Back
Back Mullins 1st Edition
Mullins 1st Edition Ch. 3 - Alkanes and Cycloalkanes: Properties and Conformational Analysis
Ch. 3 - Alkanes and Cycloalkanes: Properties and Conformational AnalysisProblem 2
What is the ground state electron configuration of carbon? How many bonds does carbon usually form?
Problem 3a
What is the hybridization of carbon in each of the following molecules?
(a)
Problem 3d
What is the hybridization of carbon in each of the following molecules?
(d)
Problem 6a
How many hydrogens would you expect a 24-carbon compound from each of the following molecular classes to have?
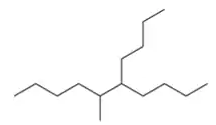
(a) Alkane
Problem 6b
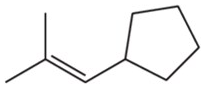
How many hydrogens would you expect a 24-carbon compound from each of the following molecular classes to have?
(b) Alkene
Problem 6c
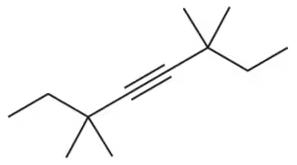
How many hydrogens would you expect a 24-carbon compound from each of the following molecular classes to have?
(c) Alkyne
Problem 7
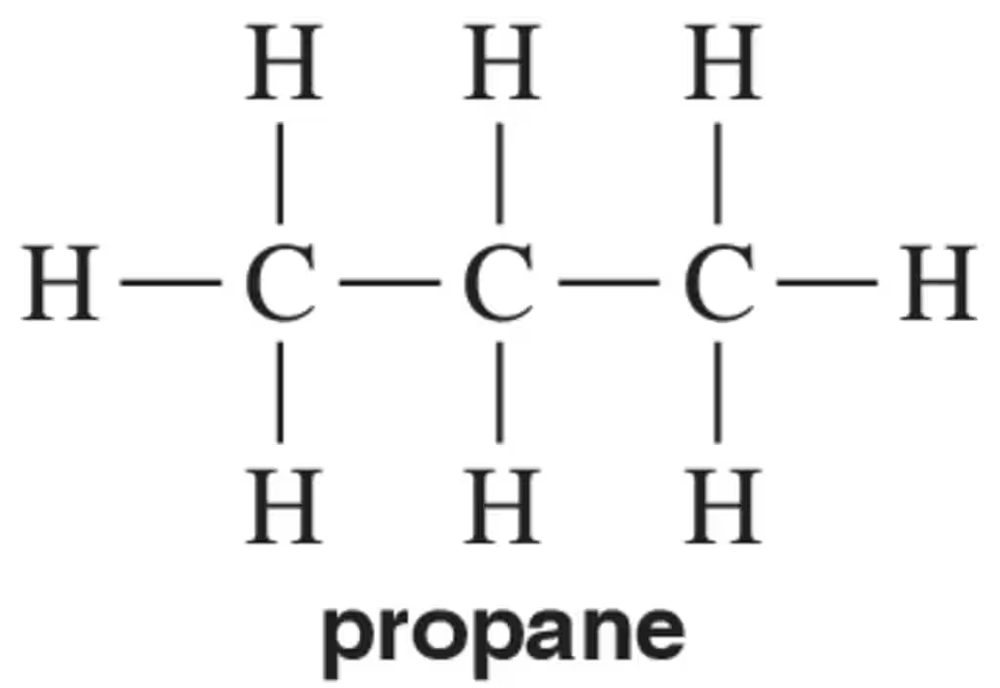
Draw the molecular orbital picture for propane. Your picture should clearly show the shape and hybridization of the carbons. Label all σ bonds.
Problem 8a
Choose the molecule in each pair you'd expect to have the higher boiling point. Explain your reasoning.
(a) eicosane ( C20H42) vs pentadecane
Problem 8b
Choose the molecule in each pair you'd expect to have the higher boiling point. Explain your reasoning.
(b)
Problem 9a
Rank the following molecules from least water soluble to most water soluble. Explain your reasoning.
(a) H3C ― OH
Problem 9b
Rank the following molecules from least water soluble to most water soluble. Explain your reasoning.
(b) LiCl
Problem 9e
Rank the following molecules from least water soluble to most water soluble. Explain your reasoning.
(e) CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
Problem 10b
For each of the following line-angle drawings,
(i) give the number of carbons,
(ii) label the carbons,
(iii) tell how many hydrogens are on each carbon, and
(iv) draw the hybrid structural formula.
(b)
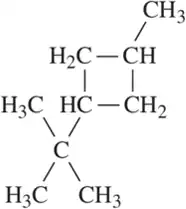
Problem 10c
For each of the following line-angle drawings,
(i) give the number of carbons,
(ii) label the carbons,
(iii) tell how many hydrogens are on each carbon, and
(iv) draw the hybrid structural formula.
