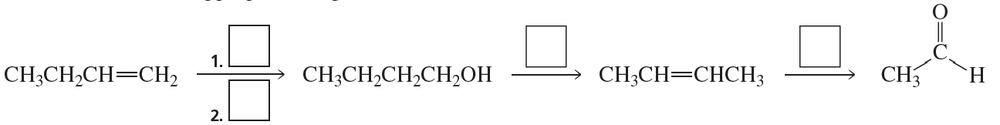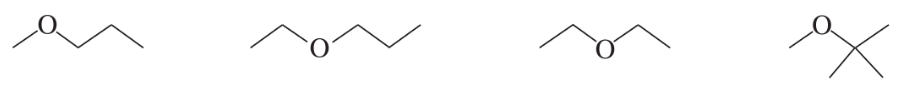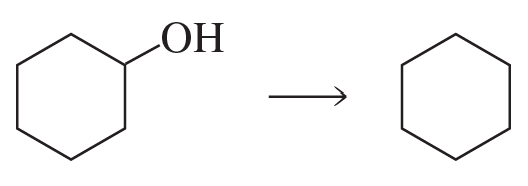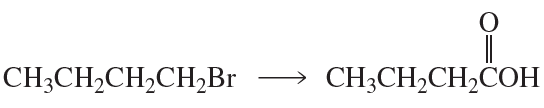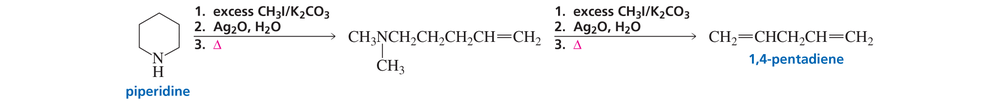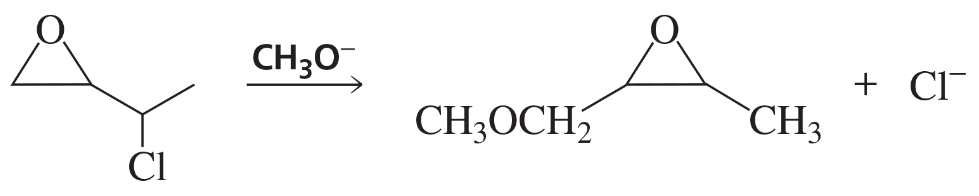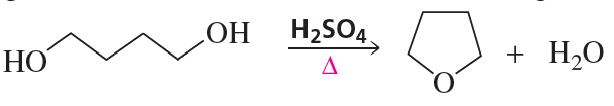Back
Back Bruice 8th Edition
Bruice 8th Edition Ch.10 - Reactions of Alcohols, Ethers, Epoxides, Amines, and Sulfur-Containing Compounds
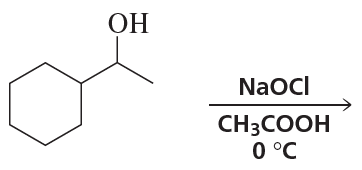
Ch.10 - Reactions of Alcohols, Ethers, Epoxides, Amines, and Sulfur-Containing CompoundsProblem 63h
What is the major product(s) of each of the following reactions?
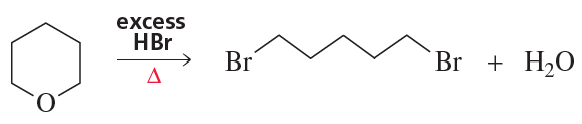
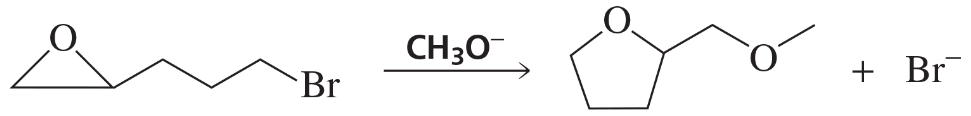
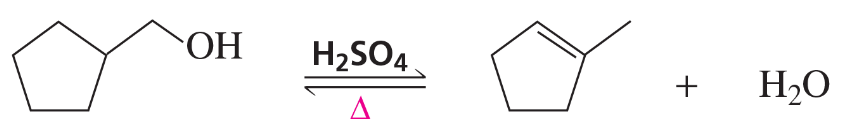
h.
