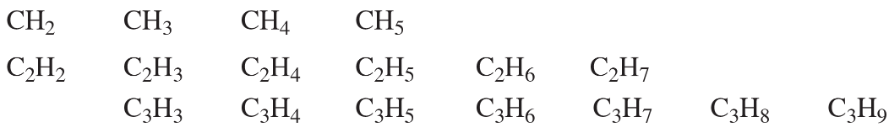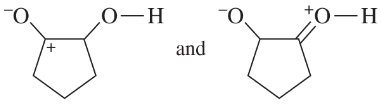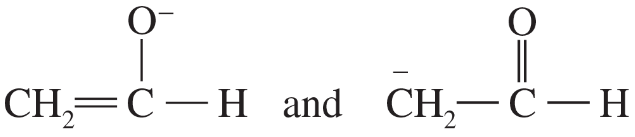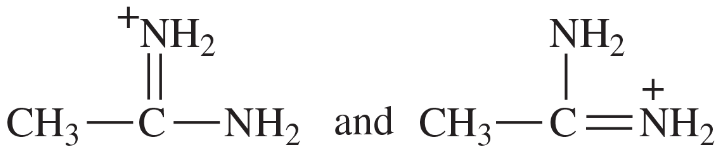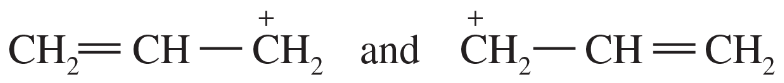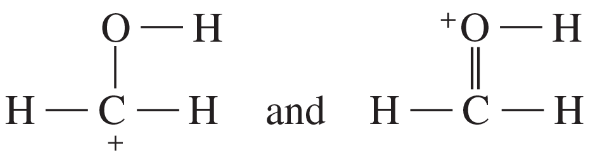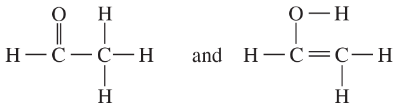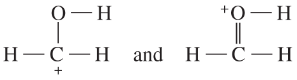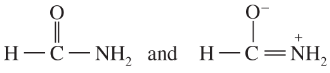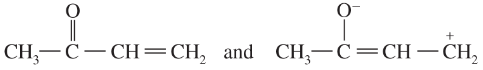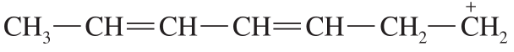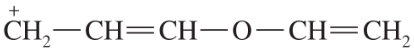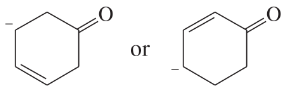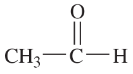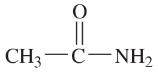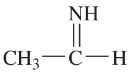Back
BackProblem 29
For each compound, state whether its bonding is covalent, ionic, or a mixture of covalent and ionic.
a. NaCl
b. NaOH
c. CH3Li
d. CH2Cl2
e. NaOCH3
f. HCO2Na
g. CF4
Problem 30a
Both PCl3 and PCl5 are stable compounds. Draw Lewis structures for these two compounds.
Problem 31a-d
Draw a Lewis Structure for each species.
a. N2H4
b. N2H2
c. (CH3)2NH2Cl
d. CH3CN
Problem 31e-h
Draw a Lewis Structure for each species.
e. CH3CHO
f. CH3S(O)CH3
g. H2SO4
h. CH3NCO
Problem 31i-k
Draw a Lewis Structure for each species.
i. CH3OSO2OCH3
j. CH3C(NH)CH3
k. (CH3)3CNO
Problem 32a,b
Draw a Lewis structure for each compound. Include all nonbonding pairs of electrons.
a. CH3COCH2CHCHCOOH
b. NCCH2COCH2CHO
Problem 33a,b
Draw a line-angle formula for each compound.
a. CH3COCH2CHCHCOOH
b. NCCH2COCH2CHO
Problem 33c,d
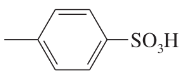
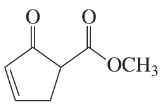
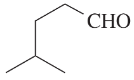
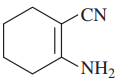
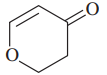
Draw a line-angle formula for each compound.
c. CH2CHCH(OH)CH2CO2H
d. CH2CHC(CH3)CHCOOCH3
Problem 34a,b
Draw Lewis structures for
a. two compounds of formula C4H10
b. two compounds of formula C2H6O
Problem 35a
Draw a complete structural formula and a condensed structural formula for
a. three compounds of formula C3H8O
Problem 35b
Draw a complete structural formula and a condensed structural formula for
b. five compounds of formula C3H6O
Problem 36
Some of the following molecular formulas correspond to stable compounds. When possible, draw a stable structure for each formula. Propose a general rule for the numbers of hydrogen atoms in stable hydrocarbons.
