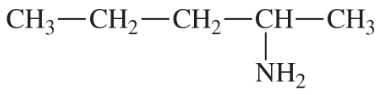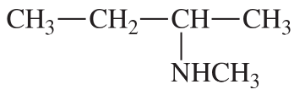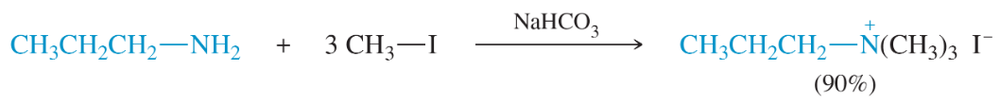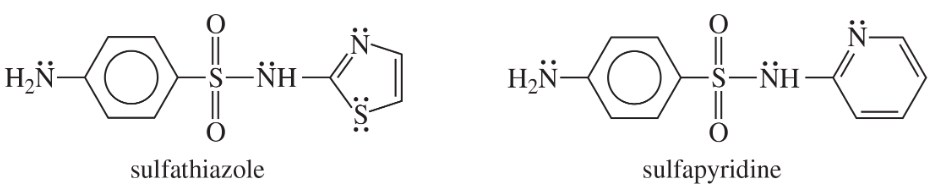Back
BackProblem 1
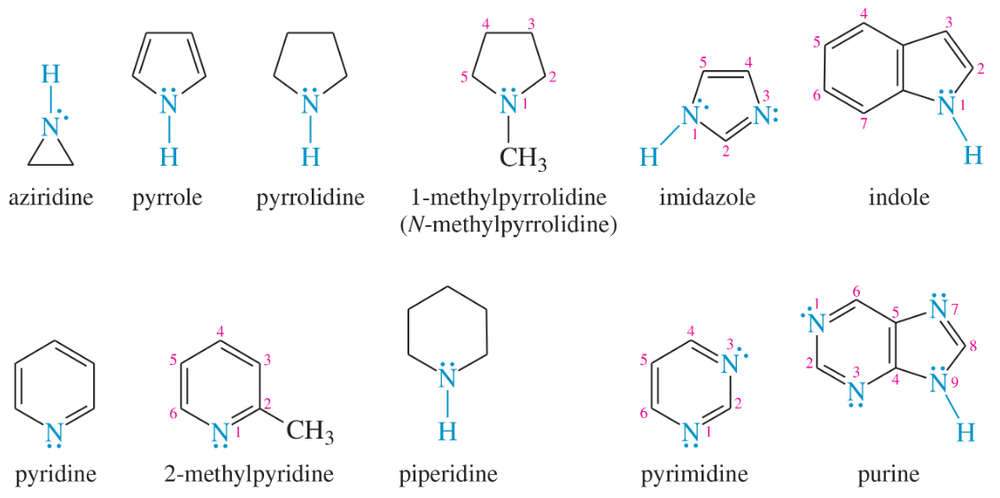
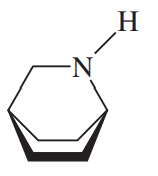
Determine which of the heterocyclic amines just shown are aromatic. Give the reasons for your conclusions.
Problem 2a,b,c
Draw the structures of the following compounds:
(a) tert-butylamine
(b) α-aminopropionaldehyde
(c) 4-(dimethylamino)pyridine
Problem 2d,e,f
Draw the structures of the following compounds:
(d) 2-methylaziridine
(e) N-ethyl-N-methylhexan-3-amine
(f) m-chloroaniline
Problem 3a,b,c
Give correct names for the following amines:
(a)
(b)
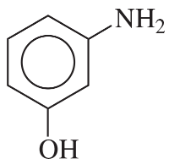
(c)
Problem 4
Which of the amines listed next is resolved into enantiomers? In each case, explain why interconversion of the enantiomers does or does not take place.
(a) cis-2-methylcyclohexanamine
(b) N-ethyl-N-methylcyclohexanamine
(c) N-methylaziridine
(d) ethylmethylanilinium iodide
(e) methylethylpropylisopropylammoniumiodide
Problem 5
Rank each set of compounds in order of increasing boiling points.
(a) triethylamine, di-n-propylamine, n-propyl ether
(b) ethanol, dimethylamine, dimethyl ether
(c) diethylamine, diisopropylamine, trimethylamine
Problem 6b
Rank each set of compounds in order of increasing basicity.
(b) aniline, p-methylaniline, p-nitroaniline
Problem 6c
Rank each set of compounds in order of increasing basicity.
(c) aniline, pyrrole, pyridine, piperidine
Problem 6d
Rank each set of compounds in order of increasing basicity.
(d) pyrrole, imidazole, 3-nitropyrrole
Problem 8
The proton and 13C NMR spectra of a compound of formula C4H11N are shown here. Determine the structure of this amine, and give peak assignments for all of the protons in the structure.