Problem 64b
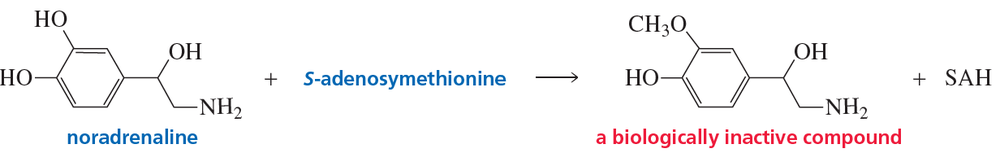
In Section 10.12, we saw that S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) methylates the nitrogen atom of noradrenaline to form adrenaline, a more potent hormone. If SAM methylates an OH group attached to the benzene ring instead, it completely destroys noradrenaline's activity.
b. Which reaction is more apt to occur, methylation on nitrogen or methylation on oxygen?
Problem 66
An unknown alcohol with a molecular formula of C7H14O was oxidized to an aldehyde with HOCl. When an acidic solution of the alcohol was distilled, two alkenes were obtained. The alkene formed in greater yield was determined to be 1-methylcyclohexene. The other alkene formed the original un-known alcohol when treated with BH3/THF followed by H2O2, HO-, and H2O. Identify the unknown alcohol.
Problem 67
Explain why the acid-catalyzed dehydration of an alcohol is a reversible reaction, whereas the base-promoted dehydrohalogenation of an alkyl halide is an irreversible reaction.
Problem 68
Explain why (S)-2-butanol forms a racemic mixture when it is heated in sulfuric acid.
Problem 69a
Fill in each box with the appropriate reagent:
a.
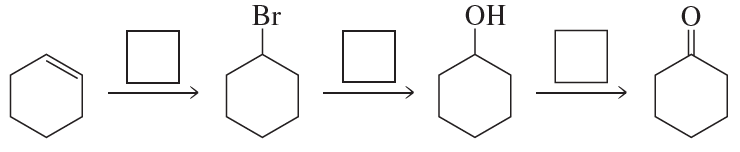
Problem 69c
Fill in each box with the appropriate reagent:
c.
Problem 70(8)
a. Draw the product or products that will be obtained from the reaction of cis-2-butene and trans-2-butene with each of the following reagents. If a product can exist as stereoisomers, show which stereoisomers are formed.
8. CH3OH + H2SO4
b. With which reagents do the two alkenes react to form different products?
Problem 71
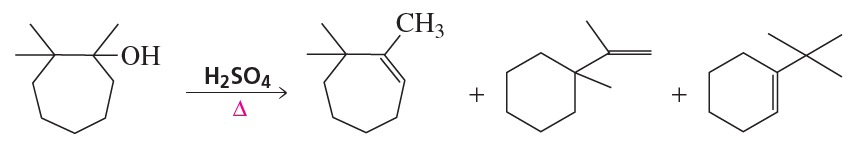
What product would be formed if the four-membered ring alcohol in Problem 70 were heated with an equivalent amount of HBr rather than with a catalytic amount of H2SO4?
Problem 72
Which of the following ethers would be obtained in greatest yield directly from alcohols?
Problem 73a
Using the given starting material, any necessary inorganic reagents, and any carbon-containing compounds with no more than two carbons, indicate how the following syntheses could be carried out:
a.
Problem 73b
Using the given starting material, any necessary inorganic reagents, and any carbon-containing compounds with no more than two carbons, indicate how the following syntheses could be carried out:
b.
