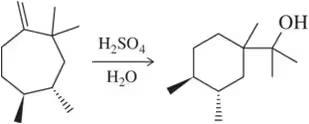
Back
BackProblem 77e
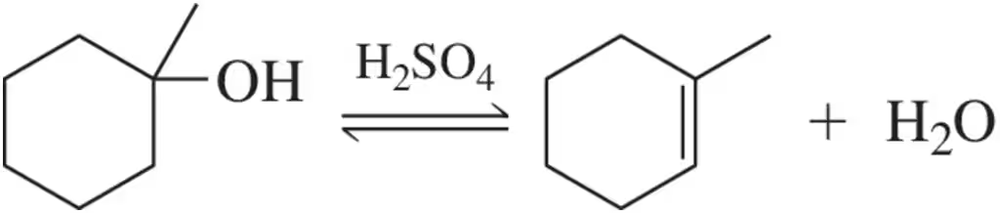
The acid-catalyzed hydration we learned here in Chapter 8 is reversible:
(e) How might you shift the equilibrium to the left?
Problem 78
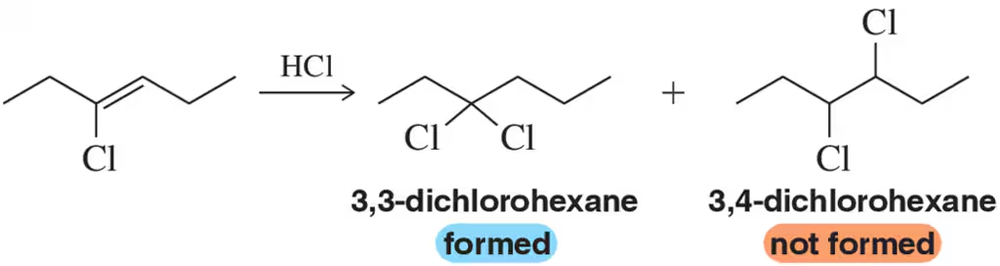
The reaction of (E)-3-chlorohex-3-ene with HCl results in the selective formation of 3,3-dichlorohexane instead of 3,4-dichlorohexane. Explain this result.
Problem 79a
In addition to radicals, anions, and cations, a fourth class of reactive intermediates is carbenes. A neutral species, the simplest carbene has a molecular formula of CH2.
(a) Draw the Lewis structure of CH2.
Problem 79b
In addition to radicals, anions, and cations, a fourth class of reactive intermediates is carbenes. A neutral species, the simplest carbene has a molecular formula of CH2.
(b) What are the hybridization and shape of the central carbon of CH2?
Problem 79e
In addition to radicals, anions, and cations, a fourth class of reactive intermediates is carbenes. A neutral species, the simplest carbene has a molecular formula of CH2 .
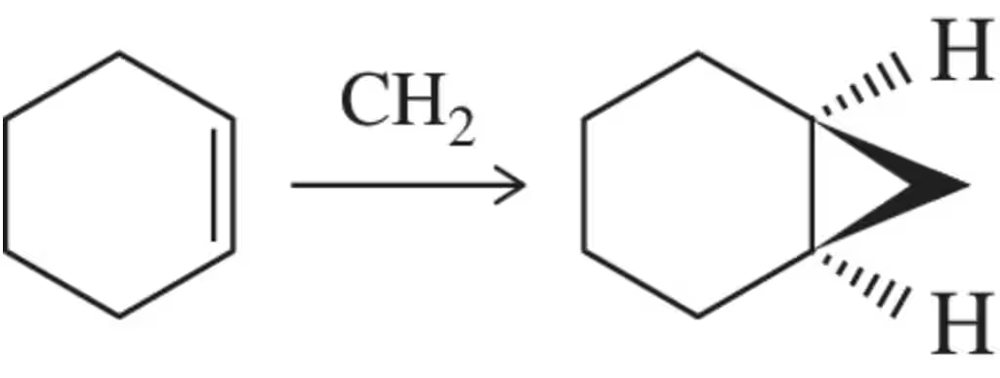
(e) Carbenes have great synthetic utility, especially in the synthesis of cyclopropanes from alkenes. Based on your answers to (a)–(d), show a mechanism for the cyclopropanation of cyclohexene.
Problem 79f
In addition to radicals, anions, and cations, a fourth class of reactive intermediates is carbenes. A neutral species, the simplest carbene has a molecular formula of CH2.
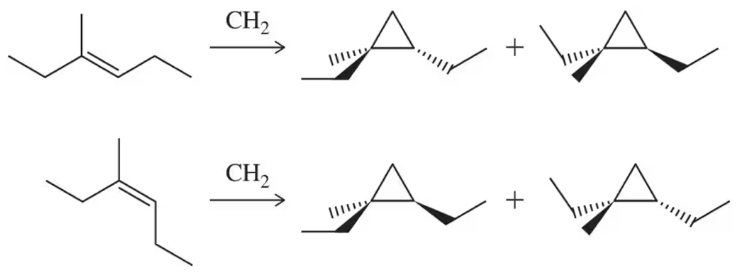
(f) Cyclopropanation of (E)- and (Z)-3-methylhex-3-ene gives two different products. Rationalize this outcome.
Problem 79h
In addition to radicals, anions, and cations, a fourth class of reactive intermediates is carbenes. A neutral species, the simplest carbene has a molecular formula of CH2.
(h) Of the reactions studied here in Chapter 8, cyclopropanation is most similar to which?
Problem 80a
Suggest an arrow-pushing mechanism that accounts for the formation of the following products.
(a)