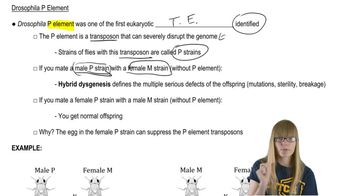
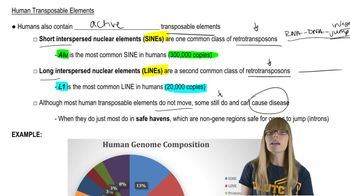
16. Transposable Elements
Transposable Elements in Eukaryotes
16. Transposable Elements
Transposable Elements in Eukaryotes
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true regarding reverse transcriptase?
- Multiple Choice
Which of the following elements is a transposable element in Drosophila?
- Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of a safe haven for transposon movement?
- Multiple Choice
Which of the following would occur if an Alu element jumped into the AG splice site of a human gene?
- Open Question
The human genome contains a large number of pseudogenes. How would you distinguish whether a particular sequence encodes a gene or a pseudogene? How do pseudogenes arise?
- Open QuestionContrast the structure of SINE and LINE DNA sequences. Why are LINEs referred to as retrotransposons?
- Open QuestionCompare DNA transposons and retrotransposons. What properties do they share?
- Open QuestionIn maize, a Ds or Ac transposon can alter the function of genes at or near the site of transposon insertion. It is possible for these elements to transpose away from their original insertion site, causing a reversion of the mutant phenotype. In some cases, however, even more severe phenotypes appear, due to events at or near the mutant allele. What might be happening to the transposon or the nearby gene to create more severe mutations?