12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes
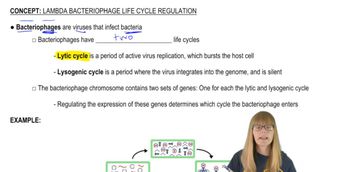
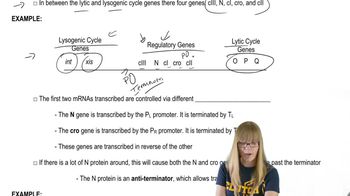
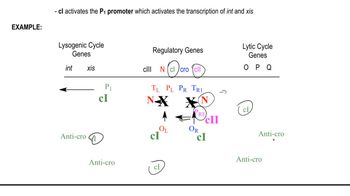
Lambda Bacteriophage and Life Cycle Regulation
12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes
Lambda Bacteriophage and Life Cycle Regulation
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
In which of the following life cycles does a bacteriophage integrate itself into the host genome?
- Multiple Choice
In good growth conditions the bacteriophage is more likely to enter into which life cycle?
- Multiple Choice
Activation of which of the following genes leads to entrance into the lysogenic cycle?
- Multiple Choice
The N protein is an anti-terminator. What does this mean?
- Open Question
Describe the difference between the bacteriophage lytic cycle and lysogenic cycle.
- Open QuestionDescribe the lytic and lysogenic life cycles of λ bacteriophage. What roles do λ repressor and Cro protein play in controlling transcription from PM and PRM, and how are these roles linked to lysis and lysogeny?
- Open QuestionKeeping in mind the life cycle of bacteriophages discussed earlier in the text (see Chapter 6), consider the following problem: During the reproductive cycle of a temperate bacteriophage, the viral DNA inserts into the bacterial chromosome where the resultant prophage behaves much like a Trojan horse. It can remain quiescent, or it can become lytic and initiate a burst of progeny viruses. Several operons maintain the prophage state by interacting with a repressor that keeps the lytic cycle in check. Insults (ultraviolet light, for example) to the bacterial cell lead to a partial breakdown of the repressor, which in turn causes the production of enzymes involved in the lytic cycle. As stated in this simple form, would you consider this system of regulation to be operating under positive or negative control?
- Open QuestionSuppose that base substitution mutations sufficient to eliminate the function of the operator regions listed below were to occur. For each case, describe how transcription or life cycle would be affected.OR1 mutation in λ phage