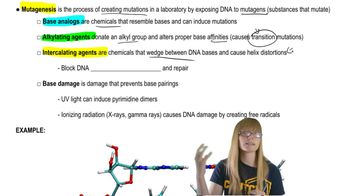
17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination
Induced Mutations
17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination
Induced Mutations
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Which of the following mutagens wedges between DNA bases to disrupt the helix structure?
- Multiple Choice
Which of the following mutagens alters base affinities by adding an alkyl group?
- Multiple Choice
Which of the following mutations would have the least effect on an individual?
- Open Question
Identify two general ways chemical mutagens can alter DNA. Give examples of these two mechanisms.
- Open QuestionIn this chapter, we focused on how gene mutations arise and how cells repair DNA damage. At the same time, we found opportunities to consider the methods and reasoning by which much of this information was acquired. From the explanations given in the chapter,How do we know that DNA repair mechanisms detect and correct the majority of spontaneous and induced mutations?
- Open QuestionIn this chapter, we focused on how gene mutations arise and how cells repair DNA damage. At the same time, we found opportunities to consider the methods and reasoning by which much of this information was acquired. From the explanations given in the chapter,How do we know that certain chemicals and wavelengths of radiation induce mutations in DNA?
- Open Question
Nitrous acid and 5-bromodeoxyuracil (BrdU) alter DNA by different mechanisms. What type of mutation does each compound produce?