5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses
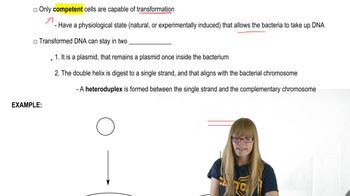
Bacterial Transformation
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Transformation is the process of what occurring with DNA?
- Multiple Choice
Scientists must use what type of cells to transform DNA in the laboratory?
- Multiple Choice
The DNA from a bacterium with the genotype a+ b+ c+ is used to transform a bacteria with the genotype a b c. Gene pairs were checked for cotransformation with the following results. Using these results determine which genes are linked.
- Open QuestionIn a transformation experiment, donor DNA was obtained from a prototroph bacterial strain (a⁺b⁺c⁺) and the recipient was a triple auxotroph (a⁻b⁻c⁻). What general conclusions can you draw about the linkage relationships among the three genes from the following transformant classes that were recovered?a⁺ b⁻ c⁻ 180a⁻ b⁺ c⁻ 150a⁺ b⁺ c⁻ 210a⁻ b⁻ c⁺ 179a⁺ b⁻ c⁺ 2a⁻ b⁺ c⁺ 1a⁺ b⁺ c⁺ 3
- Open QuestionDescribe the role of heteroduplex formation during transformation.
- Open Question
Penicillin was first used in the 1940s to treat gonorrhea infections produced by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. In 1984, according to the CDC, fewer than 1% of gonorrhea infections were caused by penicillin-resistant N. gonorrhoeae. By 1990, more than 10% of cases were penicillin-resistant, and a few years later the level of resistance was at greater than 95%. Almost every year the CDC issues new treatment guidelines for gonorrhea that identify the recommended antibiotic drugs and dosages.
What are the long-term implications of these frequent changes in treatment recommendations for the patient population? - Open Question
Penicillin was first used in the 1940s to treat gonorrhea infections produced by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. In 1984, according to the CDC, fewer than 1% of gonorrhea infections were caused by penicillin-resistant N. gonorrhoeae. By 1990, more than 10% of cases were penicillin-resistant, and a few years later the level of resistance was at greater than 95%. Almost every year the CDC issues new treatment guidelines for gonorrhea that identify the recommended antibiotic drugs and dosages.
What are the short-term implications of these frequent changes for physicians and clinics that treat sexually transmitted diseases like gonorrhea and for individuals infected with gonorrhea?