Problem 37a,b,c
Draw complete Lewis structures, including lone pairs, for the following compounds.
(a)
(b)
(c)
Problem 37g,h
Draw complete Lewis structures, including lone pairs, for the following compounds.
(g)
(h)
Problem 38a,b,c
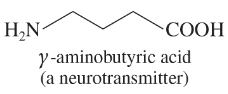
Give the molecular formula of each compound shown
(a)
(b)
(c)
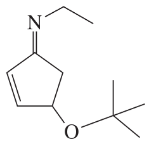
Problem 38d,e,f
Give the molecular formula of each compound shown
(d)
(e)
(f)
Problem 38g,h
Give the molecular formula of each compound shown
(g)
(h)
Problem 39a-e
1. From what you remember of electronegativities, show the direction of the dipole moments of the following bonds.
2. In each case, predict whether the dipole moment is relatively large (electronegativity difference >0.5) or small.
a. C—Cl
b. C—H
c. C—Li
d. C—N
e. C—O
Problem 40d,e,f
For each of the following structures,
1. Draw a Lewis structure; fill in any nonbonding electrons.
2. Calculate the formal charge on each atom other than hydrogen
d. [(CH3)3O]+
e. CH3NC
f. (CH3)4NBr
Problem 41a-d
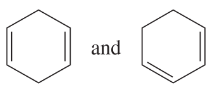
Determine whether the following pairs of structures are actually different compounds or simply resonance forms of the same compounds.
a.
b.
c.
d.
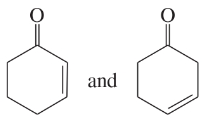
Problem 41e-h
Determine whether the following pairs of structures are actually different compounds or simply resonance forms of the same compounds.
e.
f.
g.
h.
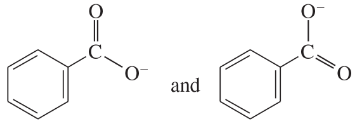
Problem 41i-l
Determine whether the following pairs of structures are actually different compounds or simply resonance forms of the same compounds.
i.
j.
k.
l.
Problem 42j,k
Draw the important resonance forms to show the delocalization of charges in the following ions. In each case, indicate the major resonance form(s).
(j)
(k)
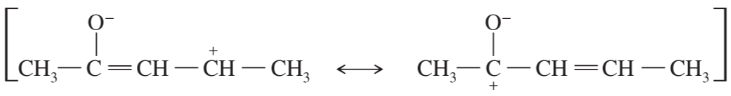
Problem 43d,e
In the following sets of resonance forms, label the major and minor contributors and state which structures would be of equal energy. Add any missing important resonance forms.
(d)
(e)
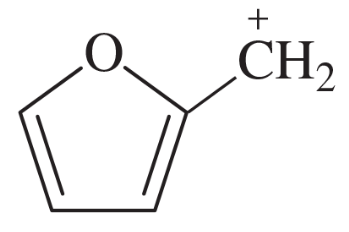
Problem 44a
For each of these ions, draw the important resonance forms and predict which resonance form is likely to be the major contributor.
(a)
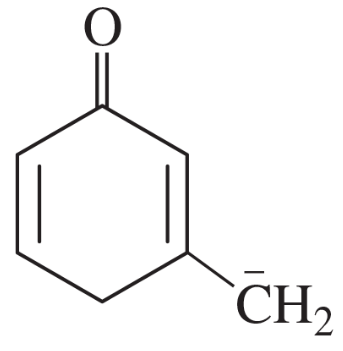
Problem 44b
For each of these ions, draw the important resonance forms and predict which resonance form is likely to be the major contributor.
(b)
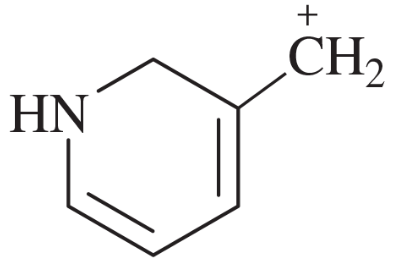
Problem 44c
For each of these ions, draw the important resonance forms and predict which resonance form is likely to be the major contributor.
(c)
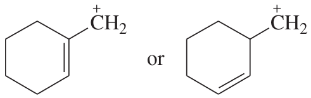
Problem 45e,f
For each pair of ions, determine which ion is more stable. Use resonance forms to explain your answers.
(e)
(f)
Problem 46a,b,c
Use resonance structures to identify the areas of high and low electron density in the following compounds:
(a)
(b)
(c)
Problem 46g,h
Use resonance structures to identify the areas of high and low electron density in the following compounds:
g.
h.