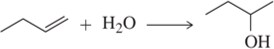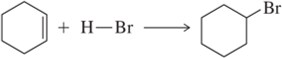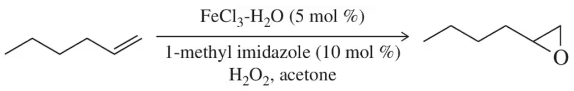Back
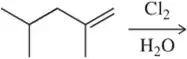
BackProblem 1a
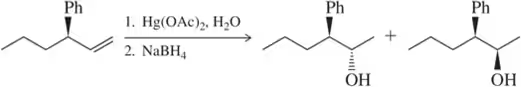
Would you expect the following to produce an equal or unequal mixture of stereoisomers?
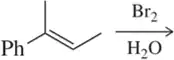
(a)
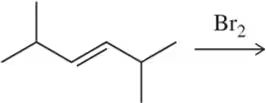
Problem 1b
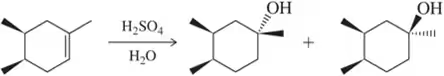
Would you expect the following to produce an equal or unequal mixture of stereoisomers?
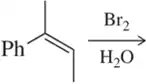
(b)
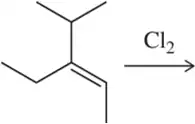
Problem 1c
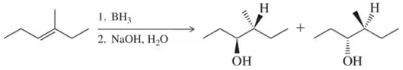
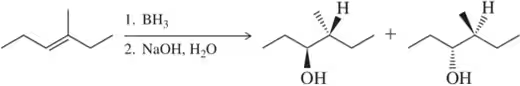
Would you expect the following to produce an equal or unequal mixture of stereoisomers?
(c)
Problem 2
Show a mechanism for the formation of one isomer in each of the reactions in Assessment 9.1.
(c)
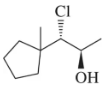
Problem 3c
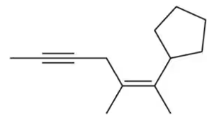
Calculate the index of hydrogen deficiency for the following molecules.
(c)
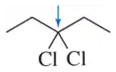
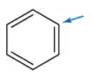
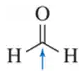
Problem 4b
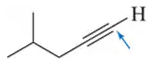
Determine the oxidation number of each carbon indicated by an arrow.
(b)
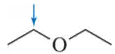
Problem 4c
Determine the oxidation number of each carbon indicated by an arrow.
(c)
Problem 4e
Determine the oxidation number of each carbon indicated by an arrow.
(e)
Problem 4f
Determine the oxidation number of each carbon indicated by an arrow.
(f)
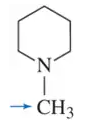
Problem 4g
Determine the oxidation number of each carbon indicated by an arrow.
(g)
Problem 4h
Determine the oxidation number of each carbon indicated by an arrow.
(h)
Problem 5b
Use oxidation numbers to determine which of the following are redox reactions.
(b)
Problem 5c
Use oxidation numbers to determine which of the following are redox reactions.
(c)
Problem 5d
Use oxidation numbers to determine which of the following are redox reactions.
(d)
Problem 5e
Use oxidation numbers to determine which of the following are redox reactions.
(e)
Problem 6b
Predict the product(s) of each of the following reactions, making sure to indicate the relative stereochemical outcome. Indicate any racemic mixtures by drawing both enantiomers.
(b)
Problem 6c
Predict the product(s) of each of the following reactions, making sure to indicate the relative stereochemical outcome. Indicate any racemic mixtures by drawing both enantiomers.
(c)
Problem 6f
Predict the product(s) of each of the following reactions, making sure to indicate the relative stereochemical outcome. Indicate any racemic mixtures by drawing both enantiomers.
(f)
- Calculate the atom economy for the reactions shown. In each, what happens to the percentage of material that is not incorporated into the major product?
Problem 7
Problem 7a
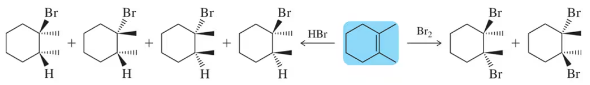
Provide an arrow-pushing mechanism that rationalizes the stereospecific formation of each dihalide in Assessment 9.6.
Problem 8
In which of the two steps in the alkene halogenation mechanism does a redox reaction occur?
- (••) Predict the product(s) that would result when the alkenes are allowed to react under the following conditions: (iii) Br₂, H₂O (h)
Problem 9
Problem 9a
In contrast to the addition of Br₂ the addition of HBr [Section 8.3] is not stereospecific. Why?
Problem 10a
Predict the product(s) of each of the following reactions, making sure to indicate the relative stereochemical outcome. Indicate any racemic mixtures by drawing both enantiomers.
(a)
Problem 11
Provide arrow-pushing mechanisms for Assessments 9.10(b) and 9.10(c) that rationalize the regioselective and stereospecific formation of each halohydrin.
(b)
(c)
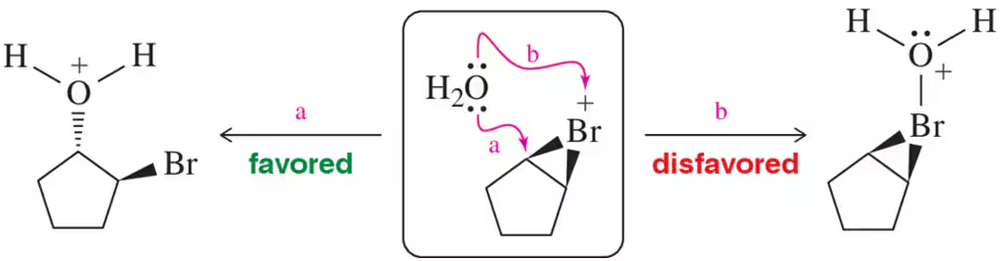
Problem 12
Explain why water attacks the carbon of the bromonium ion as opposed to the bromonium ion itself in the second step of halohydrin formation.
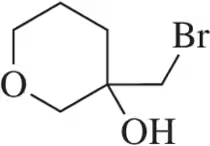
Problem 13a
Suggest an alkene that could be used to make each of the following halohydrins.
(a)
Problem 13c
Suggest an alkene that could be used to make each of the following halohydrins.
(c)
Problem 14
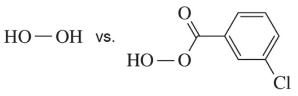
How does the carbonyl in mCPBA weaken the O―O σ bond (i.e., make a better leaving group)?
Problem 15
Calculate the atom economy of the reaction in Figure 9.24. [Catalysts are not included in the atom economy calculation.]