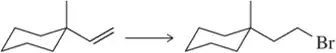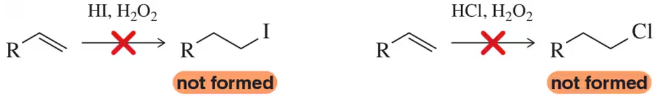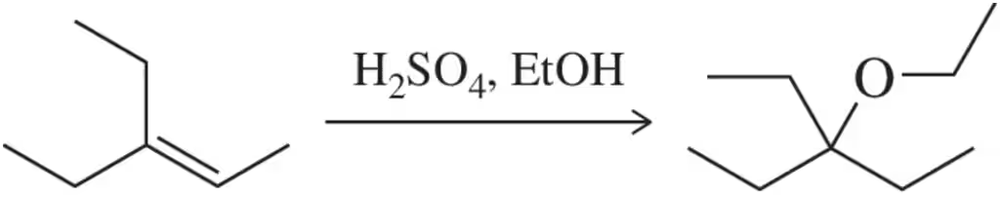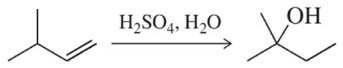Back
BackProblem 37b
Which reagent system (HBr or HBr, H2O2) would you use to carry out the following transformations?
(b)
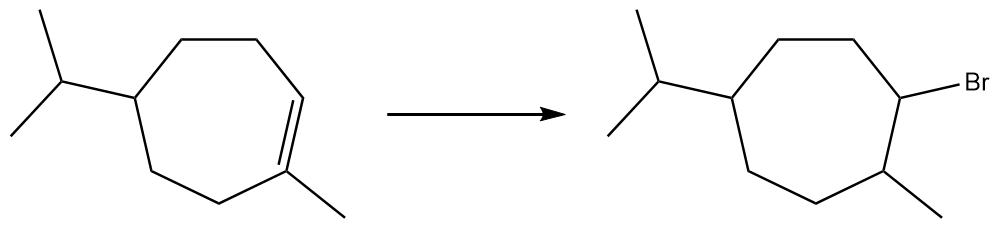
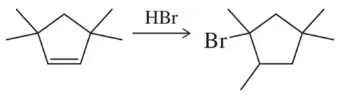
Problem 37c
Which reagent system (HBr or HBr, H2O2) would you use to carry out the following transformations?
(c)
Problem 38
Radical addition to alkenes is not effective for the synthesis of iodo- and chloroalkanes. Using your knowledge of the mechanism of this reaction, along with bond dissociation energies, explain why the radical additions of HI and HCl are not effective. (Assume ∆H = 65 kcal/ mol for the C–C π bond.)
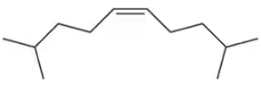
Problem 39a
Provide the expected product for the reaction of each of the following alkenes with H2SO4 and H2O.
(a)
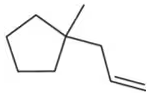
Problem 39b
Provide the expected product for the reaction of each of the following alkenes with H2SO4 and H2O.
(b)
Problem 39d
Provide the expected product for the reaction of each of the following alkenes with H2SO4 and H2O.
(d)
Problem 40
For each of the products you predicted in Assessment 8.39, provide an arrow-pushing mechanism which rationalizes the formation of each product. Make sure your mechanism accounts for all products formed, including stereoisomers and regioisomers, where applicable.
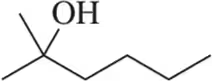
Problem 41a
Provide the alkene that would give the following alcohols under acid-catalyzed hydration conditions.
(a)
Problem 42
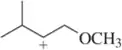
Ethers can be synthesized by substituting ethanol for water in the acid-catalyzed hydration reaction. Suggest an arrow-pushing mechanism which accounts for the formation of the ethyl ether under these conditions.
Problem 43
When combining isoprene equivalents, IPP is never the electrophile. Why might this be? What is special about DPP that allows it to function better as an electrophile? [Draw the carbocation that each becomes.]
