7. Energy and Metabolism
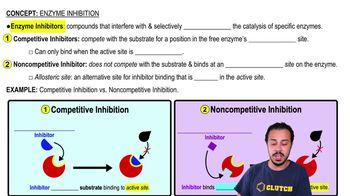
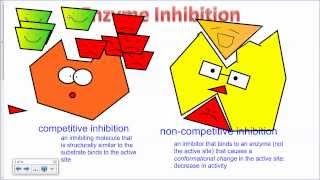
Enzyme Inhibition
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements correctly describes competitive inhibition?
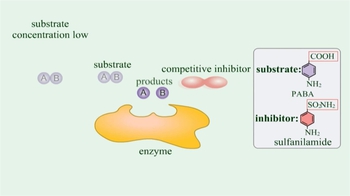
a) A competitive inhibitor binds to the substrate and inhibits it from binding to the active site of the enzyme.
b) A competitive inhibitor binds to a site other than the active site and inhibits the substrate from binding.
c) A competitive inhibitor binds to the active site and degrades the enzyme.
d) A competitive inhibitor binds to the active site of an enzyme and inhibits the substrate to bind.
- Multiple Choice
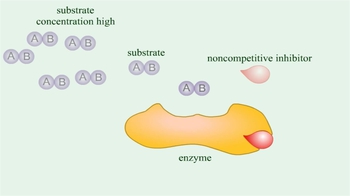
How does a noncompetitive inhibitor decrease the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction?
a) By binding to the active site of the enzyme, thus preventing binding of the normal substrate.
b) By binding to an allosteric site, thus changing the shape of the active site of the enzyme.
c) By decreasing the free-energy change of the reaction catalyzed by the enzyme.
d) By binding to the substrate, thus changing its shape so that it no longer binds to the active site of the enzyme.
- Multiple Choice
Which of the following types of enzyme inhibition is overcome by increasing the substrate concentration?
a) The need for a coenzyme.
b) Noncompetitive inhibition.
c) Competitive inhibition.
d) None of the above.
- Multiple ChoiceThe binding of an allosteric inhibitor to an enzyme causes the rate of product formation by the enzyme to decrease. Which of the following best explains why this decrease occurs?
- Open QuestionSometimes inhibitors can be harmful to a cell; often they are beneficial. Explain.
- Open QuestionOrganophosphates (organic compounds containing phosphate groups) are commonly used as insecticides to improve crop yield. Organophosphates typically interfere with nerve signal transmission by inhibiting the enzymes that degrade transmitter molecules. They affect humans and other vertebrates as well as insects. Thus, the use of organophosphate pesticides poses some health risks. On the other hand, these molecules break down rapidly upon exposure to air and sunlight. As a consumer, what level of risk are you willing to accept in exchange for an abundant and affordable food supply?