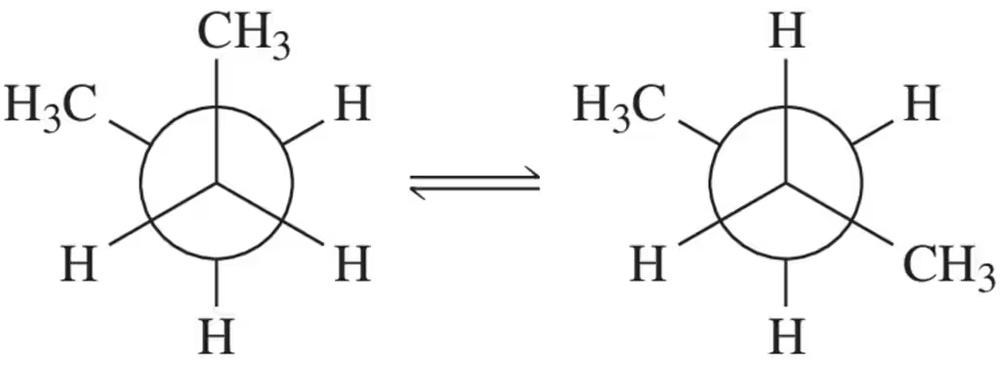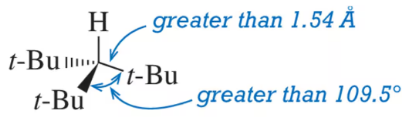Back
Back Mullins 1st Edition
Mullins 1st Edition Ch. 3 - Alkanes and Cycloalkanes: Properties and Conformational Analysis
Ch. 3 - Alkanes and Cycloalkanes: Properties and Conformational AnalysisProblem 60e
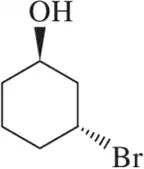
For each structure shown, draw the two chair conformations and choose which is most stable. Be sure that your second chair is the flipped version of the first. [Make sure that wedged substituents are up in the chair, regardless of whether up is equatorial or axial.]
(e)
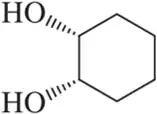
Problem 60g
For each structure shown, draw the two chair conformations and choose which is most stable. Be sure that your second chair is the flipped version of the first. [Make sure that wedged substituents are up in the chair, regardless of whether up is equatorial or axial.]
(g)
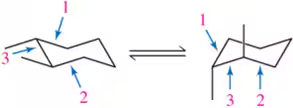
Problem 61b
Calculate the energy difference between each pair of conformations shown by drawing and comparing Newman projections down the indicated bonds in each.
(b)
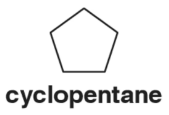
Problem 63
In contrast to ethane and other alkanes studied in this chapter, there is no free rotation around any bonds in cyclopentane (shown below). Why?
Problem 64
Looking ahead In Chapter 5, we explain that the equilibrium constant (Keq) for a reaction can be calculated based on the difference in energy between reactants and products, according to the following equation:
Using this equation, calculate the equilibrium constant for the 'reaction' shown. [For the rest of the book, if not otherwise specified, assume room temperature (298K).]
Problem 67
The normal C(sp3)–C(sp3) bond length is 1.54 Å. The normal bond angle for an sp3-hybridized carbon is 109.5°. The following molecule experiences large deviations from these normal values. Explain these deviations. [Molecular models would be helpful here.]
Problem 69
In Chapter 5, we introduce reaction coordinate diagrams as a plot of potential energy versus the progress of a reaction. Consider the reaction coordinate diagram drawn for the 'reaction' of conformation A becoming conformation B. Which structure is present at the top of the hill?
<IMAGE>
Problem 71
Correct the following incorrect names using standard IUPAC nomenclature. [Draw a compound that corresponds to the incorrect name, and then rename it.]
(a) 4-methylhexane
Problem 71b
Correct the following incorrect names using standard IUPAC nomenclature. [Draw a compound that corresponds to the incorrect name, and then rename it.]
(b) 1,5-dimethylcyclohexane
Problem 71c
Correct the following incorrect names using standard IUPAC nomenclature. [Draw a compound that corresponds to the incorrect name, and then rename it.]
(c) 6-ethyl-3-methyloctane
Problem 71d
Correct the following incorrect names using standard IUPAC nomenclature. [Draw a compound that corresponds to the incorrect name, and then rename it.]
(d) 4-butyldecane
Problem 71e
Correct the following incorrect names using standard IUPAC nomenclature. [Draw a compound that corresponds to the incorrect name, and then rename it.]
(e) 2,6-diethyl-1-methylcycloheptane
Problem 72a
Identify the mistakes contained within the following structures.
(a)
Problem 73
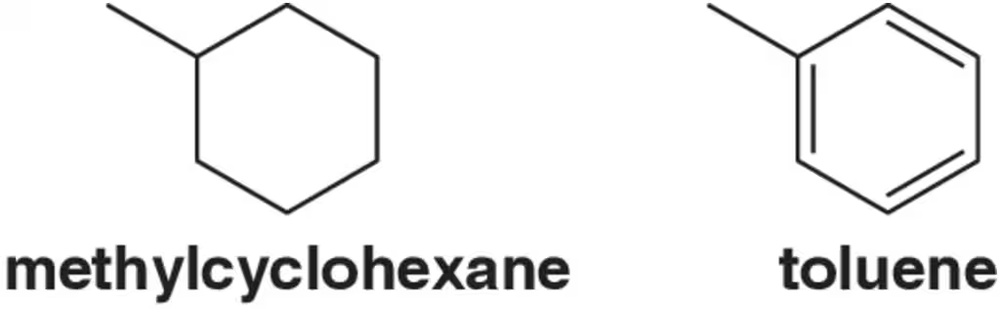
Despite methylcyclohexane (98.2 amu) having a higher molecular weight than toluene (92.1 amu), toluene melts at a higher temperature. Why? [Think about how the molecules can interact with each other based on their shape.]
Problem 74
Ionic compounds like sodium acetate have a high melting point. Despite this, they are highly soluble in water. Why?

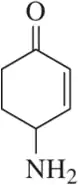
Problem 75a
Identify the functional groups in each of the following molecules. [The number of functional groups has been given to assist you.]
(a) [Three]
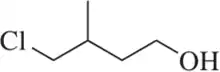
Problem 75b
Identify the functional groups in each of the following molecules. [The number of functional groups has been given to assist you.]
(b) [Two]
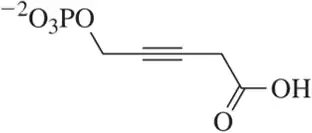
Problem 75c
Identify the functional groups in each of the following molecules. [The number of functional groups has been given to assist you.]
(c) [Three]
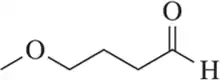
Problem 75d
Identify the functional groups in each of the following molecules. [The number of functional groups has been given to assist you.]
(d) [Two]