10. Transcription
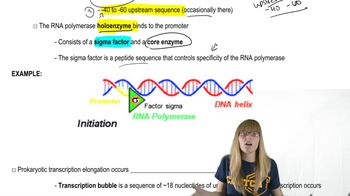
Transcription in Prokaryotes
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not an example of a prokaryotic promoter sequence?
- Multiple Choice
What is the purpose of a sigma factor in prokaryotic transcription?
- Multiple Choice
Prokaryotic transcription can create polycistronic mRNA.
- Open Question
The diagram below shows a DNA duplex. The template strand is identified, as is the location of the nucleotide.
Assume this region contains a gene transcribed in a bacterium. Identify the location of promoter consensus sequences and of the transcription termination sequence. <> - Open Question
The DNA sequences shown below are from the promoter regions of six bacterial genes. In each case, the last nucleotide in the sequence (highlighted in blue) is the nucleotide that initiates transcription. Determine the consensus sequence for the Pribnow box from these sequences. <>
- Open Question
Bacterial and eukaryotic gene transcripts can differ—in the transcripts themselves, in whether the transcripts are modified before translation, and in how the transcripts are modified. For each of these three areas of contrast, describe what the differences are and why the differences exist.
- Open Question
Describe the two types of transcription termination found in bacterial genes. How does transcription termination differ for eukaryotic genes?