6. Chromosomal Variation
Chromosomal Rearrangements: Translocations
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
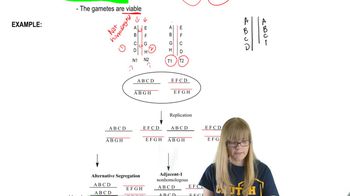
Which of the following represents the chromosomal segregation into gametes after a reciprocal translocation caused by adjacent-1 segregation? N=Normal chromosome T = Tanslocated chromosome
- Multiple Choice
Which of the following ways reciprocal translocated chromosomes are sorted produces viable gametes?
- Multiple Choice
An individual heterozygous for a reciprocal translocation has the following chromosomes. Which chromosomes do the gametes receive after alternative segregation?
A B • C D E F G J K • L M N O P
A B • C D N O P J K • L M E F G
- Multiple Choice
An individual heterozygous for a reciprocal translocation has the following chromosomes. Which chromosomes do the gametes receive after adjacent-1 segregation?
A B • C D E F G J K • L M N O P
A B • C D N O P J K • L M E F G
- Open Question
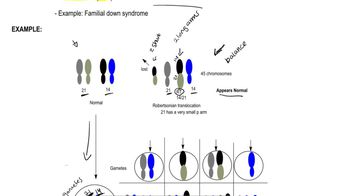
From the following list, identify the types of chromosome changes you expect to show phenotypic consequences.
reciprocal balanced translocation - Open QuestionAn animal heterozygous for a reciprocal balanced translocation has the following chromosomes: MN • OPQRSTMN • OPQRjklcdef • ghijklcdef • ghiSTAmong the three segregation patterns, which is least likely to occur? Why?
- Open Question
An animal heterozygous for a reciprocal balanced translocation has the following chromosomes:
MN • OPQRST
MN • OPQRjkl
cdef • ghijkl
cdef • ghiST
Identify the gametes produced by adjacent-2 segregation. Which if any of these gametes are viable? - Open Question
An animal heterozygous for a reciprocal balanced translocation has the following chromosomes:
MN • OPQRST
MN • OPQRjkl
cdef • ghijkl
cdef • ghiST
Identify the gametes produced by adjacent-1 segregation. Which if any of these gametes are viable?