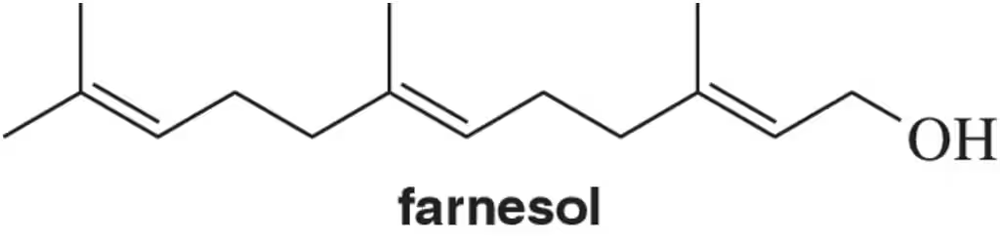
Problem 44
Suggest a mechanism for the synthesis of farnesol beginning with IPP and DPP.
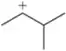
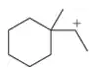
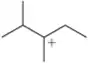
Problem 45a
Which of the following carbocations would you expect to rearrange? If you expect rearrangement, draw the carbocation you expect to form and the mechanism by which it will form.
(a)
Problem 45b
Which of the following carbocations would you expect to rearrange? If you expect rearrangement, draw the carbocation you expect to form and the mechanism by which it will form.
(b)
Problem 45c
Which of the following carbocations would you expect to rearrange? If you expect rearrangement, draw the carbocation you expect to form and the mechanism by which it will form.
(c)
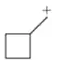
Problem 45e
Which of the following carbocations would you expect to rearrange? If you expect rearrangement, draw the carbocation you expect to form and the mechanism by which it will form.
(e)
Problem 45(e)
Which of the following carbocations would you expect to rearrange? If you expect rearrangement, draw the carbocation you expect to form and the mechanism by which it will form.
(e)
Problem 45f
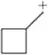
Which of the following carbocations would you expect to rearrange? If you expect rearrangement, draw the carbocation you expect to form and the mechanism by which it will form.
(f)
Problem 46a
Provide a mechanism for the following reactions occurring with rearrangement.
(a)
Problem 46b
Provide a mechanism for the following reactions occurring with rearrangement.
(b)
Problem 47
The hydration of three C5H10 alkene isomers can give 2-methylbutan-2-ol. Draw them.
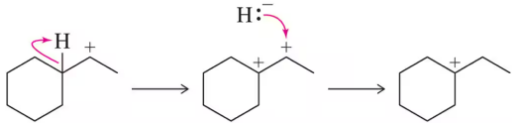
Problem 48
Our wayward chemist from Assessment 8.23 suggested the following stepwise mechanism for a hydride shift. Show this mechanism on a reaction coordinate diagram to illustrate why the concerted mechanism is more likely. Justify the picture you have drawn.
