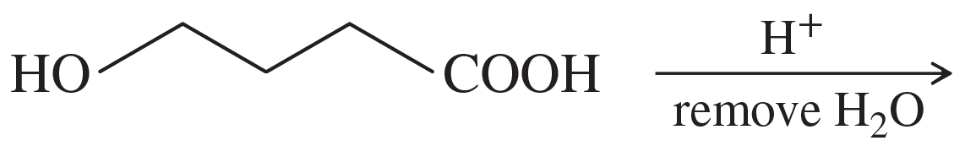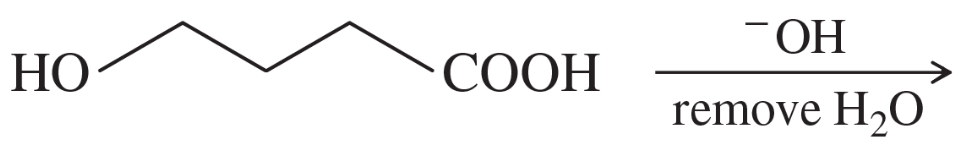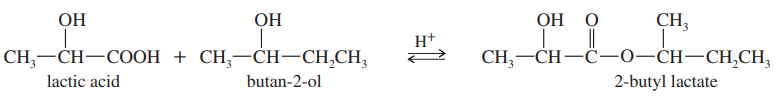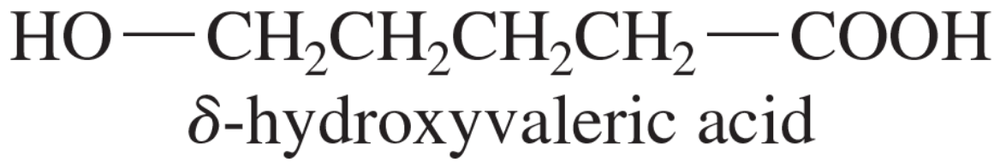Back
BackProblem 37b
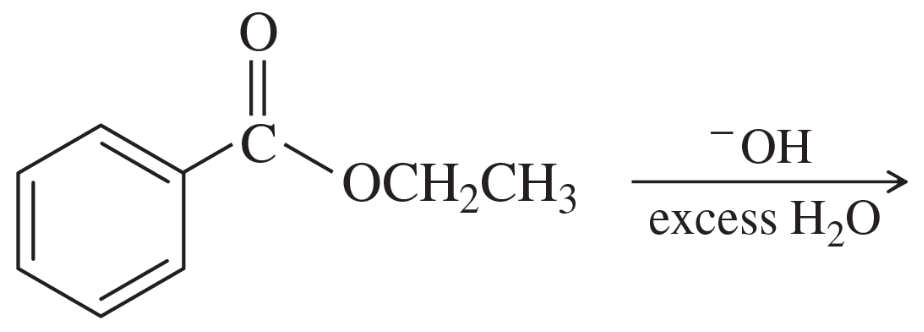
Predict the products and propose mechanisms for the following reactions.
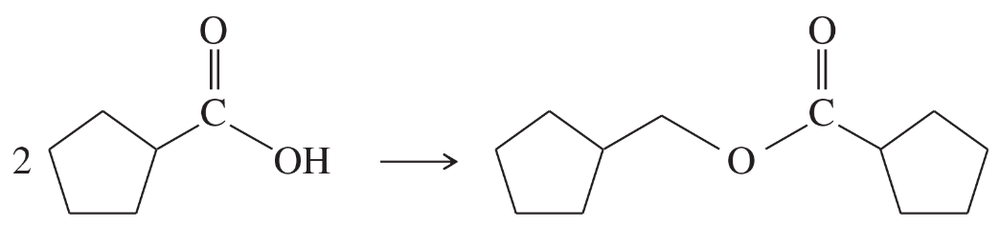
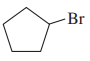
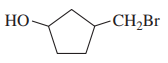
(b)
Problem 37c
Predict the products and propose mechanisms for the following reactions.
(c)
Problem 37d
Predict the products and propose mechanisms for the following reactions.
(d)
Problem 38a,b
When pure (S)-lactic acid is esterified by racemic butan-2-ol, the product is 2-butyl lactate, with the following structure:
(a) Draw three-dimensional structures of the two stereoisomers formed, specifying the configuration at each asymmetric carbon atom. (Using your models may be helpful.)
