6. Chromosomal Variation
Chromosomal Rearrangements: Duplications
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
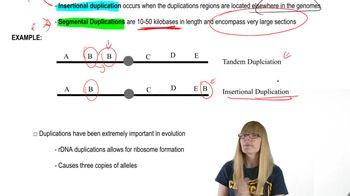
A person has a WT chromosome with the following segments. A B C • D E F G H. Which of the following shows how the chromosome would look after an insertional duplication?
- Multiple Choice
A person has a WT chromosome with the following segments. A B C • D E F G H. Which of the following shows how the chromosome would look after an tandem duplication?
- Open QuestionIn this chapter, we have focused on chromosomal mutations resulting from a change in number or arrangement of chromosomes. In our discussions, we found many opportunities to consider the methods and reasoning by which much of this information was acquired. From the explanations given in the chapter, what answers would you propose to the following fundamental questions?How do we know that the mutant Bar-eye phenotype in Drosophila is due to a duplicated gene region rather than to a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene?
- Open Question
From the following list, identify the types of chromosome changes you expect to show phenotypic consequences. duplication
- Open Question
A pair of homologous chromosomes in Drosophila has the following content (single letters represent genes): Chromosome 1RNMDHBGKWU Chromosome 2RNMDHBDHBGKWU How does the pairing diagrammed in part (b) differ from the pairing of chromosomes in an inversion heterozygote?
- Open Question
A pair of homologous chromosomes in Drosophila has the following content (single letters represent genes): Chromosome 1RNMDHBGKWU Chromosome 2RNMDHBDHBGKWU What term best describes the unusual structure that forms during pairing of these chromosomes?