Back
Back Bruice 8th Edition
Bruice 8th Edition Ch.10 - Reactions of Alcohols, Ethers, Epoxides, Amines, and Sulfur-Containing Compounds
Ch.10 - Reactions of Alcohols, Ethers, Epoxides, Amines, and Sulfur-Containing CompoundsProblem 22c(1,2,3)
What product is obtained from the reaction of each of the following alcohols with
c. the regents required for a Swern oxidation?
1. 3-pentanol
2. 1-pentanol
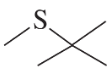
3. 2-methyl-2-pentanol
Problem 23
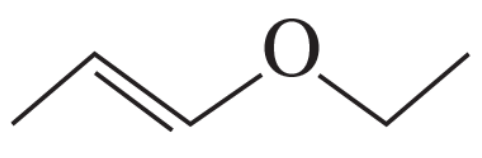
What are the major products obtained when the following ether is heated with one equivalent of HI?
Problem 24c,d
What are the major products obtained when each of the following ethers is heated with one equivalent of HI?
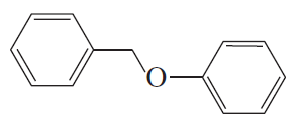
c.
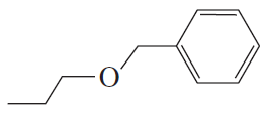
d.
Problem 24e
What are the major products obtained when each of the following ethers is heated with one equivalent of HI?
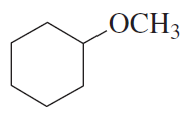
e.
Problem 25
Explain why methyl propyl ether forms both methyl iodide and propyl iodide when it is heated with excess HI.
Problem 26
Explain why HF and HCl cannot be used to cleave ethers in an SN2 reaction.
Problem 28
Would you expect the reactivity of a five-membered ring ether such as tetrahydrofuran (Table 10.2) to be more similar to the reactivity of an epoxide or to the reactivity of a noncyclic ether? Why?
Problem 29b
How can the following compounds be prepared from 3,3-dimethyl-1-butene?
b. 3,3-dimethyl-2-butanol
Problem 30a
What products are obtained from the reaction of cyclohexene oxide with
a. methoxide ion?
Problem 30b
What products are obtained from the reaction of cyclohexene oxide with
b. methylamine?
Problem 32a,b
What stereoisomers are obtained from the reaction of each of the following alkenes with OsO4 followed by aqueous H2O2?
a. trans-2-butene
b. cis-2-butene
Problem 33a,b
What stereoisomers are obtained from the reaction of the alkenes in [PROBLEM 10-32] with a peroxyacid followed by reaction with hydroxide ion?
a. trans-2-butene
b. cis-2-butene
Problem 33c,d
What stereoisomers are obtained from the reaction of the alkenes in [PROBLEM 10-32] with a peroxyacid followed by reaction with hydroxide ion?
c. cis-2-pentene
d. trans-2-pentene
Problem 34
Draw the mechanism for formation of the two addition products.
Problem 35
Draw all possible resonance contributors for the two carbocations in the preceding reaction. Use the resonance contributors to explain why 1-naphthol is the major product of the reaction.
Problem 36a
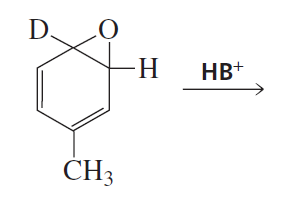
The existence of the NIH shift was established by determining the major product obtained from rearrangement of the following arene oxide, in which a hydrogen has been replaced by a deuterium.
a. What would be the major product if the NIH shift occurs? (Hint: A C—H bond is easier to break than a C—D bond.)
