12. Meiosis
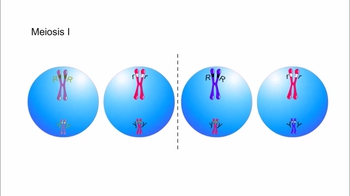
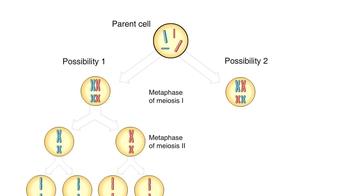
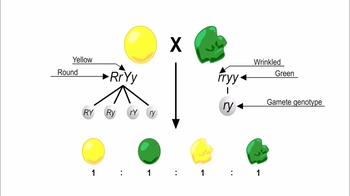
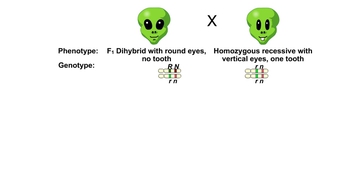
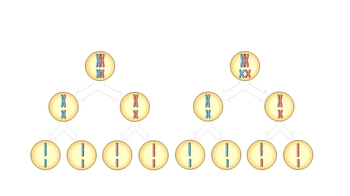
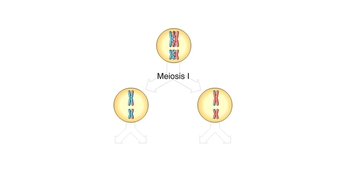
Genetic Variation During Meiosis
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Which of the following processes occurs when homologous chromosomes cross over in meiosis I?
a) Two sister chromatids get tangled, resulting in one re-sequencing its DNA.
b) Two sister chromatids exchange identical pieces of DNA.
c) Maternal alleles are "corrected" to be like paternal alleles and vice versa.
d) Corresponding segments of non-sister chromatids from homologous chromosomes are exchanged.
- Multiple Choice
Crossing over involves each of the following EXCEPT:
a) The transfer of DNA between two non-sister chromatids.
b) The transfer of DNA between two sister chromatids.
c) The formation of a synaptonemal complex.
d) The alignment of homologous chromosomes.
e) All of the above are involved in crossing over.
- Multiple Choice
How many genetically unique gametes can be created in an organism with 4 chromosomes?
a) 256.
b) 23.
c) 16.
d) 1 million.
e) 4.
- Multiple Choice
During which of the following processes does independent assortment of chromosomes occur?
a) In meiosis I only.
b) In meiosis II only.
c) In mitosis and meiosis I.
d) In mitosis and meiosis II.
e) In meiosis I and meiosis II.
- Open QuestionWhat is an outcome of genetic recombination?a. the synapsing of homologs during prophase of meiosis Ib. the new combination of maternal and paternal chromosome segments that results when homologs cross overc. the new combinations of chromosome segments that result when self-fertilization occursd. the combination of a haploid phase and a diploid phase in a life cycle
- Open QuestionA wild-type fruit fly (heterozygous for gray body color and normal wings) is mated with a black fly with vestigial wings. The offspring have the following phenotypic distribution: wild-type, 778; black vestigial, 785; black normal, 158; gray vestigial, 162. What is the recombination frequency between these genes for body color and wing size? Is this consistent with the results of the experiment in Figure 15.9?
- Open QuestionA planet is inhabited by creatures that reproduce with the same hereditary patterns seen in humans. Three phenotypic characters are height (T=tall,t=dwart), head appendages (A=antennae,a=noantennae), and nose morphology (S=upturnedsnout,s=downturnedsnout). Since the creatures are not 'intelligent,' Earth scientists are able to do some controlled breeding experiments using various heterozygotes in testcrosses. For tall heterozygotes with antennae, the offspring are tall antennae, 46; dwarf antennae, 7; dwarf no antennae, 42; tall no antennae, 5. For heterozygotes with antennae and an upturned snout, the offspring are antennae upturned snout, 47; antennae downturned snout, 2; no antennae downturned snout, 48; no antennae upturned snout, 3. Calculate the recombination frequencies for both experiments.
- Open QuestionNondisjunction that leads to problems in offspring can occur in:a. mitosisb. meiosis I onlyc. meiosis I and IId. mitosis, meiosis I, and meiosis II