<IMAGE>
Problem 11
Propose a mechanism for nitration of pyridine at the 4-position, and show why this orientation is not observed.
Problem 12
Propose a mechanism for the sulfonation of pyridine, and point out why sulfonation occurs at the 3-position.
Problem 13
We have considered nucleophilic aromatic substitution of pyridine at the 2-position and 3-position but not at the 4-position. Complete the three possible cases by showing the mechanism for the reaction of methoxide ion with 4-chloropyridine. Show how the intermediate is stabilized by delocalization of the charge onto the nitrogen atom.
Problem 14a
(a) Propose a mechanism for the reaction of 2-bromopyridine with sodium amide to give 2-aminopyridine.
Problem 14b
(b) When 3-bromopyridine is used in this reaction, stronger reaction conditions are required and a mixture of 3-aminopyridine and 4-aminopyridine results. Propose a mechanism to explain this curious result.
Problem 15
Propose a mechanism to show the individual alkylations that form this quaternary ammonium salt.
Problem 16
Show how you would use direct alkylation to synthesize the following compounds.
(a) benzyltrimethylammonium iodide
(b) pentan-1-amine
(c) benzylamine
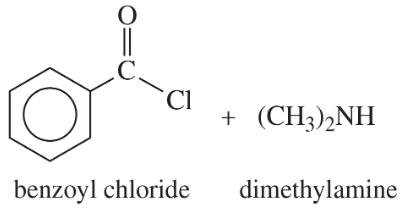
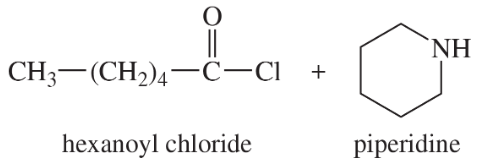
Problem 17
Give the products expected from the following reactions.
(a) acetyl chloride + ethylamine
(b)
(c)
Problem 18
What would happen in the synthesis of sulfanilamide if the amino group were not protected as an amide in the chlorosulfonation step?
Problem 19
Show how you would use the same sulfonyl chloride as used in the sulfanilamide synthesis to make sulfathiazole and sulfapyridine.
Problem 19.39i
Predict the products of the following reactions:
(i) <IMAGE of reaction>
Problem 20a,b,c
Predict the major products formed when the following amines undergo exhaustive methylation, treatment with Ag2O, and heating.
(a) hexan-2-amine
(b) 2-methylpiperidine
(c) N-ethylpiperidine
Problem 20e
Predict the major products formed when the following amines undergo exhaustive methylation, treatment with Ag2O, and heating.
(e)
Problem 21a
Give the products expected when the following tertiary amines are treated with a peroxyacid and heated.
(a) N,N-dimethylhexan-2-amine
Problem 21b
Give the products expected when the following tertiary amines are treated with a peroxyacid and heated.
(b) N,N-diethylhexan-2-amine
Problem 21c
Give the products expected when the following tertiary amines are treated with a peroxyacid and heated.
(c) cyclohexyldimethylamine
Problem 21d
Give the products expected when the following tertiary amines are treated with a peroxyacid and heated.
(d) N-ethylpiperidine
Problem 22a
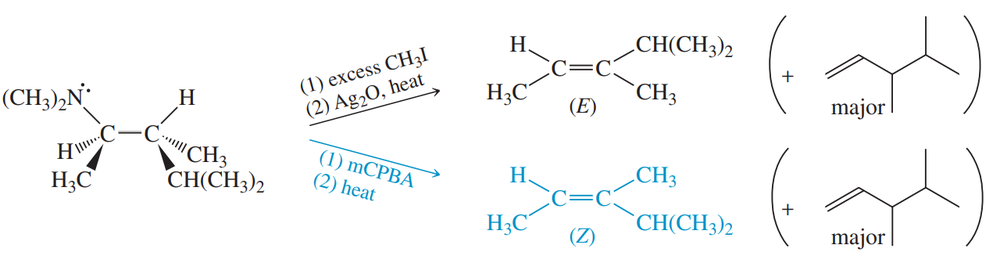
When the (R,R) isomer of the amine shown is treated with an excess of methyl iodide, then silver oxide, then heated, the major product is the Hofmann product.
(a) Draw the structure of the major (Hofmann) product.
Problem 22b
When the (R,R) isomer of the amine shown is treated with an excess of methyl iodide, then silver oxide, then heated, the major product is the Hofmann product.
(b) Some Zaitsev product is also formed. It has the (E) configuration. When the same amine is treated with mCPBA and heated, the Zaitsev product has the (Z) configuration. Use stereochemical drawings of the transition states to explain these observations.
Problem 23b
Predict the products from the reactions of the following amines with sodium nitrite in dilute HCl.
(b) N-ethylhexan-2-amine