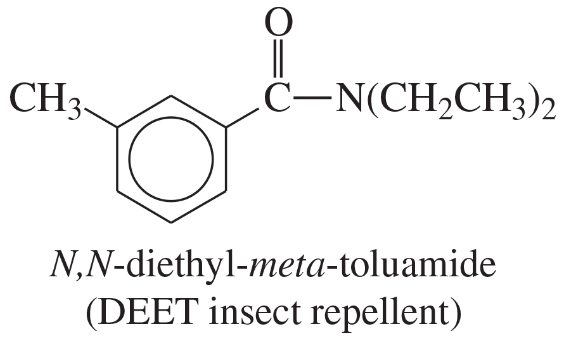
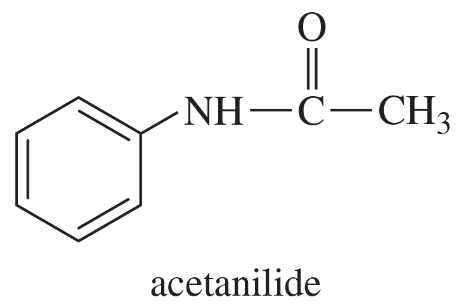
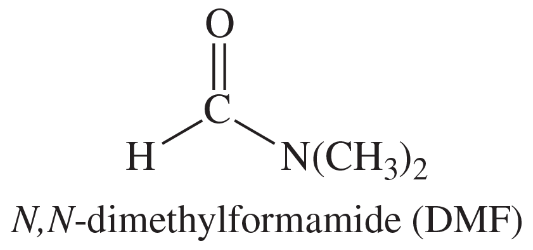
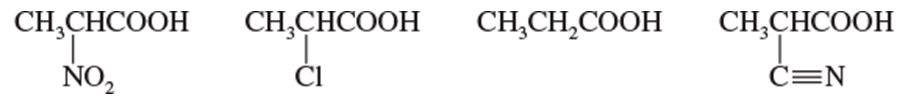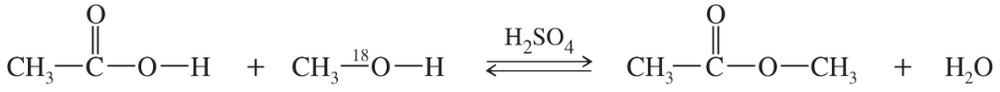Back
BackProblem 1a-d
Draw the structures of the following carboxylic acids.
(a) α-methylbutyric acid
(b) 2-bromobutanoic acid
(c) 4-aminopentanoic acid
(d) cis-4-phenylbut-2-enoic acid
Problem 1e-h
Draw the structures of the following carboxylic acids.
(e) trans-2-methylcyclohexanecarboxylic acid
(f) 2,3-dimethylfumaric acid
(g) m-chlorobenzoic acid
(h) 3-methylphthalic acid
Problem 2a,b,c
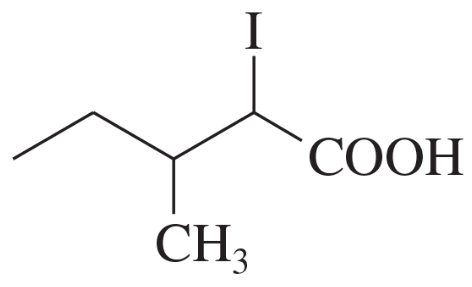
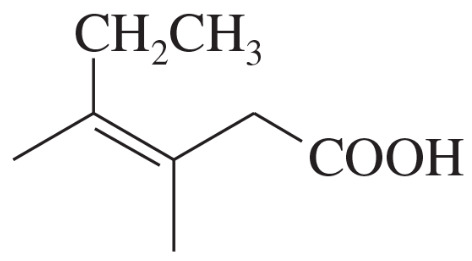
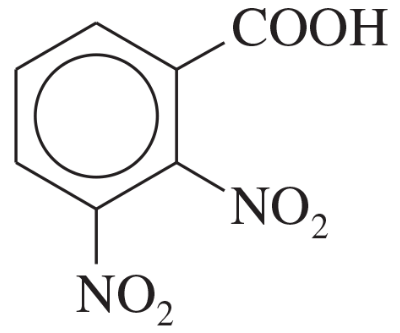
Name the following carboxylic acids (when possible, give both a common name and a systematic name).
