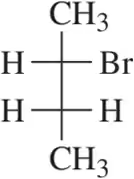Back
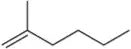
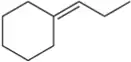
BackProblem 17
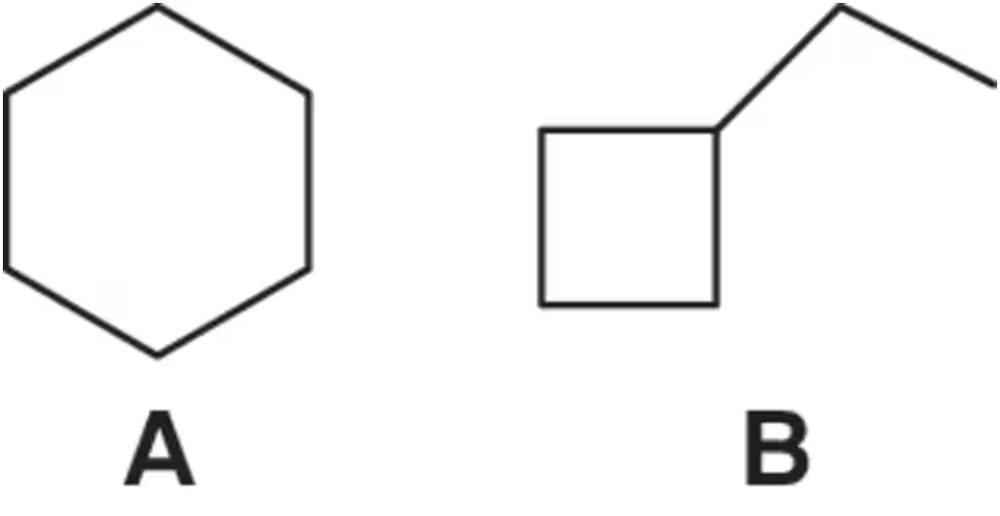
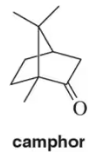
Which constitutional isomer, A or B, would you expect to have the highest heat of combustion (∆Hcombustion)?
Problem 18a
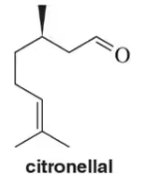
For the following terpenes, identify the isoprene units. In cross-linked or ring-containing terpenes, linkages can be formed between more than just C1 and C4 of isoprene.
(a)
Problem 18b
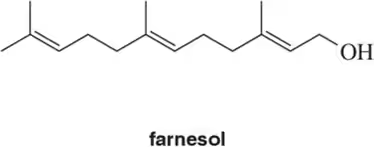
For the following terpenes, identify the isoprene units. In cross-linked or ring-containing terpenes, linkages can be formed between more than just C1 and C4 of isoprene
(b)
Problem 18c
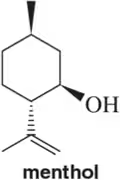
For the following terpenes, identify the isoprene units. In cross-linked or ring-containing terpenes, linkages can be formed between more than just C1 and C4 of isoprene
(c)
Problem 18d
For the following terpenes, identify the isoprene units. In cross-linked or ring-containing terpenes, linkages can be formed between more than just C1 and C4 of isoprene.
(d)
Problem 19c
Predict the product(s) of each of the following reactions. If you expect a racemic mixture, draw both enantiomers.
(c)
Problem 20a(b)
The following reaction steps are shown using conventional electron pushing. (b) Use the bouncing arrow formalism to illustrate the formation of only the product shown.
(a)
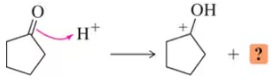
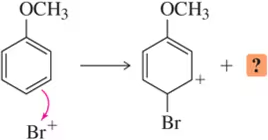
Problem 20a(a)
The following reaction steps are shown using conventional electron pushing. (a) Draw the second product whose formation would have been rationalized with this same arrow.
(a)
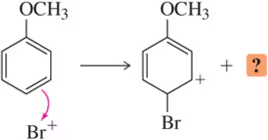
Problem 20c(a)
The following reaction steps are shown using conventional electron pushing. (a) Draw the second product whose formation would have been rationalized with this same arrow.
(c)
Problem 20c(b)
The following reaction steps are shown using conventional electron pushing. (b) Use the bouncing arrow formalism to illustrate the formation of only the product shown.
