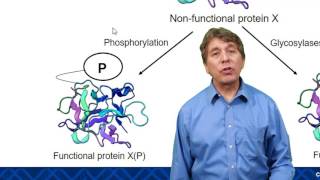
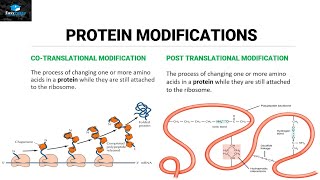
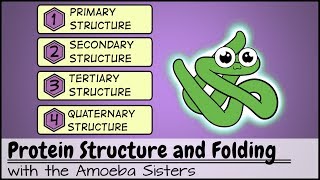
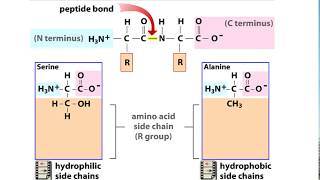
4. Biomolecules
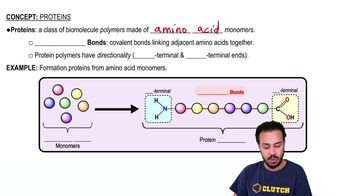
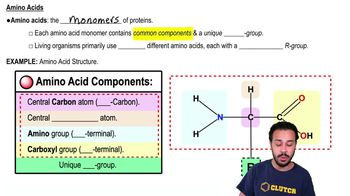
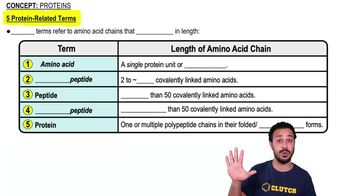
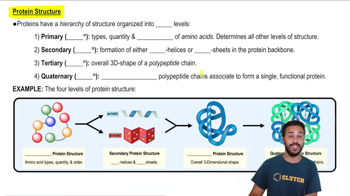
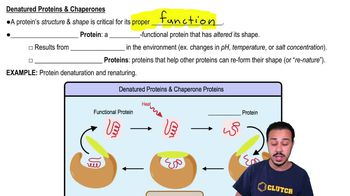
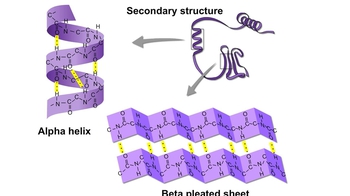
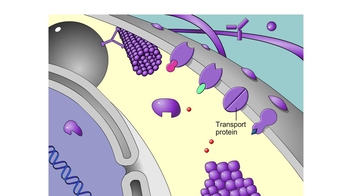
Proteins
4. Biomolecules
Proteins
Additional 13 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 16 of 16 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
The primary building blocks (monomers) of proteins are:
a) Glucose molecules.
b) Lipids.
c) Nucleotides.
d) Amino acids.
e) None of these.
- Multiple Choice
Which two functional groups are always found in amino acids?
a) Carbonyl and amino groups.
b) Carboxyl and amino groups.
c) Amino and sulfhydryl groups.
d) Hydroxyl and carboxyl groups.
- Multiple Choice
What term is used for an amino acid chain that has greater than 50 covalently linked amino acids?
a) Protein.
b) Peptide.
c) Amino acid.
d) Polypeptide.
- Multiple Choice
The specific amino acid sequence in a protein is its:
a) Primary structure.
b) Secondary structure.
c) Tertiary structure.
d) Quaternary structure.
- Open QuestionWhat two functional groups are bound to the central carbon of every free amino acid monomer?a. an R-group and a hydroxyl groupb. an N—H group and a ═(C═O) groupc. an amino group and a hydroxyl groupd. an amino group and a carboxyl group
- Open QuestionWhat type of bond is directly involved in the formation of an α-helix?a. peptide bonds between amino acid residuesb. hydrogen bonds between amino acid residuesc. van der Waals interactions between nonpolar residuesd. disulfide bonds between cysteine residues
- Open QuestionWhat type of information is used to direct different polypeptides to fold into different shapes?
- Open QuestionThe structural level of a protein least affected by a disruption in hydrogen bonding is thea. primary level.b. secondary level.c. tertiary level.d. quaternary level.