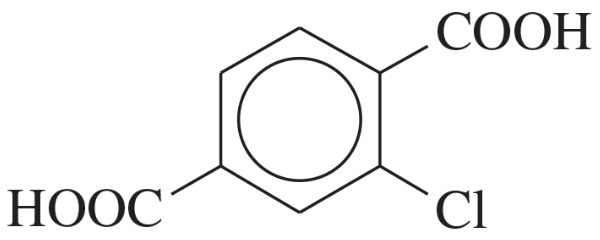
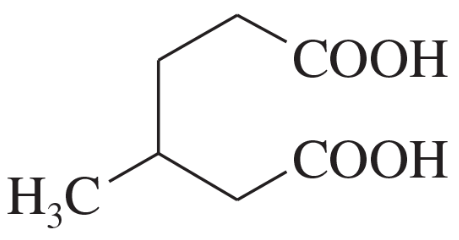
(a)
(b)
(c)
Problem 2d,e,f
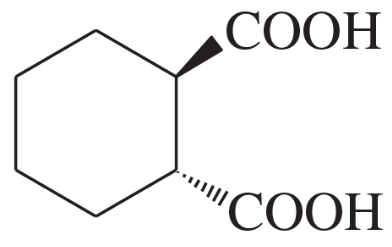
Name the following carboxylic acids (when possible, give both a common name and a systematic name).
(d)
(e)
(f)
Problem 3a
Rank the compounds in each set in order of increasing acid strength.
(a) CH3CH2COOH, CH3CHBrCOOH, CH3CBr2COOH
Problem 3b
Rank the compounds in each set in order of increasing acid strength.
(b) CH3CH2CH2CHBrCOOH, CH3CH2CHBrCH2COOH, CH3CHBrCH2CH2COOH
Problem 3c
Rank the compounds in each set in order of increasing acid strength.
(c)
Problem 4
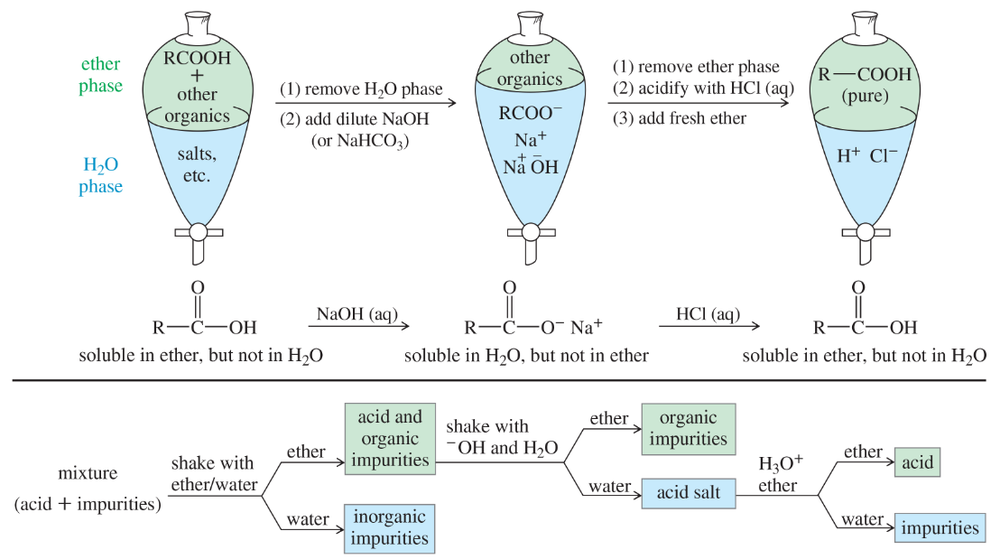
Suppose you have just synthesized heptanoic acid from heptan-1-ol. The product is contaminated by sodium dichromate, sulfuric acid, heptan-1-ol, and possibly heptanal. Explain how you would use acid–base extractions to purify the heptanoic acid. Use a chart, like that in Figure 20-3, to show where the impurities are at each stage.
Problem 5
Phenols are less acidic than carboxylic acids, with values of pKa around 10. Phenols are deprotonated by (and therefore soluble in) solutions of sodium hydroxide but not by solutions of sodium bicarbonate. Explain how you would use extractions to isolate the three pure compounds from a mixture of p-cresol (p-methylphenol), cyclohexanone, and benzoic acid.
Problem 6
Oxidation of a primary alcohol to an aldehyde usually gives some over-oxidation to the carboxylic acid. Assume you have used PCC to oxidize pentan-1-ol to pentanal.
(a) Show how you would use acid–base extraction to purify the pentanal.
(b) Which of the expected impurities cannot be removed from pentanal by acid–base extractions? How would you remove this impurity?
Problem 7
The IR spectrum of trans-oct-2-enoic acid is shown. Point out the spectral characteristics that allow you to tell that this is a carboxylic acid, and show which features lead you to conclude that the acid is unsaturated and conjugated.
<IMAGE>
Problem 8c
How many stereoisomers are possible for c. a ketotriose?
Problem 10
Write the mechanism for the base-catalyzed conversion of D-fructose to D-glucose and D-mannose.
Problem 11a,b
Show how you would synthesize the following carboxylic acids, using the indicated starting materials.
(a) oct-4-yne → butanoic acid
(b) trans-cyclodecene → decanedioic acid
Problem 11d
Show how you would synthesize the following carboxylic acids, using the indicated starting materials.
(d) butan-2-ol → 2-methylbutanoic acid
Problem 11e
Show how you would synthesize the following carboxylic acids, using the indicated starting materials.