(c)
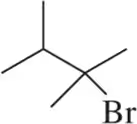
Problem 21a
Provide an arrow-pushing mechanism that rationalizes the formation of each alkyl halide in Assessment 8.19.
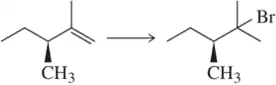
Problem 22b
Suggest an alkene that, upon reaction with the appropriate hydrohalic acid, will produce only the alkyl halide shown. [Ignore stereochemistry.]
(b)
Problem 22d
Suggest an alkene that, upon reaction with the appropriate hydrohalic acid, will produce only the alkyl halide shown. [Ignore stereochemistry.]
(d)
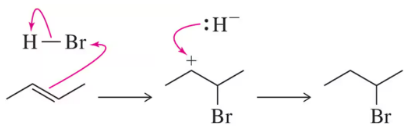
Problem 23
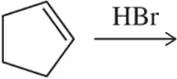
A wayward chemist proposed the following mechanism for the addition of HBr to an alkene.
(a) Why is this mechanism unlikely?
(b) Compare the reaction coordinate diagrams for the actual mechanism studied in Section 8.3.1 and this alternate mechanism on the same graph.
Problem 25
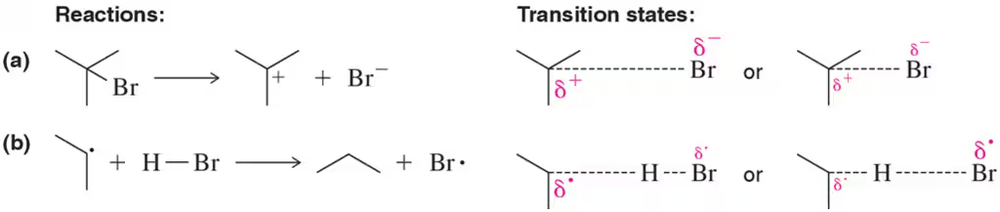
Which is the most likely transition state for the reactions shown? Explain your answer. [Note the difference in the size of the partial charges or partial unpaired electrons.]
Problem 26
Which would you expect to be more selective for carbocation formation, the electrophilic addition of HF or HBr to 2-methylbut-2-ene? Explain your answer.
Problem 27
Imagine an electrophilic addition where the first step is exothermic. Which carbocation—2°, 3°, or neither—would you expect to form preferentially? Explain.
Problem 28
For the enzyme isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase, IPP binds tightly as a result of interactions between the active site amino acid residues and the diphosphate of IPP. Without concerning yourself with the structure of amino acids, what charges might you expect to be present in the active site to hold IPP in place so that the enzymatic reactions can occur?
Problem 29
Draw a mechanism for the acid-catalyzed conversion of DPP to IPP. How do you know that your mechanism is correct?
Problem 31d
What is the expected product for the reaction of each of the following alkenes with (i) HBr and (ii) HCl?
(d)
Problem 31e
What is the expected product for the reaction of each of the following alkenes with (i) HBr and (ii) HCl?
(e)
Problem 32
Provide an arrow-pushing mechanism that rationalizes the formation of each of the products you predicted in Assessment 8.31. Make sure your mechanism accounts for all products formed, including stereoisomers and regioisomers, where applicable.
Problem 33
Would you expect but-2-ene or 2-methylbut-2-ene to react more quickly with HBr?
Problem 34
In your own words, explain why it is not possible to make primary alkyl halides, such as 1-bromopentane, using the electrophilic addition of HCl or HBr to an alkene.
Problem 35b
Provide the expected product for the reaction of each of the following alkenes with (i) HBr and (ii) HBr, H2O2
(b)
Problem 35c
Provide the expected product for the reaction of each of the following alkenes with (i) HBr and (ii) HBr, H2O2
(c)
Problem 35d
Provide the expected product for the reaction of each of the following alkenes with (i) HBr and (ii) HBr, H2O2.
(d)
Problem 35e
Provide the expected product for the reaction of each of the following alkenes with (i) HBr and (ii) HBr, H2O2.
(e)
Problem 36
Provide an arrow-pushing mechanism that rationalizes the formation of each of the products you predicted in Assessment 8.35 (ii). Make sure your mechanism accounts for all products formed, including stereoisomers and regioisomers, where applicable.
Problem 37a
Which reagent system (HBr or HBr, H2O2) would you use to carry out the following transformations?
(a)