Problem 74
When piperidine undergoes the series of reactions shown here, 1,4-pentadiene is obtained as the product. When the four different methyl-substituted piperidines undergo the same series of reactions, each forms a different diene: 1,5-hexadiene; 1,4-pentadiene; 2-methyl-1,4-pentadiene; and 3-methyl-1,4-pentadiene. Which methyl-substituted piperidine forms which diene?
Problem 75
When 3-methyl-2-butanol is heated with concentrated HBr, a rearranged product is obtained. When 2-methyl-1-propanol reacts under the same conditions, a rearranged product is not obtained. Explain.
Problem 76
Draw structures for compounds A–F.
Problem 77a
Propose a mechanism for each of the following reactions:
a.
Problem 77b
Propose a mechanism for each of the following reactions:
b.
Problem 78
How could you synthesize isopropyl propyl ether, using isopropyl alcohol as the only carbon-containing reagent?
Problem 79
When ethyl ether is heated with excess HI for several hours, the only organic product obtained is ethyl iodide. Explain why ethyl alcohol is not obtained as a product.
Problem 80
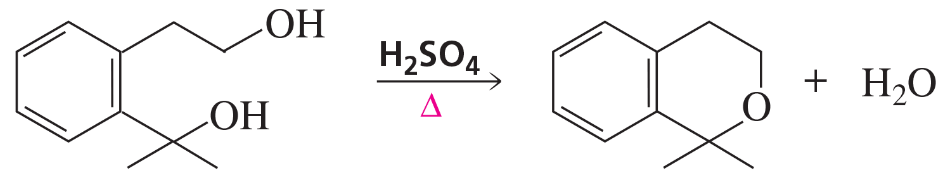
When the following seven-membered ring alcohol is dehydrated, three alkenes are formed. Propose a mechanism for their formation.
Problem 81
Ethylene oxide reacts readily with HO- because of the strain in the three-membered ring. Explain why cyclopropane, a compound with approximately the same amount of strain, does not react with HO-.
Problem 82a
Describe how each of the following compounds could be synthesized from the given starting material.
a.
Problem 83a
Propose a mechanism for each of the following reactions:
a.
Problem 83b
Propose a mechanism for each of the following reactions:
b.
Problem 84
Triethylene glycol is one of the products obtained from the reaction of excess ethylene oxide and hydroxide ion. Propose a mechanism for its formation.
Problem 85a
a. Propose a mechanism for the following reaction:
Problem 85b,c
b. A small amount of a product containing a six-membered ring is also formed. Draw the structure of that product.
c. Why is so little six-membered ring product formed?
Problem 86
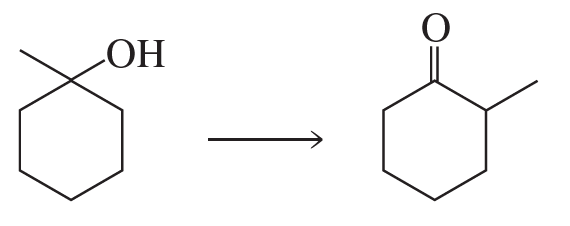
Propose a mechanism for the following reaction:
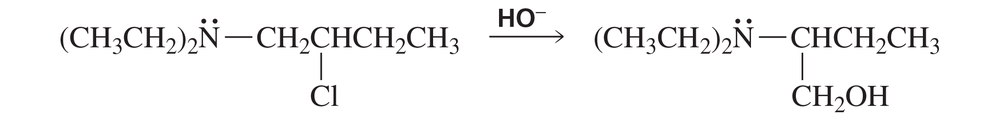
Problem 89a
The following reaction takes place several times faster than the reaction of 2-chlorobutane with HO-:
a. Explain the enhanced reaction rate.
Problem 89b
The following reaction takes place several times faster than the reaction of 2-chlorobutane with HO-:
b. Explain why the OH group in the product is not bonded to the carbon that was bonded to the Cl group in the reactant.