(e) p-xylene → terephthalic acid
Problem 11f
Show how you would synthesize the following carboxylic acids, using the indicated starting materials.
(f) allyl iodide → but-3-enoic acid
Problem 12b
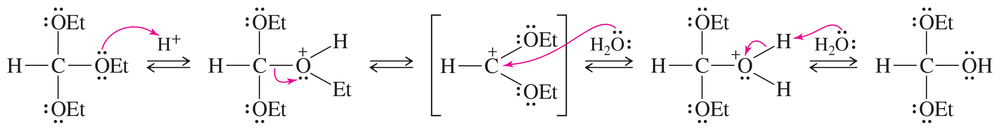
Propose a mechanism for the acid-catalyzed reaction of acetic acid with ethanol to give ethyl acetate.
Problem 12c
The Principle of Microscopic Reversibility states that a forward reaction and a reverse reaction taking place under the same conditions (as in an equilibrium) must follow the same reaction pathway in microscopic detail. The reverse of the Fischer esterification is the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of an ester. Propose a mechanism for the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of ethyl benzoate, PhCOOCH2CH3.
Problem 14
A carboxylic acid has two oxygen atoms, each with two nonbonding pairs of electrons.
(a) Draw the resonance forms of a carboxylic acid that is protonated on the hydroxy oxygen atom.
(b) Compare the resonance forms with those given previously for an acid protonated on the carbonyl oxygen atom.
(c) Explain why the carbonyl oxygen atom of a carboxylic acid is more basic than the hydroxy oxygen.
Problem 15a
Show how Fischer esterification might be used to form the following esters. In each case, suggest a method for driving the reaction to completion.
(a) methyl salicylate
Problem 15b
What monosaccharides are formed in a modified Kiliani–Fischer synthesis starting with each of the following monosaccharides?
b. L-threose
Problem 15c
Show how Fischer esterification might be used to form the following esters. In each case, suggest a method for driving the reaction to completion.
(c) ethyl phenylacetate
Problem 16a,b
The mechanism of the Fischer esterification was controversial until 1938, when Irving Roberts and Harold Urey of Columbia University used isotopic labeling to follow the alcohol oxygen atom through the reaction. A catalytic amount of sulfuric acid was added to a mixture of 1 mole of acetic acid and 1 mole of special methanol containing the heavy 18O isotope of oxygen. After a short period, the acid was neutralized to stop the reaction, and the components of the mixture were separated.
(a) Propose a mechanism for this reaction.
(b) Follow the labeled 18O atom through your mechanism, and show where it is found in the products.
Problem 17a
The given was missing some important resonance forms of the intermediates shown in brackets. Complete this mechanism by drawing all the resonance forms of these intermediates. Do your resonance forms help to explain why this reaction occurs under very mild conditions (water with a tiny trace of acid)?
Problem 17b
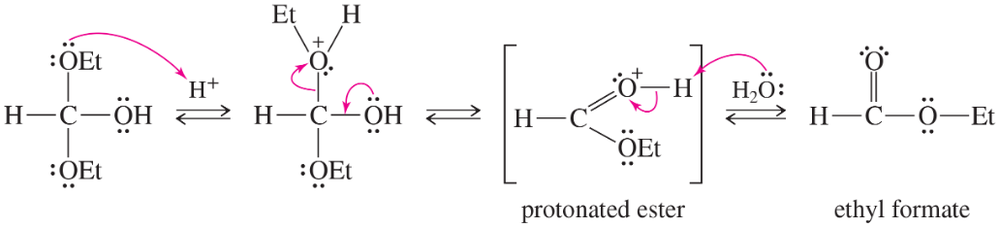
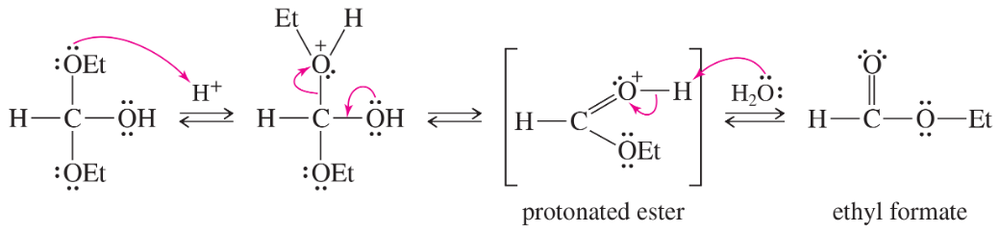
(b) Finish the solution for Solved Problem 20-1 by providing a mechanism for the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of ethyl formate.
Problem 18a
Show how to synthesize the following compounds, using appropriate carboxylic acids and amines.
(a)
Problem 18b
Show how to synthesize the following compounds, using appropriate carboxylic acids and amines.
(b)
Problem 18c
Show how to synthesize the following compounds, using appropriate carboxylic acids and amines.
(c)
Problem 19
Show how you would synthesize the following compounds from the appropriate carboxylic acids or acid derivatives.