(c)
Problem 10d
For each of the following line-angle drawings,
(i) give the number of carbons,
(ii) label the carbons,
(iii) tell how many hydrogens are on each carbon, and
(iv) draw the hybrid structural formula.
(d)
Problem 11b
Convert the following hybrid structural formulas into the line-angle drawings.
(b)
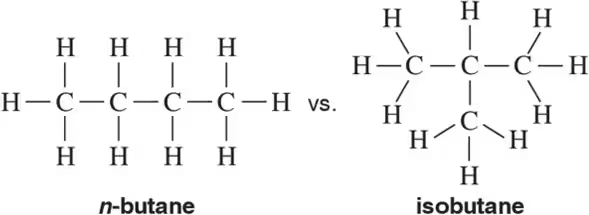
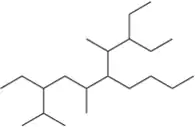
Problem 13a
There are five alkane constitutional isomers with the molecular formula C6H14. Draw them.
Problem 14a
There are nine alkane constitutional isomers with the molecular formula C7H16. Draw them.
Problem 15j
Name the following alkanes using the IUPAC system of nomenclature. [Each molecule exemplifies one of the nomenclature rules in Tables 3.7 and 3.8.]
(j) rule 5
Problem 15k
Name the following alkanes using the IUPAC system of nomenclature. [Each molecule exemplifies one of the nomenclature rules in Tables 3.7 and 3.8.]
(k) rule 6
Problem 15n
Name the following alkanes using the IUPAC system of nomenclature. [Each molecule exemplifies one of the nomenclature rules in Tables 3.7 and 3.8.]
(n) rule 7
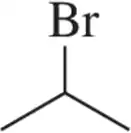
Problem 16b
When we begin studying functional groups, the designation of substitution will be especially important. Label the following bromoalkanes as 1° , 2°, 3°, or 4° based on the carbon to which the bromine is attached.
(b)
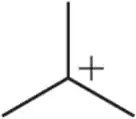
Problem 17b
When we begin studying reactive intermediates, the designation of substitution will be especially important. Label the following carbocations as 1° , 2°, 3°, or 4° or based on the carbon bearing the positive charge.
(b)
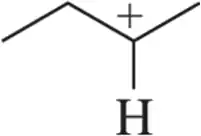
Problem 17c
When we begin studying reactive intermediates, the designation of substitution will be especially important. Label the following carbocations as 1° , 2°, 3°, or 4° or based on the carbon bearing the positive charge.
(c)
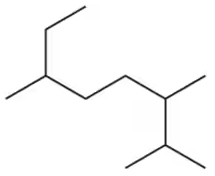
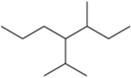
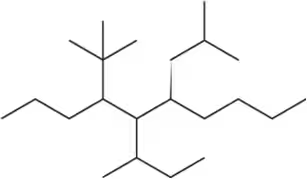
Problem 19c
Name the following alkanes using the common names for branched substituents.
(c)
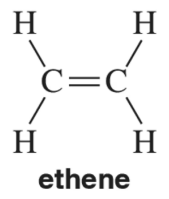
Problem 20
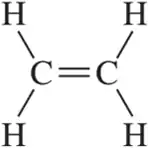
In Chapter 8, we study the chemistry of alkenes, like ethene. In contrast to ethane, there is no free rotation around the C = C double bond of ethene. Explain this in the context of the molecular orbital picture of ethene.
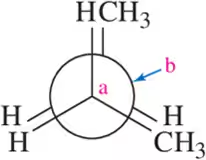
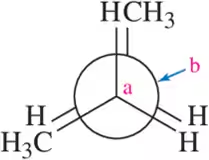
Problem 21d
For each molecule, draw the Newman projection you would observe if you looked down the Ca - Cb bond in the direction indicated.
(d) <IMAGE>
Problem 22b
Using the Newman projections shown, draw each molecule in its line-angle drawing with all hydrogens and substituents shown. [Carbon b is behind carbon a in these structures.] Wedges and dashes should be used to indicate whether a substituent is coming out of, or going into, the plane of the page.
(b)
Problem 22d
Using the Newman projections shown, draw each molecule in its line-angle drawing with all hydrogens and substituents shown. [Carbon b is behind carbon a in these structures.] Wedges and dashes should be used to indicate whether a substituent is coming out of, or going into, the plane of the page.
(d)
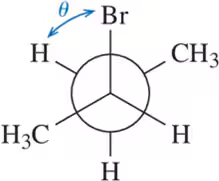
Problem 23a
Calculate the dihedral angle (θ) for the conformations shown.
(a)