Problem 50a(ii)
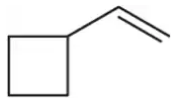
Predict the products you would get when the following alkenes react under the following conditions: (ii) 1. Hg(OAc)2 , H2O , 2. NaBH4
(a)
Problem 50a(i)
Predict the products you would get when the following alkenes react under the following conditions: (i) H2SO4 , H2O
(a)
Problem 50c
Predict the products you would get when the following alkenes react under the following conditions: (i) H2SO4, H2O and (ii) 1. Hg(OAc)2, H2O , 2. NaBH4
(c)
Problem 50d
Predict the products you would get when the following alkenes react under the following conditions: (i) H2SO4, H2O and (ii) 1. Hg(OAc)2, H2O , 2. NaBH4
(d)
Problem 51
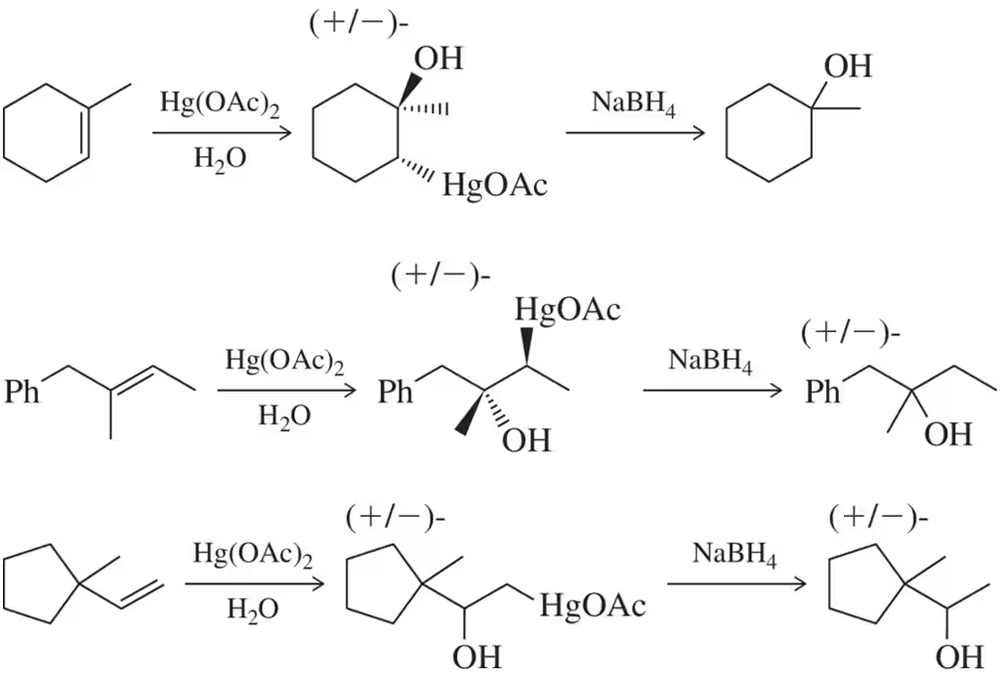
Provide an arrow-pushing mechanism, accounting also for the stereochemical outcome, of the first step (oxymercuration) of the three reactions in Figure 8.63.
Problem 51a
Provide an arrow-pushing mechanism, accounting also for the stereochemical outcome, of the first step (oxymercuration) of the three reactions in Figure 8.63.
Problem 52
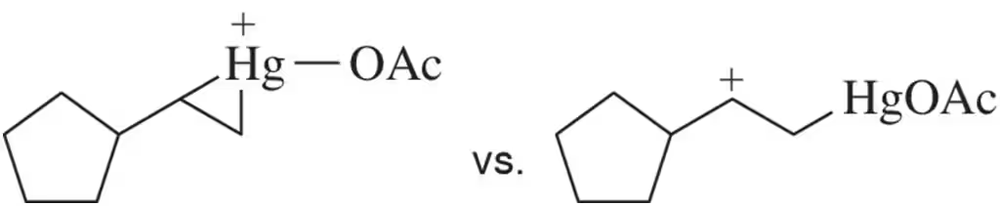
Which is more stable, a carbocation or a mercurinium ion? How do you know?
Problem 53a
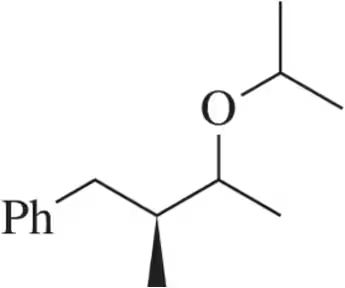
Oxymercuration–reduction, like acid-catalyzed hydration, can be modified to synthesize ethers. Suggest an alkene and the appropriate reaction conditions to synthesize the following ethers.
(a)
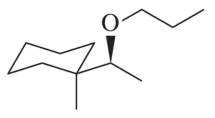
Problem 53b
Oxymercuration–reduction, like acid-catalyzed hydration, can be modified to synthesize ethers. Suggest an alkene and the appropriate reaction conditions to synthesize the following ethers.
(b)