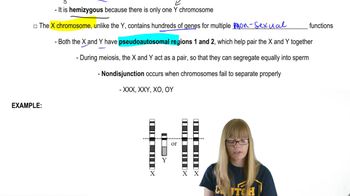2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance
Sex-Linked Genes
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Which of the following sex chromosome pairs is caused from nondisjunction?
- Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of sex-limited inheritance?
- Open QuestionIn this chapter, we focused on extensions and modifications of Mendelian principles and ratios. In the process, we encountered many opportunities to consider how this information was acquired. On the basis of these discussions, what answers would you propose to the following fundamental questions?For genes whose expression seems to be tied to the sex of individuals, how do we know whether a gene is X-linked in contrast to exhibiting sex-limited or sex-influenced inheritance?
- Open QuestionIn this chapter, we focused on extensions and modifications of Mendelian principles and ratios. In the process, we encountered many opportunities to consider how this information was acquired. On the basis of these discussions, what answers would you propose to the following fundamental questions?How do we know that specific genes are located on the sex-determining chromosomes rather than on autosomes?
- Open Question
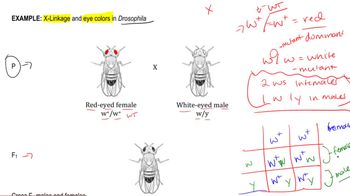
In a test of his chromosome theory of heredity, Morgan crossed a female Drosophila with red eyes to a male with white eyes. The females were produced from Cross A shown in Figure 3.19. Predict the offspring Morgan would have expected under his hypothesis that the gene for eye color is on the X chromosome in fruit flies.
- Open Question
In Drosophila, the map positions of genes are given in map units numbering from one end of a chromosome to the other. The X chromosome of Drosophila is 66 m.u. long. The X-linked gene for body color—with two alleles, y⁺ for gray body and y for yellow body—resides at one end of the chromosome at map position 0.0. A nearby locus for eye color, with alleles w⁺ for red eye and w for white eye, is located at map position 1.5. A third X-linked gene, controlling bristle form, with f⁺ for normal bristles and f for forked bristles, is located at map position 56.7. At each locus the wild-type allele is dominant over the mutant allele.
Explain how each of the predicted progeny classes is produced.