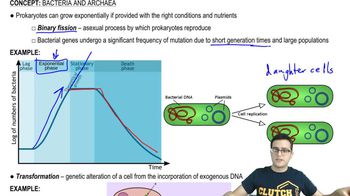
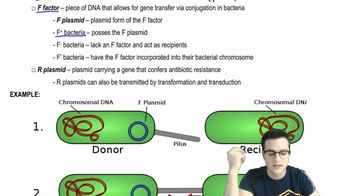
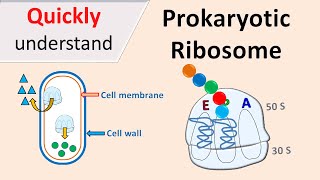
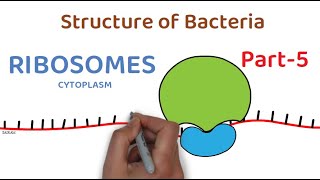
26. Prokaryotes
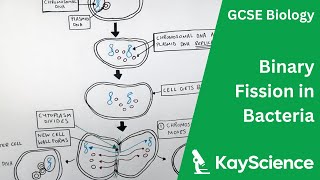
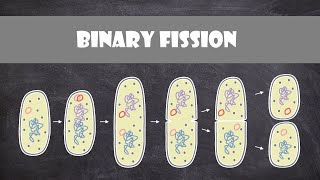
Prokaryotic Reproduction
26. Prokaryotes
Prokaryotic Reproduction
Additional 12 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 15 of 15 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple ChoiceWhy is salt a good preservative to use for foods such as pork and fish?
- Multiple ChoicePlasmids __________.
- Multiple ChoiceHow is it possible that as many as 9 million mutations can arise each day in the population of E. coli inhabiting one human?
- Multiple ChoiceIn the absence of meiosis and sexual reproduction, what general process allows genetic recombination among prokaryotes?
- Open QuestionGenetic variation in bacterial populations cannot result froma. transduction.b. conjugation.c. mutation.d. meiosis.
- Open QuestionWhat has metagenomic analysis allowed researchers to do for the first time?a. sample organisms from an environment and grow them under defined conditions in the labb. isolate organisms from an environment and sequence their entire genomec. study organisms that cannot be cultured (grown in the lab)d. identify important morphological differences among species
- Open QuestionWhat has metagenomic analysis allowed researchers to do for the first time?a. sample organisms from an environment and grow them under defined conditions in the labb. isolate organisms from an environment and sequence their entire genomec. study organisms that cannot be cultured (grown in the lab)d. identify important morphological differences among species
- Open QuestionBacteria are able to divide on a faster schedule than eukaryotic cells. Some bacteria can divide every 20 minutes, while the minimum time required by eukaryotic cells in a rapidly developing embryo is about once per hour, and most cells divide much less often than that. State at least two testable hypotheses explaining why bacteria can divide at a faster rate than eukaryotic cells.