Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Biology
- 2. Chemistry
- 3. Water
- 4. Biomolecules
- 5. Cell Components
- 6. The Membrane
- 7. Energy and Metabolism
- 8. Respiration
- 9. Photosynthesis
- 10. Cell Signaling
- 11. Cell Division
- 12. Meiosis
- 13. Mendelian Genetics
- Introduction to Mendel's Experiments
- Genotype vs. Phenotype
- Punnett Squares
- Mendel's Experiments
- Mendel's Laws
- Monohybrid Crosses
- Test Crosses
- Dihybrid Crosses
- Punnett Square Probability
- Incomplete Dominance vs. Codominance
- Epistasis
- Non-Mendelian Genetics
- Pedigrees
- Autosomal Inheritance
- Sex-Linked Inheritance
- X-Inactivation
- 14. DNA Synthesis
- 15. Gene Expression
- 16. Regulation of Expression
- Introduction to Regulation of Gene Expression
- Prokaryotic Gene Regulation via Operons
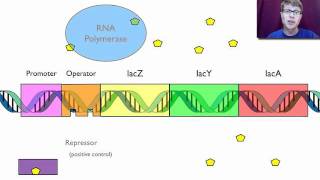
- The Lac Operon
- Glucose's Impact on Lac Operon
- The Trp Operon
- Review of the Lac Operon & Trp Operon
- Introduction to Eukaryotic Gene Regulation
- Eukaryotic Chromatin Modifications
- Eukaryotic Transcriptional Control
- Eukaryotic Post-Transcriptional Regulation
- Eukaryotic Post-Translational Regulation
- 17. Viruses
- 18. Biotechnology
- 19. Genomics
- 20. Development
- 21. Evolution
- 22. Evolution of Populations
- 23. Speciation
- 24. History of Life on Earth
- 25. Phylogeny
- 26. Prokaryotes
- 27. Protists
- 28. Plants
- 29. Fungi
- 30. Overview of Animals
- 31. Invertebrates
- 32. Vertebrates
- 33. Plant Anatomy
- 34. Vascular Plant Transport
- 35. Soil
- 36. Plant Reproduction
- 37. Plant Sensation and Response
- 38. Animal Form and Function
- 39. Digestive System
- 40. Circulatory System
- 41. Immune System
- 42. Osmoregulation and Excretion
- 43. Endocrine System
- 44. Animal Reproduction
- 45. Nervous System
- 46. Sensory Systems
- 47. Muscle Systems
- 48. Ecology
- 49. Animal Behavior
- 50. Population Ecology
- 51. Community Ecology
- 52. Ecosystems
- 53. Conservation Biology
16. Regulation of Expression
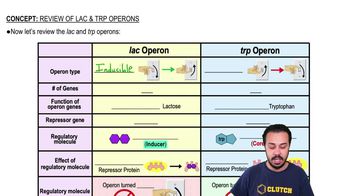
Review of the Lac Operon & Trp Operon
16. Regulation of Expression
Review of the Lac Operon & Trp Operon
+2
Additional 2 creators.
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
- Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
- Multiple ChoiceA bacterium can make the amino acid glycine or absorb it from its surroundings. A biochemist finds that glycine binds to a repressor protein and causes the repressor to bind to the bacterial chromosome, turning off an operon. If it is like other similar operons, the presence of glycine will result in the __________.
- Multiple ChoiceIn general, operons that encode the enzymes of a biosynthetic (anabolic) pathway (such as the trp operon) are __________, and those encoding the enzymes of a catabolic pathway (such as the lac operon) are __________.