27. Protists
Eukaryotic Supergroups: Exploring Protist Diversity
27. Protists
Eukaryotic Supergroups: Exploring Protist Diversity
Additional 21 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 24 of 24 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple ChoiceWhich of the following is one of the main weaknesses of the proposed classification scheme in which all eukaryotes are divided into four supergroups?
- Multiple ChoiceWhich of the listed examples is a characteristic shared by diplomonads and parabasalids?
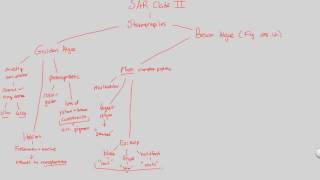
- Multiple ChoiceApicomplexans are currently assigned to the SAR clade because __________.
- Multiple ChoiceWhich of these groups includes photosynthetic unicellular organisms with flagella and contractile vacuoles?
- Open QuestionThe most important primary producers in marine ecosystems are .
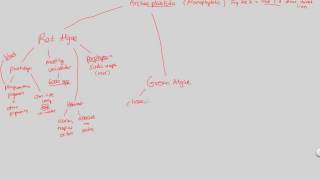
- Open QuestionWhich group is incorrectly paired with its description?a. diatoms—important producers in aquatic communitiesb. red algae—eukaryotes that acquired plastids by secondary endosymbiosisc. apicomplexans—unicellular parasites with intricate life cyclesd. diplomonads—unicellular eukaryotes with modified mitochondria
- Open QuestionWhat is the role of PEP carboxylase in C4 and CAM plants?a. It fixes CO2 into an organic acid.b. It produces ATP for the Calvin cycle.c. It replaces rubicso in the Calvin cycle.d. It releases CO2 from organic acids.
- Open QuestionAccording to the phylogeny presented in this chapter, which protists are in the same eukaryotic supergroup as plants?a. green algaeb. dinoflagellatesc. red algaed. both A and C