(b) Determine the relationship between the two stereoisomers you have drawn
Problem 39a
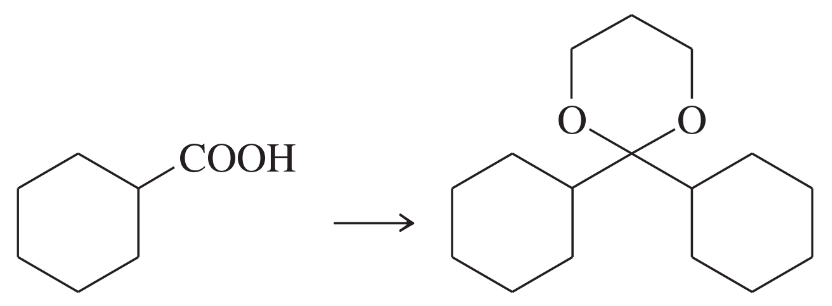
Show how you would accomplish the following multistep syntheses. You may use any additional reagents and solvents you need.
(a) PhCH2CH2OH → PhCH2CH2COOH
Problem 39b
Show how you would accomplish the following multistep syntheses. You may use any additional reagents and solvents you need.
(b)
Problem 39c
Show how you would accomplish the following multistep syntheses. You may use any additional reagents and solvents you need.
(c)
Problem 39d
Show how you would accomplish the following multistep syntheses. You may use any additional reagents and solvents you need.
(d)
Problem 39e
Show how you would accomplish the following multistep syntheses. You may use any additional reagents and solvents you need.
(e)
Problem 39f
Show how you would accomplish the following multistep syntheses. You may use any additional reagents and solvents you need.
(f)
Problem 40a
The following NMR spectra correspond to compound of formula (A) C9H10O2. Propose structure, and show how it is consistent with the observed absorptions.
<IMAGE>
Problem 40c
The following NMR spectra correspond to compound of formula (C) C6H10O2. Propose structure, and show how it is consistent with the observed absorptions.
<IMAGE>
Problem 41
In the presence of a trace of acid, δ-hydroxyvaleric acid forms a cyclic ester (lactone).
(a) Give the structure of the lactone, called δ-valerolactone.
(b) Propose a mechanism for the formation of δ-valerolactone.
Problem 42c
Peroxyacetic acid (bp = 105 °C) has a lower boiling point than acetic acid (bp = 118 °C), even though peroxyacetic acid has a higher molecular weight. Explain why peroxyacetic acid is more volatile than acetic acid.
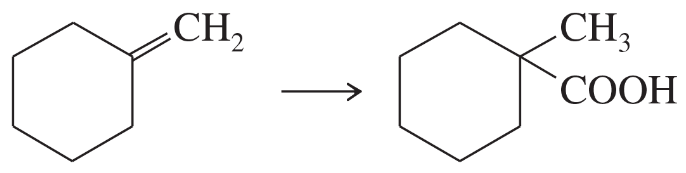
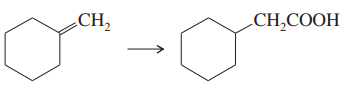
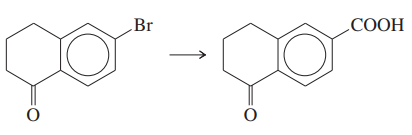
Problem 44a,b
Two of the methods for converting alkyl halides to carboxylic acids are covered in Sections 20-8B and 20-8C. One is formation of a Grignard reagent followed by addition of carbon dioxide and then dilute acid. The other is substitution by cyanide ion, followed by hydrolysis of the resulting nitrile. For each of the following conversions, decide whether either or both of these methods would work, and explain why. Show the reactions you would use.
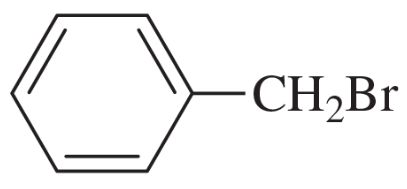
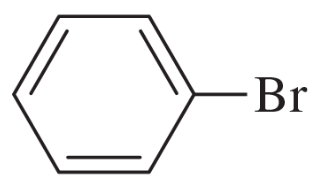
(a)
(b)
Problem 44e,f
Two of the methods for converting alkyl halides to carboxylic acids are covered in Sections 20-8B and 20-8C. One is formation of a Grignard reagent followed by addition of carbon dioxide and then dilute acid. The other is substitution by cyanide ion, followed by hydrolysis of the resulting nitrile. For each of the following conversions, decide whether either or both of these methods would work, and explain why. Show the reactions you would use.
(e)
(f)
Problem 57
Draw the mechanism for the last step in the Kiliani-Fischer synthesis.