Problem 36b
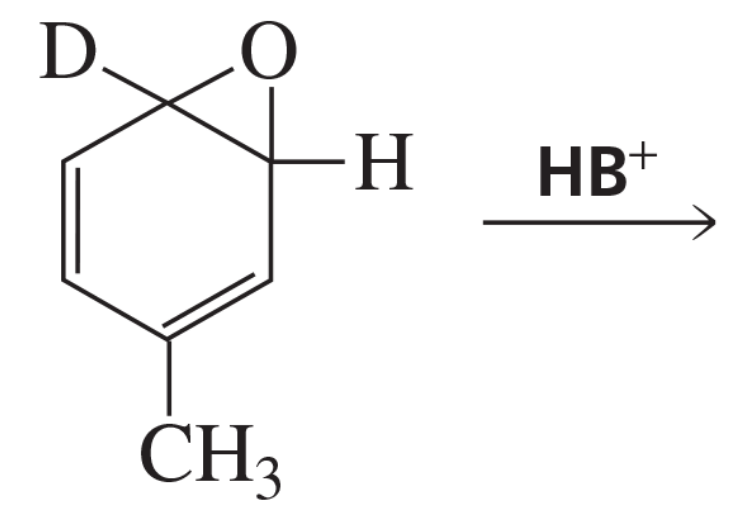
The existence of the NIH shift was established by determining the major product obtained from rearrangement of the following arene oxide, in which a hydrogen has been replaced by a deuterium.
b. What would be the major product if the carbocation forms phenol by losing H+ or D+, rather than by going through the NIH shift?
Problem 37
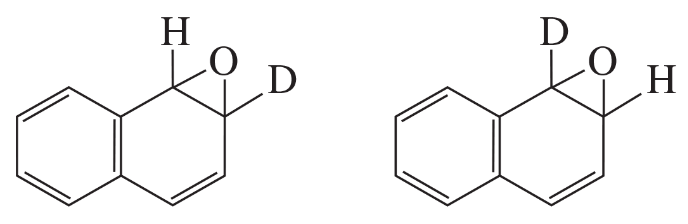
How do the major products obtained from rearrangement of the following arene oxides differ?
Problem 39
Explain why the two arene oxides in [PROBLEM 10-38] open in opposite directions.
Problem 41a
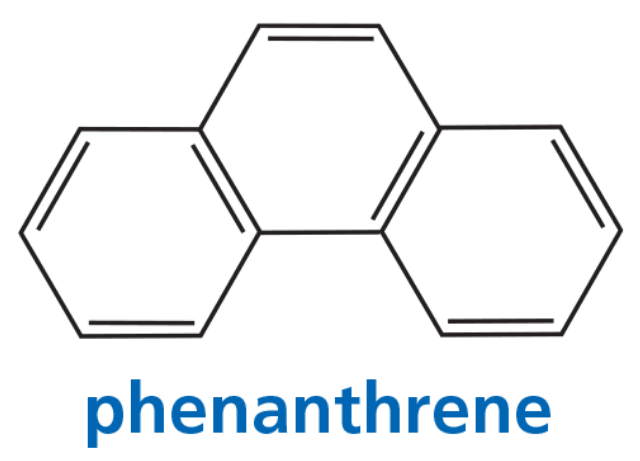
Three arene oxides can be obtained from phenanthrene.
a. Draw the structures of the three phenanthrene oxides.
Problem 41c
Three arene oxides can be obtained from phenanthrene.
c. If a phenanthrene oxide can lead to the formation of more than one phenol, which phenol will be obtained in greater yield?
Problem 41d
Three arene oxides can be obtained from phenanthrene.
d. Which of the three phenanthrene oxides is most likely to be carcinogenic?
Problem 42
Explain why the half-life (the time it takes for one-half of the compound to be metabolized) of Xylocaine is longer than that of Novocaine.
Problem 43
If a quaternary ammonium ion can undergo an elimination reaction with a strong base, why can’t a protonated tertiary amine undergo the same reaction?
Problem 44
What are the major products of the following reaction?
Problem 45
What are the minor products of the preceding Hofmann elimination reaction?
Problem 47b
What is the major product of each of the following reactions?
b
.
Problem 49b
Describe a synthesis for each of the following compounds, using the given starting material and any necessary reagents:
b.
Problem 50a
Using an alkyl halide and a thiol as starting materials, how would you prepare the following thioethers?
a.
Problem 50b
Using an alkyl halide and a thiol as starting materials, how would you prepare the following thioethers?
b.